Enable Port Mirroring
Port mirroring copies source traffic traversing one or more interfaces and forwards it at line rate to a specified destination. It is useful for monitoring network traffic, enforcing network policies, identifying network issues, and as a part of intrusion detection.
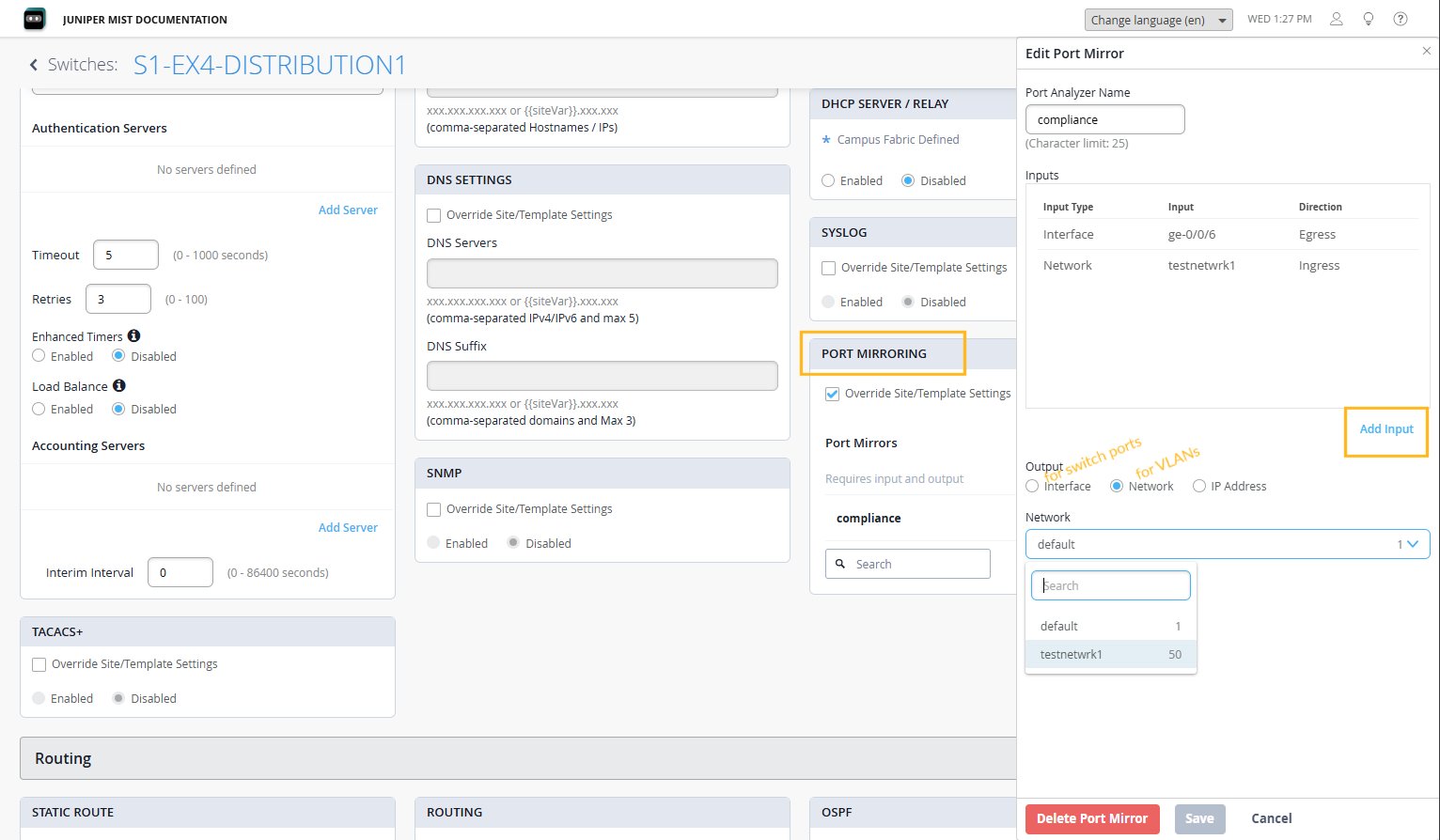
You can set up port mirroring for ingress and/or egress traffic on any interface on the switch (except those identified below), as well as for ingress traffic on a VLAN (network, in the terminology of Mist dashboard), private VLAN, or bridge domain. You can apply it to all traffic on the port, or a filtered subset of the traffic, as defined in a firewall policy. Mirrored traffic is sent to a local interface, VLAN, or bridge domain for remote monitoring or analysis.
From the Mist dashboard, you can configure port mirroring for managed switches that are part of a switch template, as well as for independent switches. To do so, you'll need to have an input, that is, the source of the traffic, and an output, that is, the destination mirrored traffic will be forwarded to. For switch ports, you can specify whether you want to mirror traffic in the ingress direction or egress. If you select a VLAN as the source, ingress mirroring is assumed.
Mirroring is not supported for management interfaces (such as me0 or vme0), fiber channel interfaces, or integrated routing and bridging (IRB) interfaces (which are also known as routed VLAN interfaces or RVIs). A maximum of four port mirroring configurations is allowed.
To set up port mirroring on a managed switch that is part of a switch template: