ON THIS PAGE
Understand vSRX Virtual Firewall with AWS
This section presents an overview of vSRX Virtual Firewall on Amazon Web Services (AWS).
vSRX Virtual Firewall with AWS
AWS provides on-demand services in the cloud. Services range from Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (SaaS), to Application and Database as a Service. AWS is a highly flexible, scalable, and reliable cloud platform. In AWS, you can host servers and services on the cloud as a pay-as-you-go (PAYG) or bring-your-own-license (BYOL) service.
vSRX Virtual Firewall PAYG images do not require any Juniper Networks licenses.
You can deploy vSRX Virtual Firewall in a virtual private cloud (VPC) in the Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud. You can launch vSRX Virtual Firewall as an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance in an Amazon VPC dedicated to a specific user account. The vSRX Virtual Firewall Amazon Machine Image (AMI) uses hardware virtual machine (HVM) virtualization.
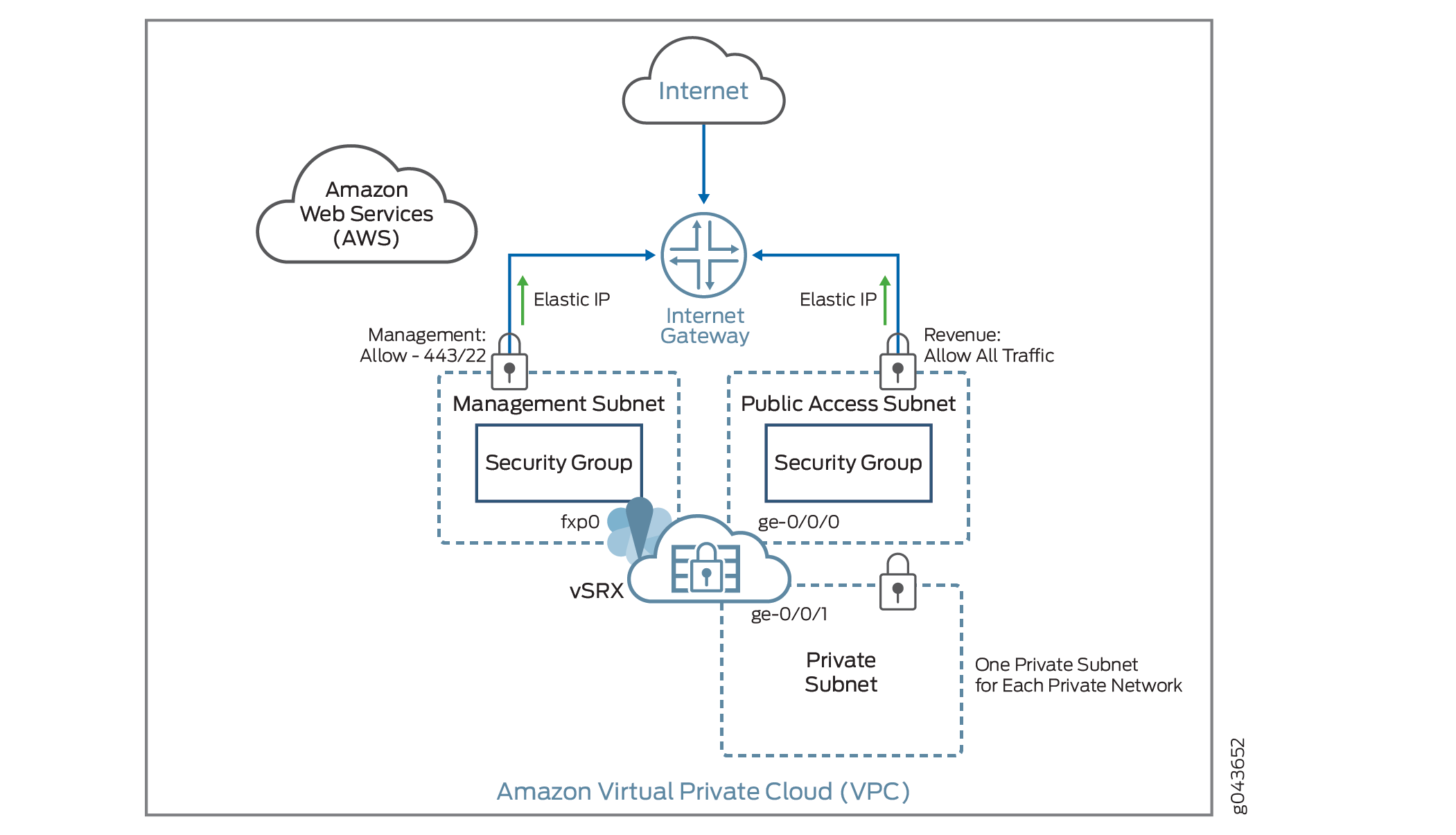
Figure 1 shows an example of deploying a vSRX Virtual Firewall instance to provide security for applications running in a private subnet of an Amazon VPC.
In the Amazon VPC, public subnets have access to the Internet gateway, but private subnets do not. vSRX Virtual Firewall requires two public subnets and one or more private subnets for each individual instance group. The public subnets consist of one for the management interface (fxp0) and one for a revenue (data) interface. The private subnets, connected to the other vSRX Virtual Firewall interfaces, ensure that all traffic between applications on the private subnets and the Internet must pass through the vSRX Virtual Firewall instance.
AWS Marketplace also enables you to discover and to subscribe to software that supports regulated workloads through AWS Marketplace for AWS GovCloud (US).
Starting in Junos OS Release 15.1X49-D70 and Junos OS Release 17.3R1, vSRX Virtual Firewall supports two bundles for PAYG that are available as 1-hour or 1-year subscriptions.
vSRX Virtual Firewall Next Generation Firewall—Includes standard (STD) features of core security, including core firewall, IPsec VPN, NAT, CoS, and routing services, as well as advanced Layer 4 through 7 security services such as AppSecure features of AppID, AppFW, AppQoS, and AppTrack, IPS and rich routing capabilities.
vSRX Virtual Firewall Premium-Next Generation Firewall with Anti-Virus Protection—Includes the features in the vSRX Virtual Firewall Next- Generation Firewall package, including the Content Security antivirus feature.
You deploy vSRX Virtual Firewall in an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) as an application instance in the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2). Each Amazon EC2 instance is deployed, accessed, and configured over the Internet using the AWS Management Console, and the number of instances can be scaled up or down as needed.
In the current release, each vSRX Virtual Firewall instance uses two vCPUs and 4 GB of memory, even if the instance type selected on AWS provides more resources.
vSRX Virtual Firewall uses hardware assisted virtual machines (HVM) for high performance (enhanced networking), and supports the following deployments on AWS cloud environments:
As a firewall between other Amazon EC2 instances on your Amazon VPC and the Internet
As a VPN endpoint between your corporate network and your Amazon VPC
As a firewall between Amazon EC2 instances on different subnets
There are default limits for AWS services for an AWS account. For more information about AWS service limits, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/aws_service_limits.html and https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-eni.html .
AWS Glossary
This section defines some common terms used in an AWS configuration. Table 1 defines common terms used for Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) and Table 2 defines common terms for Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) services.
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
Internet gateways |
Amazon VPC components that allow communications between your instances in the Amazon VPC and the Internet. |
IP addressing |
AWS includes three types of IP address:
Each network interface can be associated with multiple private IP addresses. Public subnets can have multiple private IP addresses, public addresses, and Elastic IP addresses associated with the private IP address of the network interface. Instances in private and public subnets can have multiple private IP addresses. One Elastic IP address can be associated with each private IP address for instances in public subnets. You can assign static private IP addresses in the subnet. The first five IP addresses and the last IP address in the subnet are reserved for Amazon VPC networking and routing. The first IP address is the gateway for the subnet. |
Network ACL |
AWS stateless virtual firewall operating at the subnet level. |
Route tables |
A set of routing rules used to determine where the network traffic is directed. Each subnet needs to be associated with a route table. Subnets not explicitly associated with a route table are associated with the main route table. Custom route tables can be created other than the default table. |
Subnet |
A virtual addressing space in the Amazon VPC CIDR block. The IP addresses for the Amazon EC2 instances are allocated from the subnet pool of IP addresses. You can create two types of subnets in the Amazon VPC:
Note:
With vSRX Virtual Firewall Network Address Translation (NAT), you can launch all customer instances in private subnets and connect vSRX Virtual Firewall interfaces to the Internet. This protects customer instances from being directly exposed to Internet traffic. |
VPC |
Virtual private cloud. |
Term |
Description |
|---|---|
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) |
Persistent block storage that can be attached to an Amazon EC2 instance. Block storage volumes can be formatted and mounted on an instance. Amazon EBS optimized instances provide dedicated throughput between Amazon EC2 and Amazon EBS. |
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) |
Amazon Web service that enables launch and management of elastic virtual servers or computers that run on the Amazon infrastructure. |
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) |
Amazon image format that contains the information, such as the template for root volume, launch permissions, and block device mapping, that is required to launch an Amazon EC2 instance. |
Elastic IP |
A static IP designed for dynamic cloud computing. The public IP is mapped to the privet subnet IP using NAT. |
Enhanced networking |
Provides high packet per second performance, low latency, higher I/O performance, and lower CPU utilization compared to traditional implementations. vSRX Virtual Firewall leverages this networking with hardware virtualized machine (HVM) Amazon Machine Images (AMIs). |
Instance |
A virtual machine or server on Amazon EC2 that uses XEN or, XEN-HVM hypervisor types. Amazon EC2 provides a selection of instances optimized for different use cases. |
Keypair |
Public key cryptography used by AWS to encrypt and decrypt login information. Create these keypairs using AWS-EC2 or import your own keypair. Note:
AWS does not accept DSA. Limit the public key access permissions to 400. For more information about key rotation, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/kms/latest/developerguide/rotate-keys.html. |
Network interfaces |
Virtual network interfaces that you can attach to an instance in the Amazon VPC. An Elastic Network Interface (ENI) can have a primary private IP address, multiple secondary IP addresses, one Elastic IP address per private IP address, one public IP address, one or more security groups, one MAC address, and a source/destination check flag. For vSRX Virtual Firewall instances, disable the source/destination check for all interfaces. Note:
ENIs use the IP addresses within the subnet range. So, the ENI IP addresses are not exhausted. |
Network MTU |
All Amazon instance types support an MTU of 1500. Some instance types support jumbo frames (9001 MTU). Note:
Use C3, C4, C5, CC2, M3, M4, or T2 AWS instance types for vSRX Virtual Firewall instances with jumbo frames. |
Placement Groups |
Instances launched in a common cluster placement group. Instances within the cluster have networks with high bandwidth and low latency. |
Security groups |
An AWS-provided virtual firewall that controls the traffic for one or more instances. Security groups can be associated with an instance only at launch time. Note:
Because vSRX Virtual Firewall manages your firewall settings, we recommend that you ensure there is no contradiction between rule sets on AWS security groups and rule sets in your vSRX Virtual Firewall configuration. |
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
