Application Settings
Define the applications that you want to use in your application policies, which allow or deny access to network destinations.
Custom Applications
When you select the Custom Apps as the application type, you'll define traffic destinations by IP address range, domain name, and protocol. This approach is useful for internal services, specific IP ranges, and unique protocols used in your network.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| IP Address | Enter the network IP address, including prefix (if any) of the application. You can enter multiple destination IP addresses or domain names separated by a comma. |
| Domain Names | Enter the domain name of the application, such as juniper.example.com. The domain name is used in cloud breakout profiles to generate the fully qualified domain name (FQDN). The cloud security providers use the FQDN to identify the IPsec tunnels. |
| Protocol, Port Number, and Port Ranges | Select a protocol and specify the port ranges (start and end
ports) that the application is using. If you select Custom (SRX Only) as the protocol, also enter a protocol number from 1-254. Note:
If you need to add more protocols for this application, click the + button at the top-right corner of the protocol section. |
Consider using variables to represent values. If you see the VAR label next to a field heading, you can enter variables in that field to match destinations without having to enter specific values.
It's a good practice to create an application with a less specific address. For example, you might have a data center with a 10.0.0.0/8 prefix. A more specific address can be contained within this prefix for more specific path selection.
The following table provides examples.
| Custom Application | IP Address | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ANY | 0.0.0.0/0 |
Use this address to match all or any IPv4 address destinations. The IP address 0.0.0.0 also serves as a placeholder address. |
| SPOKE-LAN1 | 10.0.0.0/8 | A match criterion for all IP addresses inside the corporate VPN. |
| HUB1-LAN1 | 10.66.66.0/24 |
A match criterion for all IP addresses attached at the LAN-interface of the Hub1 device. |
| HUB2-LAN1 | 10.55.55.0/24 |
A match criterion for all IP addresses attached at the LAN interface of the Hub2 device. |
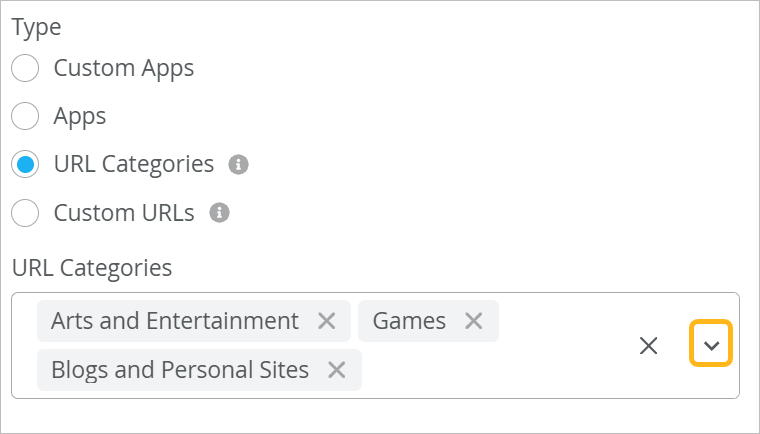
URL Categories
Applications represent the endpoints users are trying to reach—these can be IPs, domain names, or URLs. URL patterns help define these destinations more flexibly. The Juniper Mist cloud provides a list of URL categories based on types (example: shopping, sports) and grouped by severity (all, standard, strict). You can use the URL categories to define an application. Additional sub-categories offer even more granular filtering for application creation. You can select a single or multiple URL categories for an application.
For example: You can create an application and name it "social media" and select URL categories as Social Networking or Instant Messaging. Then you can create policies to block or restrict access during work hours.
When adding an application, you can use the URL Categories type to define destinations by categories such as entertainment, shopping, and sports.
For example, create an application called Social Media and select URL categories Social Networking and Instant Messaging. Later, on the Application Policies page, create policies to block or restrict access to these URLs during work hours.
For Session Smart Routers, we recommend configuring Applications with URL categories on spoke devices only, and not on hub devices.
Custom URLs
When defining applications, you can enter custom URLs for services not covered by predefined applications.
You can enter:
-
Exact domain names.
example.com -
Wildcard domains using an asterisk. Example:
*.example.comWith this approach, you can group related services under one application. For example,
*.google.comincludes Gmail, Drive, Meet, and other Google sites. -
Use a comma separator to specify multiple URLs.
-
You can specify up to 15 URL patterns for an application.
-
Only the
*wildcard is supported. -
You can view the supported patterns by hovering the mouse over the tooltip icon. Note that you can use the https://abc.com pattern only for SRX Series devices.
Figure 2: Custom URLs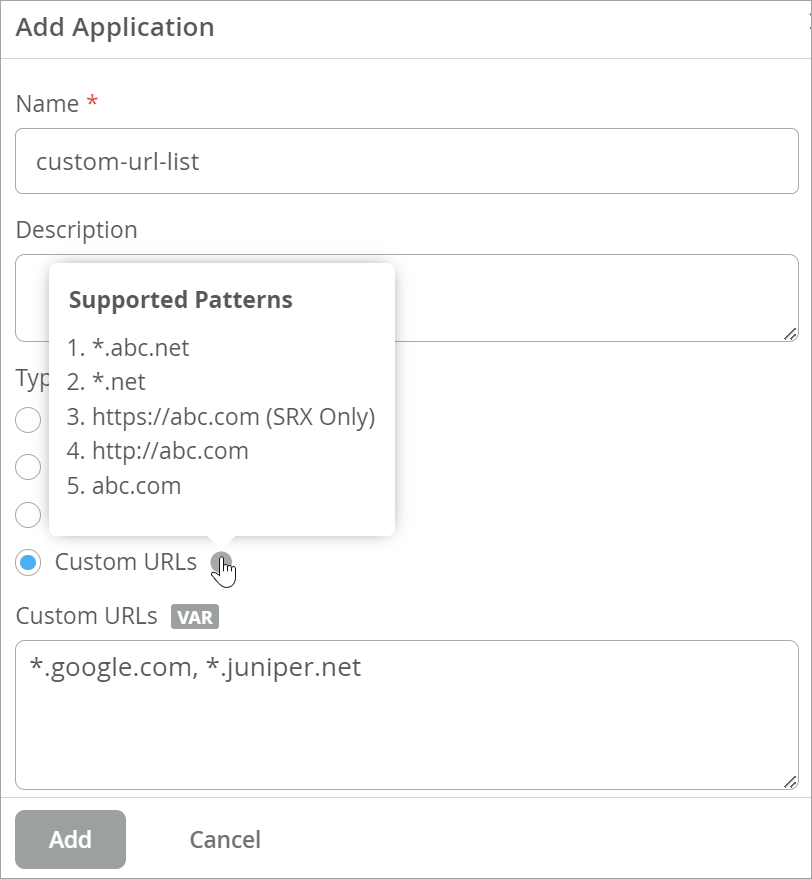
Advanced Settings
Under Advanced Settings, specify the Traffic Type. Keep Default for general traffic, select a preset traffic type, or select Custom.
-
If you select a preset traffic type, you'll see the values for settings such as failover (SSR only), latency, jitter, and loss.
Note:For Apps and URL Categories, you can only select a specific traffic type after you select the Override Settings check box.
-
If you select Custom as the traffic type, also select a Traffic Class, and then adjust the preset values as described in the following table.
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Failover Policy (SSR Only) | Applies only to SSRs
|
| Traffic Class |
These options provide granular control over traffic prioritization. Specify the priority for this application.
|
| DSCP Class (SSR Only) | Applies only to traffic through SSRs The Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) value tags packets for specialized handling across the network. When you select a traffic class (Best Effort, High, Medium, or Low), the applicable default DSCP Class value is displayed as a help text. You can choose to override it to fine-tune this application to your specifications. Range: 0-63 |
| Maximum Latency |
By setting maximum latency in milliseconds, you can ensure that delay-sensitive applications like voice and video meet your performance requirements. Based on this threshold, SD-WAN avoids links with excessive delay. Range: 0-4294967295 (milliseconds) |
| Maximum Jitter |
You can constrain jitter, or the variation in latency, by setting a maximum value in milliseconds. Based on this threshold, SD-WAN selects stable links to maintain predictable performance. Range: 0-4294967295 (milliseconds) |
| Maximum Loss |
For further fine-tuning, you can specify the maximum acceptable percentage of packet loss to maintain application reliability. Based on this threshold, SD-WAN avoids links with high packet loss rates. Range: 0-100 |
