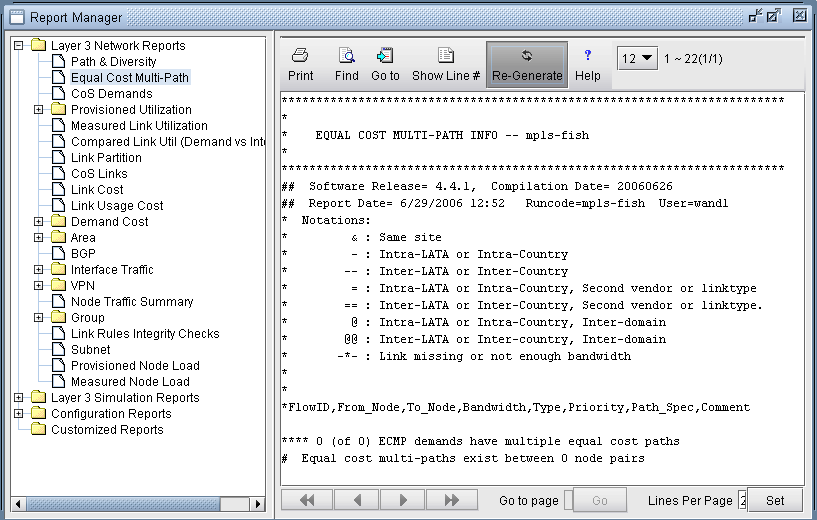
View Equal Cost Multiple-Paths
Equal Cost Multiple-Paths (ECMP) reports provide a list of all the ECMPs available in your network. You can also view each individual paths highlighted in a separate window.
To view ECMPs in your network:
- Right-click on the topology map and select Labels
> Link Labels > Show Link Metrics.Figure 1: Show Link Distance
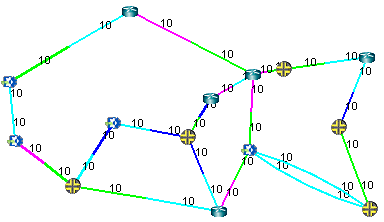
-
The link
metrics are displayed.
Figure 2: Topology Map with Link Distances
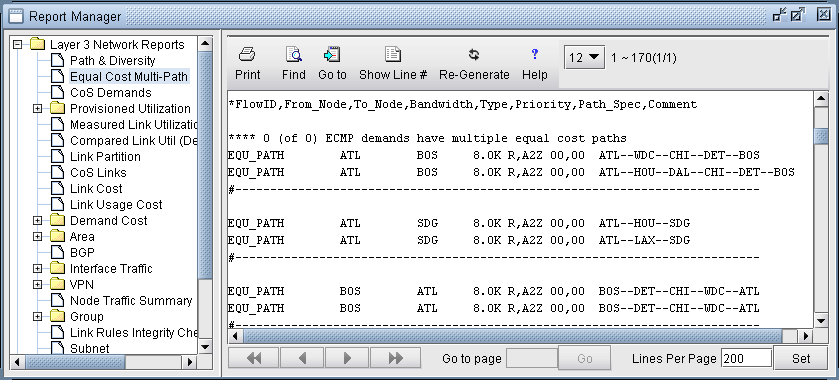
- Select Report > Report Manager to open up the Report Manager.
- Select Network Reports > Demand Reports > Equal Cost
Multi-Path Report from the left panel to bring up the report
listing all of the equal cost multiple-paths of the network. As can
be seen in Figure 3,
there are many such paths. This report is also saved on the server
as EQPATHRPT. runcode. Note that the ECMP paths
are calculated based on IP metric only, and do not factor in the influence
of MPLS traffic engineering tunnels on the demand routing.Figure 3: Equal Cost Multiple-Paths Report
- Select Network > Path & Capacity > Equivalent
Path to bring up the Demand Equivalent Path window.Figure 4: Network > Path & Capacity > Equivalent Path
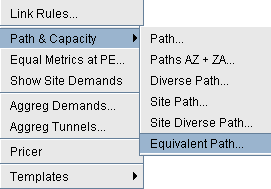
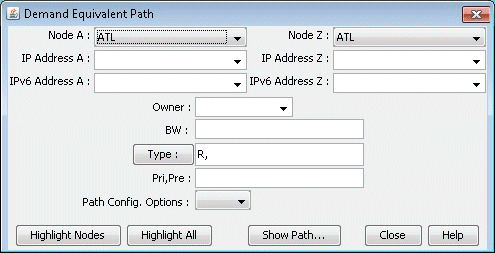
- Select Node A and Node B, then click
Show Path. The Path window will be displayed.Figure 5: Demand Equivalent Path
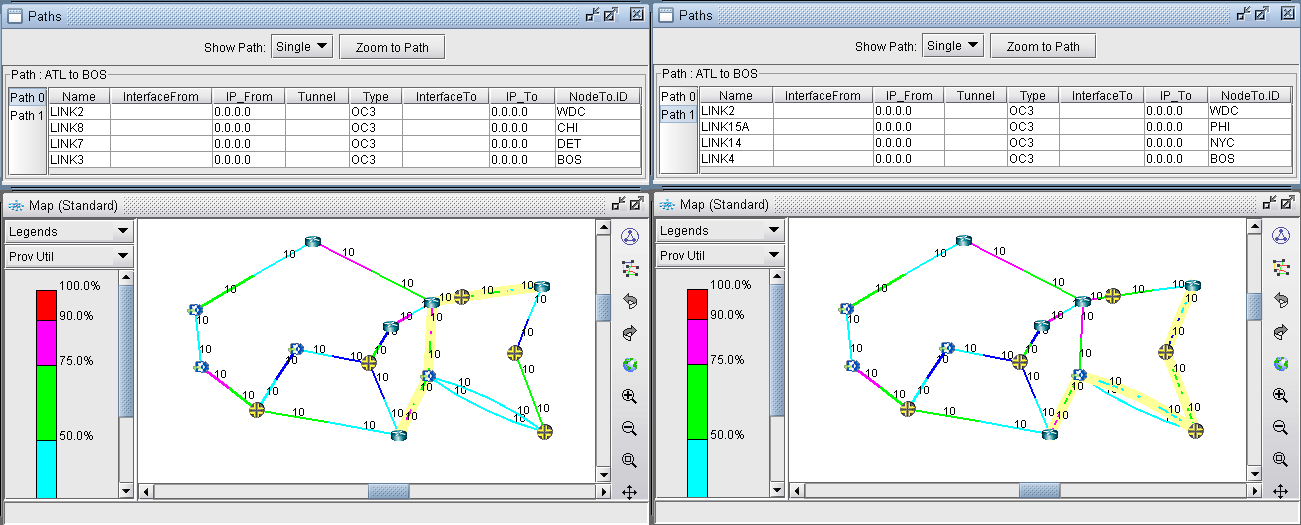
- All of the equivalent paths between the two selected nodes
will be displayed in the Paths window. Select a path to view its detailed
information and highlight it on the topology map.Figure 6: Equivalent Cost Paths
Reducing Equal Cost Multiple Paths
- If you choose your link metrics wisely (such as using
the real distance in miles like in Figure 7), you can increase
the variability of the path costs which will make it less likely for
equal cost multiple-paths to occur.Figure 7: Topology Map With New Link Distances
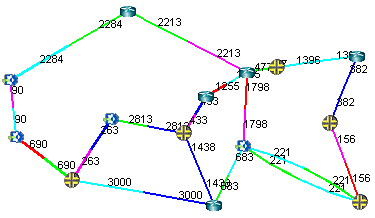 Figure 8: Routing according to Actual Mileage
Figure 8: Routing according to Actual Mileage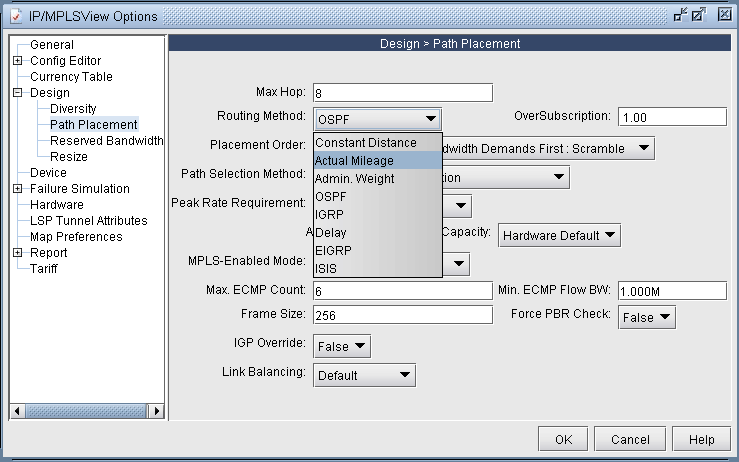
-
Open
the Equal Cost Multi-Path Report again and you will see that there are no longer
any equal cost multiple-paths in the network with the new link metrics.
Figure 9: New Equal Cost Multiple-Paths Report