ON THIS PAGE
Addresses Overview
An address specifies an IP address or a hostname. You can create addresses that you can use across all policies. Addresses are used in firewall and NAT services and apply to the corresponding policies. You can also resolve an IP address to the corresponding hostname.
Juniper Security Director Cloud manages its address book at the global level, assigning objects to devices that are required to create policies. An address book is a collection of addresses and address groups. If the device is capable of using a global address book, Juniper Security Director Cloud pushes address objects used in the policies to the global address book of the device.
Use this page to create, edit, clone, and delete addresses and address groups, and manage addresses. Addresses and address groups are used in firewall and NAT services. After you create an address, you can combine it with other addresses to form an address group. Address groups are useful when you want to apply the same policy to multiple services.
If you have configured an external probe setting at , then a new shared address object Secure-Edge-External-Probe-Source-Address is automatically created. This address is used as the source address in the default security policy rule, Secure-Edge-External-Probe-Rule, to allow traffic. You cannot modify or delete the Secure-Edge-External-Probe-Source-Address.
Variable Address Overview
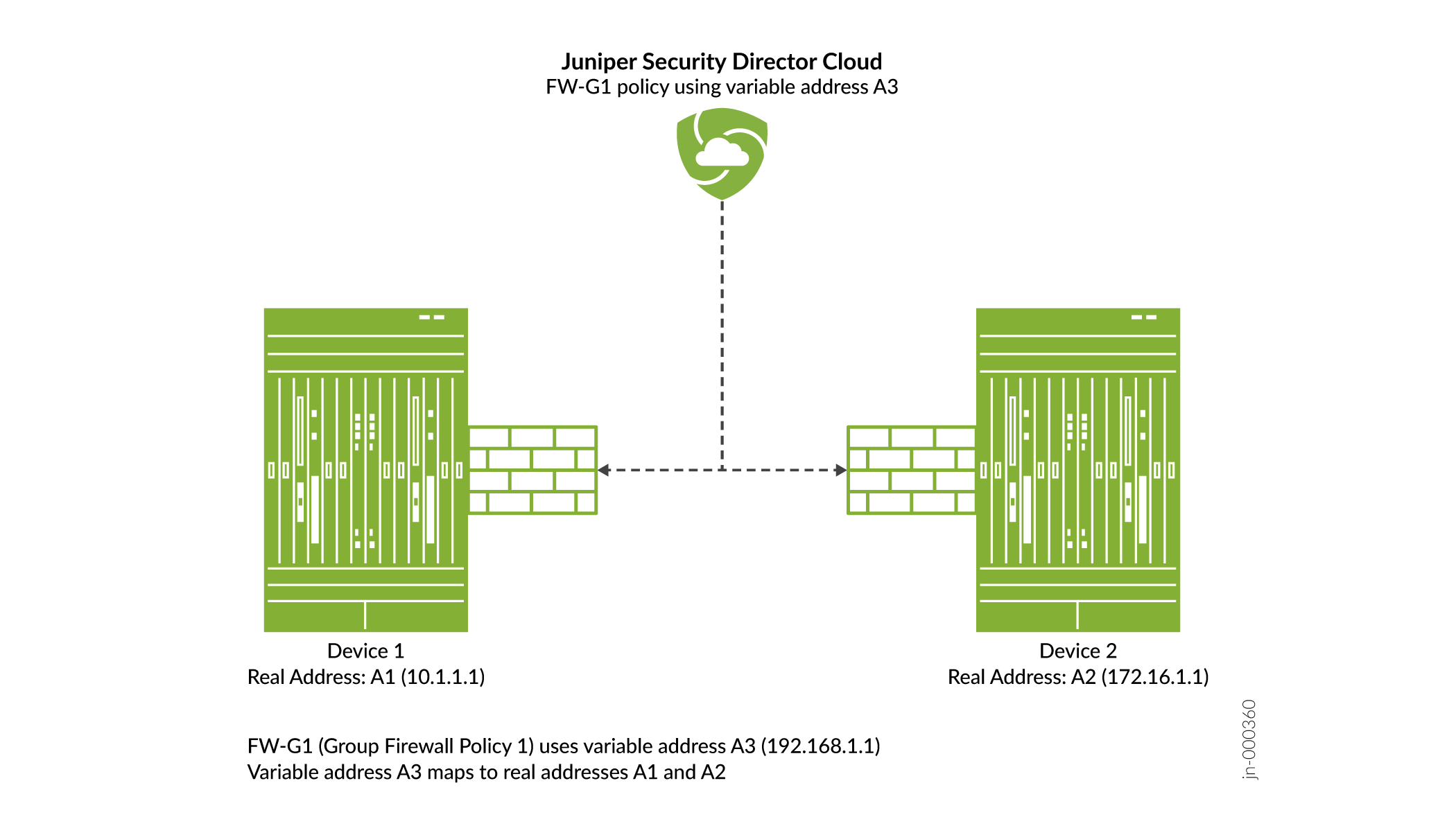
A variable is useful when you want to apply similar rules across devices where only the address might differ. Instead of using static values, you can use variables to create fewer rules and use them more widely. You can achieve this by creating and configuring a variable address for all devices to which you are applying a group policy.
For example:
-
Group firewall policy FW-G1 has two devices, Dev-1 and Dev-2. Each device has its own unique address. Dev-1 has address A1. Dev-2 has address A2.
-
You want to apply the same rule to both devices, but you do not want to configure two rules with all the same criteria except for the address. It is more efficient to configure one rule with a variable default address and apply it to both devices.
-
You can achieve this by creating an address variable with a default address A3, and making A3 common to Dev-1 and Dev-2 in your rule. When you configure default address A3, you map it to the real address of each device, A1 for Dev-1 and A2 for Dev-2.
-
When group firewall policy FW-G1 is applied, these mappings are used to replace the default address with the real address for each device.
-
Note:
Variable addresses are used in group policies only. Variable addresses are not applicable to device policies.
Field Descriptions
To access this page, select .
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
The name of the address or address group. |
|
Type |
The type of the address object. |
|
Hostname |
The hostname of the address. |
|
IP Address |
The IP address associated with the address. |
|
Description |
The description about the address or address group which was entered when the address or address group was created. |
