Option: Configuring VPLS Traffic Flooding over a Point-to-Multipoint LSP
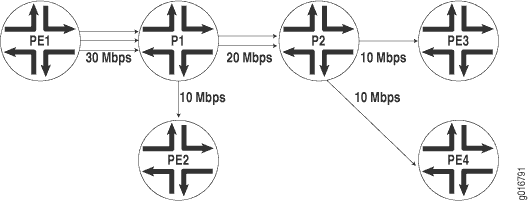
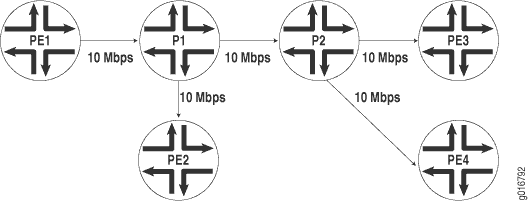
In each VPLS routing instance, you can configure a dedicated point-to-multipoint LSP to carry all unknown unicast, broadcast, and multicast traffic. Enabling this feature increases the efficiency of your network, because duplicate copies of flooded traffic do not have to be created for each PE router in the VPLS routing instance. Figure 1 shows how flooded traffic reaches PE routers in a VPLS routing instance when a point-to-multipoint LSP is not configured for flooding. Figure 2 shows an example of a VPLS routing instance configured with point-to-multipoint LSP flooding.
You cannot configure point-to-multipoint LSP flooding if your VPLS network is configured for interoperability between BGP and LDP signaling.
You have three options when configuring a point-to-multipoint LSP for flooding:
Static point-to-multipoint LSP—Configure this option to control which path each PE sub-LSP takes. When using this option, ensure that all PEs within the VPLS routing instance are part of the static point-to-multipoint LSP. When you add PEs to the VPLS routing instance, you must configure a sub-LSP for the new PE and add the sub-LSP to the static point-to-multipoint LSP. To configure a static point-to-multipoint LSP, include the
label-switched-pathpath-namestatement at the [edit protocols mpls] hierarchy level.Dynamic point-to-multipoint LSP with a preconfigured template—Configure this option to create a dynamic point-to-multipoint LSP with specific parameters such as link protection and optimized time. With this option, newly added PEs are automatically added to the point-to-multipoint LSP. To use the preconfigured template, include the
templatestatement at the [edit protocols mpls label-switch-path path-name] hierarchy level.Dynamic point-to-multipoint LSP with a default template—Configure this option to automatically create a dynamic point-to-multipoint LSP with default parameters. With this option, newly added PEs are automatically added to the point-to-multipoint LSP. To use a default template, include the
default-templatestatement at the [edit routing-instances routing-instance-name provider-tunnelrsvp-te label-switched-path-template] hierarchy level.
To define the parameters for a static point-to-multipoint
LSP, include the label-switched-path path-name statement at the [edit protocols mpls] hierarchy
level:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
label-switched-path vpls-bar-p2mp-s21_lsp_a {
to 192.168.1.1
p2mp vpls-bar-p2mp-lsp;
}
label-switched-path vpls-bar-p2mp-s21_lsp_b {
to 192.168.1.2
p2mp vpls-bar-p2mp-lsp;
}
}
}
To add a new PE router to the static point-to-multipoint
LSP, include the label-switched-path sub-path-name statement at the [edit protocols mpls] hierarchy
level:
[edit]
protocols {
mpls {
label-switched-path added-PE3 {
to 1.1.1.1
p2mp vpls-bar-p2mp-lsp;
}
}
}
For more information on configuring static and dynamic point-to-multipoint LSPs, see the Junos MPLS Applications Configuration Guide.
To enable this feature, configure either the static or label-switched-path-template options for
the rsvp-te statement at the [edit routing-instance routing-instance-name provider-tunnel] hierarchy
level:
[edit]
routing-instance foo {
provider-tunnel {
rsvp-te {
static-lsp vpls-bar-p2mp-lsp;
}
}
}
To verify your work, enter the show vpls connection
extensive command:
Router_1# show vpls connection extensive .... status-vector: BF connection-site Type St Time last up # Up trans 2 rmtUpJan 31 10:14:37 2007 1 Local interface: lsi.32768, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VPLS Description: Intf -vpls VPLS-A local site 1 remote site 2 Remote PE: 10.255.164.2, Negotiated control-word: No Incoming label: 262153, Outgoing label: 800000 RSVP-TE P2MP lsp: Ingress branch LSP: 13:vpls:10.255.164.1:BPLS-A, State: Up Egress branch LSP: 4:vpls:10.255.164.2:VPLS-A, Statue: Up TimeEventInterface/Lb1/PE Jan 31 10:14:37 2007 status update timer Ingress RSVP-TE P2MP LSP: 11:vpls:10.255.164.1:VPLS-A, Flood next-hop ID: 476
