Configuring an OpenRoaming Passpoint
Use RadSec with Passpoint for Juniper Mist WLANs.
Juniper Mist supports Wi-Fi certified Passpoint™ (previously called Hotspot 2.0). Passpoint connections are secured with WPA-2/WPA-3-Enterprise for authentication and connectivity, which means Wi-Fi users can connect to Passpoint-configured WLANs as if they were cellular towers. Passpoint supports operator-specific subscriber policies, one of which is network selection, that you can then leverage in Mist when configuring WLANs. Mist also supports OpenRoaming. OpenRoaming uses RadSec, also known as RADIUS over TLS, to securely transfer the RADIUS packets over a public network.
When the RadSec option is enabled in a WLAN, Mist automatically generates a unique CA certificate for the organization, as well as certificates for Juniper APs. The Juniper APs must be running firmware version 0.8x or later to support RadSec, and by extension, be able to implement OpenRoaming. In addition, to complete the set up, you will need to import the Mist CA certificate to your RADIUS server so it can authenticate the certificates presented by the APs in your org.
On the Mist side, you will need to get the RADIUS server certificate and import it to Mist, as described in the following procedure.
Set up the OpenRoaming Certificates
To import an existing RadSec server CA certificate to your org:
- From the Mist portal, click Organization > Admin > Settings and then scroll down to the RadSec Certificates section.
- Click the Add a RadSec certificate link to open the RadSec certificate window.
- Copy your RadSec server CA cert and paste it into the RadSec certification
window. It should look something like this:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- HASHHASHA7qgAwIBAgIBATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADBbMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEN HASHHASHHASHHASHAgIBATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADBbMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEN HASHHASHHASHHASHHASHHASHBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADBbMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEN -----END CERTIFICATE-----
-
Click the Add button, and then Save in the upper right corner of the Mist console.
Create an OpenRoaming WLAN
With all the required the certs configured in your organization, you can create a WLAN that uses OpenRoaming. This can be either site specific (Site | Wireless > WLANs) or global (Organization | Wireless > WLAN Templates > Create Template).
Note that when updating an existing WLAN to use OpenRoaming, Wi-Fi service on Juniper APs attached to the WLAN template will be interrupted during the update.
To create a site-level WLAN with OpenRoaming using RadSec:
- From the Mist portal, click Site | Wireless > WLANs and then click the Add WLAN button to create a new WLAN.
- Give the WLAN a name in the SSID field.
- Scroll down the page to the Security section, and choose
the following Security Type:
- WPA2 or WPA3
Enterprise (802.1X)
- As shown in Figure 1, the Passpoint section becomes
available when you select Enterprise (802.1X). Figure 1: OpenRoaming PasspointChoose Enable, and select the following Operators:
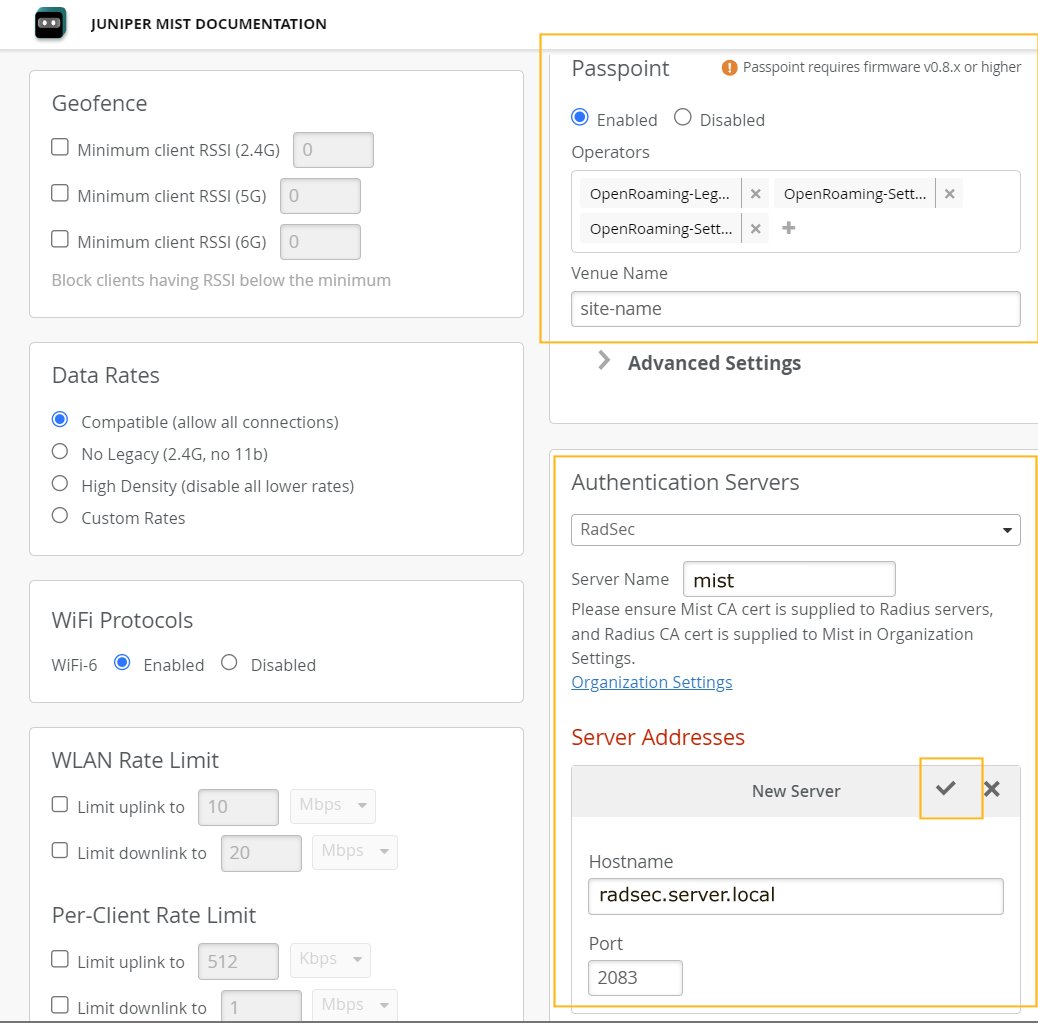
OpenRoaming-Legacy
OpenRoaming-Settled
OpenRoaming-Settlement-Free
- In the Authentication Servers section, choose
RadSec from the drop-down.
- For Server Name, use the name specified for your RadSec proxy as it appears in the server certificate. Juniper APs will use this name to verify the RadSec server.
- For Port, the default is 2083. If you use something else for your RadSec server, specify that.
- Click the check mark to add the RadSec server configuration.
- At the top of the configuration page, click the Create button to complete the set up.
About RadSec
With RADIUS alone, clients use a trusted network to connect to the RADIUS server, which then authenticates their identity and provides authorization. Part of this handshake involves exchanging IP addresses, in plain text, and uses a shared secret to establish the connection. This sequence repeats each time the client connects or reconnects. There are shortcomings, though, because UDPs are not acknowledged by the receiver, the connection may not be secure, and roaming can interrupt users with the need to re-authenticate.
RadSec, on the other hand, forms an encrypted TLS tunnel between the client and server, which allows OpenRoaming traffic to be sent securely over public networks. RadSec also leverages Enterprise Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and x.509 digital certificates to allow dynamic connections to be created on the fly. The organization issues certificates to both the client and the server, thus allowing each to prove the authenticity of the other (and so prevents man-in-the-middle attacks). Organization-level PKI certificates are also able to provide seamless roaming because the client simply resubmits the certificate at each call for reauthentication. Finally, the RadSec proxy uses OpenRoaming protocols to route authentication requests from roaming users to the correct RADIUS according to their credentials.
