EVE-NG BMS Environment
If you have not installed EVE-NG 5.x or later on a BMS, check the download link to get to the Professional or Community ISOs.
Use only the ISO files and install on a BMS. Avoid using the OVA VM images as they would cause the unsupported double-nesting issue.
Copy the VM Image to Your EVE-NG Environment
- Go to the vJunos-switch download link https://support.juniper.net/support/downloads/?p=vjunos and select
the latest image as shown below.
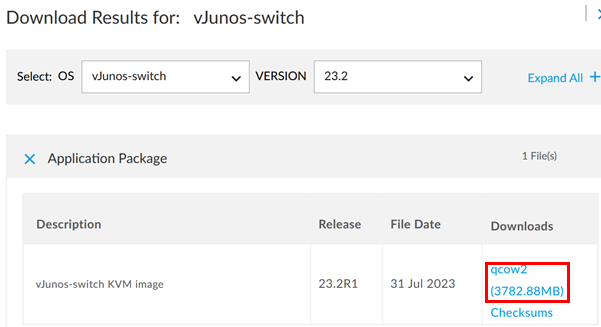
- Click copy to copy the temporary URL, which is valid for 10 minutes.
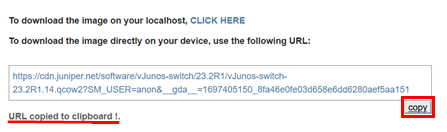
- Access SSH to connect to your EVE-NG BMS as root to install the image. Embed the
copied URL to
wget "<download-url>"as shown below.sudo -i # create a directoy with "vjunosswitch-version" pattern mkdir /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/vjunosswitch-23.2 cd /opt/unetlab/addons/qemu/vjunosswitch-23.2 # download the image wget "https://cdn.juniper.net/software/vJunos-switch/23.2R1/vJunos-switch-23.2R1.14.qcow2?SM_USER=anon&__gda__=1697405150_8fa46e0fe03d658e6dd6280aef5aa151" # rename the image to hda.qcow2 NOT virtioa.qcow2 mv "vJunos-switch-23.2R1.14.qcow2?SM_USER=anon&__gda__=1697405150_8fa46e0fe03d658e6dd6280aef5aa151" hda.qcow2
Use hda.qcow2 as VM image name, which causes
integrated development environment (IDE) instead of virtio drivers
environment. Else, a custom Junos OS will not work as described in
chapter Default Junos OS Configuration for
vJunos-switch.
Create Template Files for the VM
Continue your SSH access to your EVE-NG BMS as root. Create two
template files for the supported Intel and the unsupported AMD
version as shown below. The unique Qemu parameters that are
required to start the image are shown in bold below. A Stop-Command
in the UI is added shutdown: 0 for the community
version that enables a graceful shutdown. Else, you might run into
issues as described in chapter Deployment
and Feature Restrictions of vJunos-switch VM.
cat <<EOF >/opt/unetlab/html/templates/intel/vjunosswitch.yml
---
type: qemu
description: Juniper vEX Switch
name: vEX
cpulimit: 4
icon: JunipervQFXpfe.png
cpu: 4
ram: 5120
eth_name:
- fxp0
eth_format: ge-0/0/{0-9}
ethernet: 11
console: telnet
shutdown: 0
qemu_arch: x86_64
qemu_version: 5.2.0
qemu_nic: virtio-net-pci
qemu_options: -machine type=pc,accel=kvm -serial mon:stdio -nographic -smbios type=1,product=VM-VEX -cpu IvyBridge,ibpb=on,md-clear=on,spec-ctrl=on,ssbd=on,vmx=on
...
EOF
cat <<EOF >/opt/unetlab/html/templates/amd/vjunosswitch.yml
---
type: qemu
description: Juniper vEX Switch
name: vEX
cpulimit: 4
icon: JunipervQFXpfe.png
cpu: 4
ram: 5120
eth_name:
- fxp0
eth_format: ge-0/0/{0-9}
ethernet: 11
console: telnet
shutdown: 0
qemu_arch: x86_64
qemu_version: 5.2.0
qemu_nic: virtio-net-pci
qemu_options: -machine type=pc,accel=kvm -serial mon:stdio -nographic -smbios type=1,product=VM-VEX -cpu IvyBridge,ibpb=on,spec-ctrl=on,ssbd=on,virt-ssbd=on,svm=on,erms=off
...
EOFRun the following command for the system (and the UI) to know your template changes:
/opt/unetlab/wrappers/unl_wrapper -a fixpermissions
Optional: Attach Customized Junos OS Configuration
vJunos-switch similar to Juniper MX Series router, comes with almost no default Junos OS configuration. Hence, to start a new VM easily, use at least the minimal Junos OS configuration as shown below.
The following example creates a virtual configuration image with a predefined Junos OS configuration:
- Enables SSH access for the root account using the password “ABC123”.
- Enables fxp0 to get a DHCP lease for allowing SSH access to the image.
- Sets an external global name-server.
- Enables LLDP to view each link on other nodes in your network.
cat <<EOF >juniper.conf system { host-name vjunos; root-authentication { encrypted-password "\$6\$DOvFAxW9\$HpxgOaGEe5L6MtDJqbWepS5NT6EW23rCuu69gwwGVFr7BpzY2MHS34mPrR0LKRqoGI19tRgpz3vFJkEueW9mQ1"; ## SECRET-DATA } services { ssh { root-login allow; protocol-version v2; } } name-server { 8.8.8.8; 9.9.9.9; } arp { aging-timer 5; } syslog { file interactive-commands { interactive-commands any; } file messages { any notice; authorization info; } } } interfaces { fxp0 { unit 0 { family inet { dhcp force-discover; } } } } protocols { lldp { interface all; } lldp-med { interface all; } } EOF
The default vJunos-switch image activates only the first 10 ge-0/0/x interfaces, which is enough. But with Junos OS Release 23.2 or later, you can activate maximum of 96 interfaces. So, you can add commands as shown below to have that higher range and to edit the EVE-NG templates.
set chassis fpc 0 pic 0 number-of-ports 96
If you enable more than 20 interfaces using this method, you cannot use the resulting vJunos-switch to build campus fabric configurations in the Mist GUI.
In the next step, you can use the original bash script
make-config.sh from the vJunos-switch support site.
The script creates an IDE-HD image to load your custom
configuration.
You can download the image through a link. For example: https://webdownload.juniper.net/swdl/dl/anon/site/1/record/168885.html
As the script does not change with every vJunos-switch release, you can create the script using the below steps using a base64 encoded gzip file.
cat <<EOF >make-config.sh.gz.uue H4sICG8BK2UAA21ha2UtY29uZmlnLnNoAI1T0W7TMBR9nr/iLO1DKy1pG97oOjRtMBWtHYKxF4So lzitaZ1ktpPC0P4dO3azMopEnqLre88599x7O8eDe54P7qlakQ7pQNA1C5Miz/gy8qGLovwp+XKl 0Uv6iIfxqxO8r3JeMok509tCrtUJpnkSmeTzzQZNsoJkismapZFDkYxqBgoHDsE0TblaI5OFMGFV leWGsxTfHXRk86ALUK1pYpQ0/6gNc6FwNwPPlaZ5wgx6peiS9fr4RY5YsioQfLYBvMaLdnDqwX3o DKfuJ7RKzgJT/oNrDMfkiSQbRvOqxD7shY3xfImqjKLIpFeiqHKNMEP4gO5sfns5/UiONoVi2pSG KbrXNzcfLt/ekSMpEMqsRvfT7fnVdH61F/F1T2RH+i2jfGOscNw+ON6riL3SkS3iGb6g28HxBDG+ jqFXLDfSrAVjknFCiKecLMRaM9EIC0sMaioHWpQL4gT881msUy5b4QNnGUlMopEy+uvhgYkq5GKJ xI3cuCPp1ojGaEa8H5NFa1KoVsXWJnXjhe/lje1l+NzLn7Y0TYl1pqI6oxpWRZgjqIUIU6pp8Gz6 YTQ3y3fOYrNUWSGFwWmWcVc6hvXXjDo4zO7GrtEo2BW1kzzIC/+9pHdY7Tn8jwIrwW+kuU27kJl5 6Km+xfP35cDigPSStB2RkUIlkvox22kdWNv8gejlI6L+bglbhn04P9M0IO5SCPkNKH2wR0EEAAA= EOF base64 -d make-config.sh.gz.uue make-config.sh.gz gunzip make-config.sh.gz cat make-config.sh
If you plan to onboard vJunos-switch to a Mist Cloud: You can directly connect VM to the Mist Cloud. Then, use the embedded device adoption commands to add the VM to the inventory. Review chapter Default Junos OS Configuration for vJunos-switch and then run the following example there before you create the final configuration disk.
Use the following two CLI commands to create an image called
hdb.qcow2 in your custom configuration.
chmod 777 make-config.sh ; ./make-config.sh juniper.conf hdb.qcow2 'juniper.conf' -> '/var/tmp/tmp.TYloe3JQtd/config/juniper.conf' Formatting 'hdb.qcow2', fmt=raw size=1048576 mkfs.fat 4.1 (2017-01-24) mkfs.fat: warning - lowercase labels might not work properly with DOS or Windows /dev/loop4 has 64 heads and 32 sectors per track, hidden sectors 0x0000; logical sector size is 512, using 0xf8 media descriptor, with 2048 sectors; drive number 0x80; filesystem has 2 12-bit FATs and 4 sectors per cluster. FAT size is 2 sectors, and provides 502 clusters. There is 1 reserved sector. Root directory contains 512 slots and uses 32 sectors. Volume ID is f9fd5527, volume label vmm-data . Copying file(s) to config disk hdb.qcow2 ./ ./config/ ./config/juniper.conf Cleaning up... removed '/var/tmp/tmp.TYloe3JQtd/config/juniper.conf' removed directory '/var/tmp/tmp.TYloe3JQtd/config' removed directory '/var/tmp/tmp.TYloe3JQtd' removed directory '/var/tmp/tmp.SbTNcpocEl' Config disk hdb.qcow2 created ls -l *.qcow2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4011065344 Oct 11 00:08 hda.qcow2 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1048576 Oct 14 21:20 hdb.qcow2 # again execute the permissions fix /opt/unetlab/wrappers/unl_wrapper -a fixpermissions
