Comparing Multicast with Unicast
It may be of interest to see what the network would look like if, instead of multicast, all the demands were routed according to traditional unicast protocols. This can be done easily by disabling multicast on all the demands. To do this, a cnavigate to the Demands tab on the Network Info table.
In the Demands tab, click the Modify button and then select “All Entries”.
A Modify Demands window will appear. Click the Type button in this window to bring up the Demand Type Parameter Generation window.
Click the dropdown menu next to the Multicast field and select No.
Figure 1: Modifying the Demand Type to Disable Multicast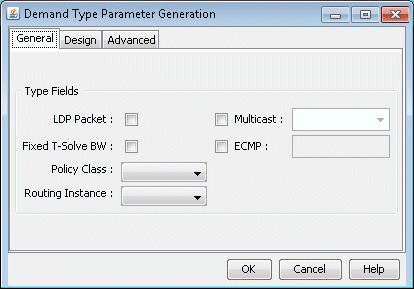
Click the OK button in the Demand Type Parameter Generation window, then click the OK button in the Modify Demands window. Multicast will now be disabled on all the demands, which will now be routed according to traditional unicast protocols.
Click the Update button on the main menu bar. This is required to force the program to recalculate paths for demands after they have been modified.
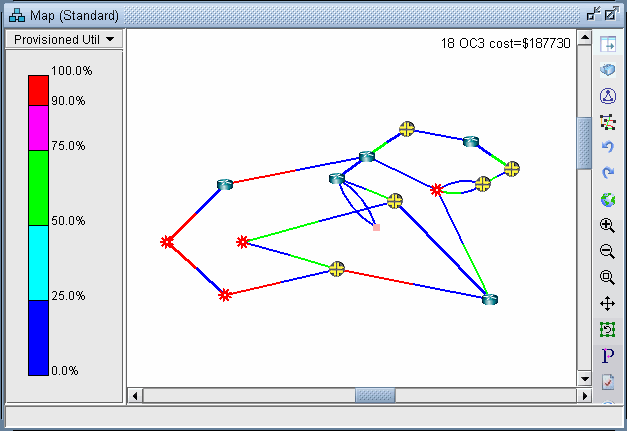
Now the link utilization displayed in the Map window will reflect the unicast “version” of the network. Notice the difference between the link utilization colors of this network and those of the multicast network. In particular, note that the links near the source, SFO, all appear to be overutilized in the unicast network, whereas in the multicast network the links near the source were only moderately utilized, similar to the links near the recipients.
Figure 2: Link Utilization in a Unicast Network