How to Configure a Virtual Mist Edge Appliance
This chapter provides information about the overview and various tasks that you perform to configure a virtual Mist edge appliance.
Virtual Mist Edge Overview
You can run Juniper Mist Edge as a hypervisor on VMware to implement a virtual Mist Edge architecture using a Juniper Mist Edge appliance as the virtual machine (VM).
- Hardware Specifications for a Mist Edge Virtual Machine
- Virtual Network Interfaces
- Firewall Port Requirements
Hardware Specifications for a Mist Edge Virtual Machine
The following are the minimum hardware requirements to implement a Mist Edge VM.
| Hardware Component | Quantity or Capacity |
|---|---|
| CPU |
4 vCPUs |
| RAM |
32 GB |
| Hard disk |
100 GB (thick provisioned) |
| NIC |
Three virtual NICs |
-
Supported VMware hypervisor—VMware ESXi, tested versions - 6.7.0, 7.0
-
CPU support—Juniper Mist Edge requires 1G HugePages support from the CPU. Hence, the minimum supported CPU is Intel Haswell family and above. Juniper Mist Edge does not work on older Intel CPUs or on AMD CPUs.
-
NIC Support—Juniper Mist Edge requires Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) support. Please refer to https://core.dpdk.org/supported/nics/intel/ to see if your NIC is supported.
-
Preferred NICs—Intel x520 Dual Port 10GbE SFP+, Intel i350 Dual Port 1GbE, rNDC Qlogic Quad Port 10GbE SFP+, and rNDC Intel i350
Contact Juniper Mist Sales team to obtain a link to Mist Edge ISO file for installation.
Virtual Network Interfaces
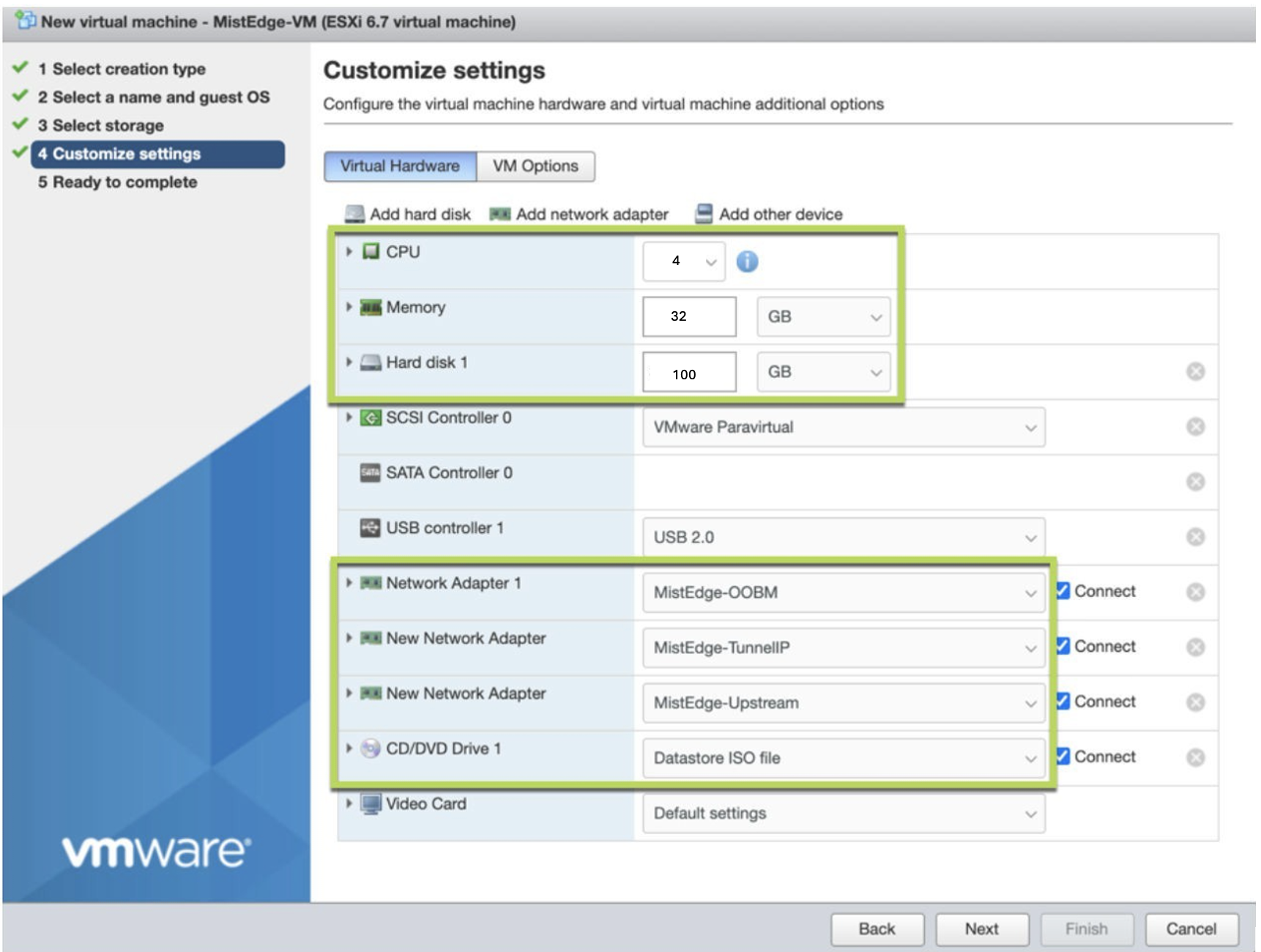
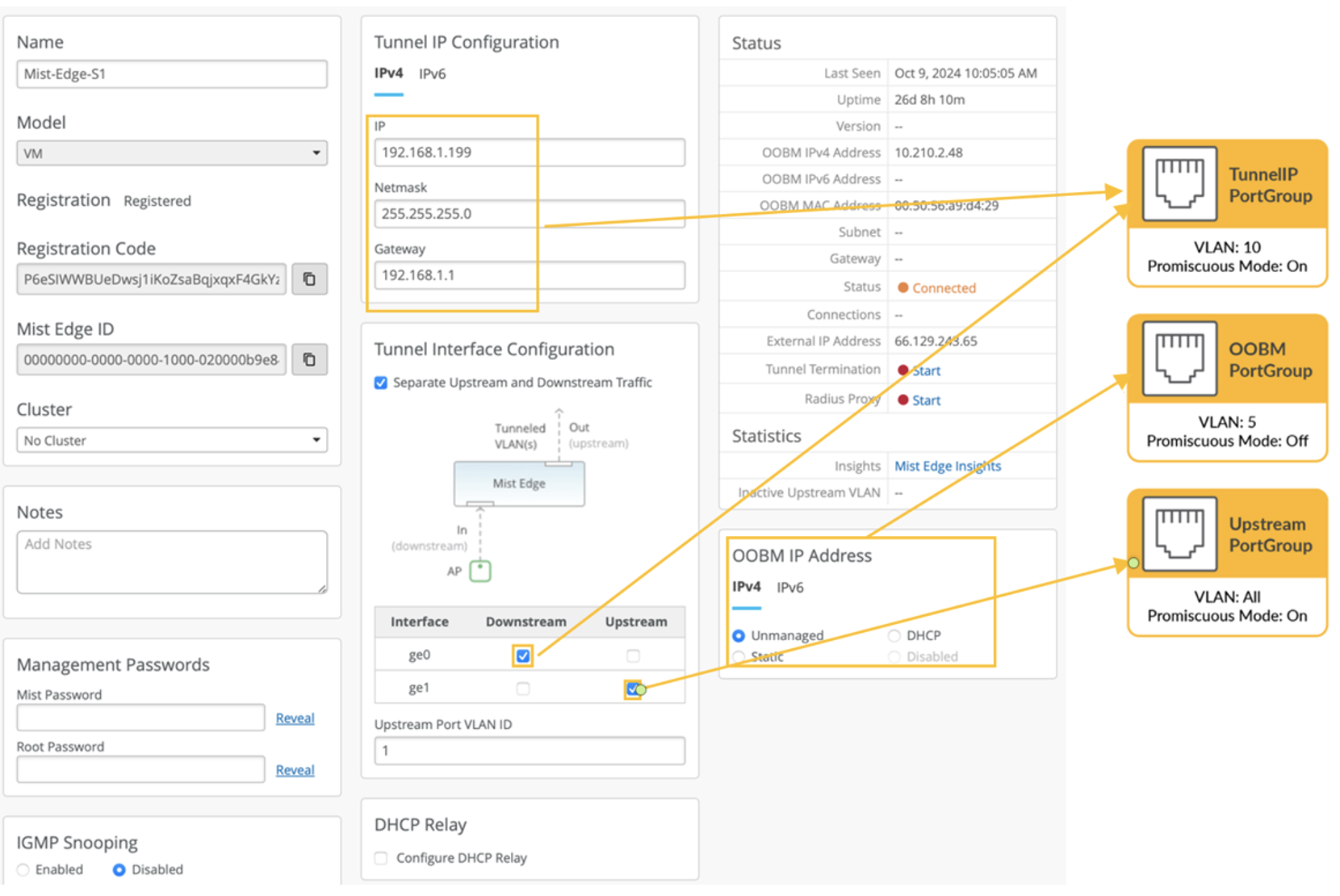
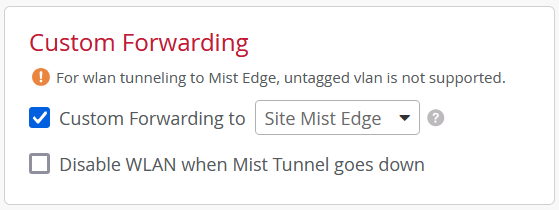
Juniper Mist Edge requires the following three virtual NIC interfaces:
-
Out-of-Band Management (OOBM) Port Group—To connect Juniper Mist Edge to the Juniper Mist™ cloud and Radius Proxy service.
-
Downstream (Tunnel IP) Port Group—To allow Mist Tunnel (L2TPv3 or IPSEC) establishment from a Mist access point (AP).
-
Upstream Port Group—To uplink to the wired network with all the VLANs that need to be extended for clients.
The following image illustrates virtual NIC interfaces:
Firewall Port Requirements
Configure the firewall to allow the following connections:
-
The OOBM interface must have outbound access to ep-terminator.mistsys.net or ep-terminator.eu.mistsys.net (for the EU AWS environment) on TCP port 443.
-
The tunnel IP interface must allow incoming traffic on UDP Port 1701 (either the non IPsec campus or the branch use case).
-
For remote teleworker use cases with IPsec encryption, the tunnel IP interface must allow incoming traffic on UDP port 500 and UDP port 4500. Also, the firewall needs to execute port translation from outside to the tunnel IP address.
-
For a remote user in a Dot1x RadSec Proxy implementation, the OOBM interface should be able to access the RADIUS server. Also, the firewall must execute port translation on TCP port 2083 toward the tunnel IP address.
-
Ensure the following domains are accessible through your firewall for proper installation and functionality:
-
*.mistsys.net
-
*.debian.org
-
VMware Port Groups
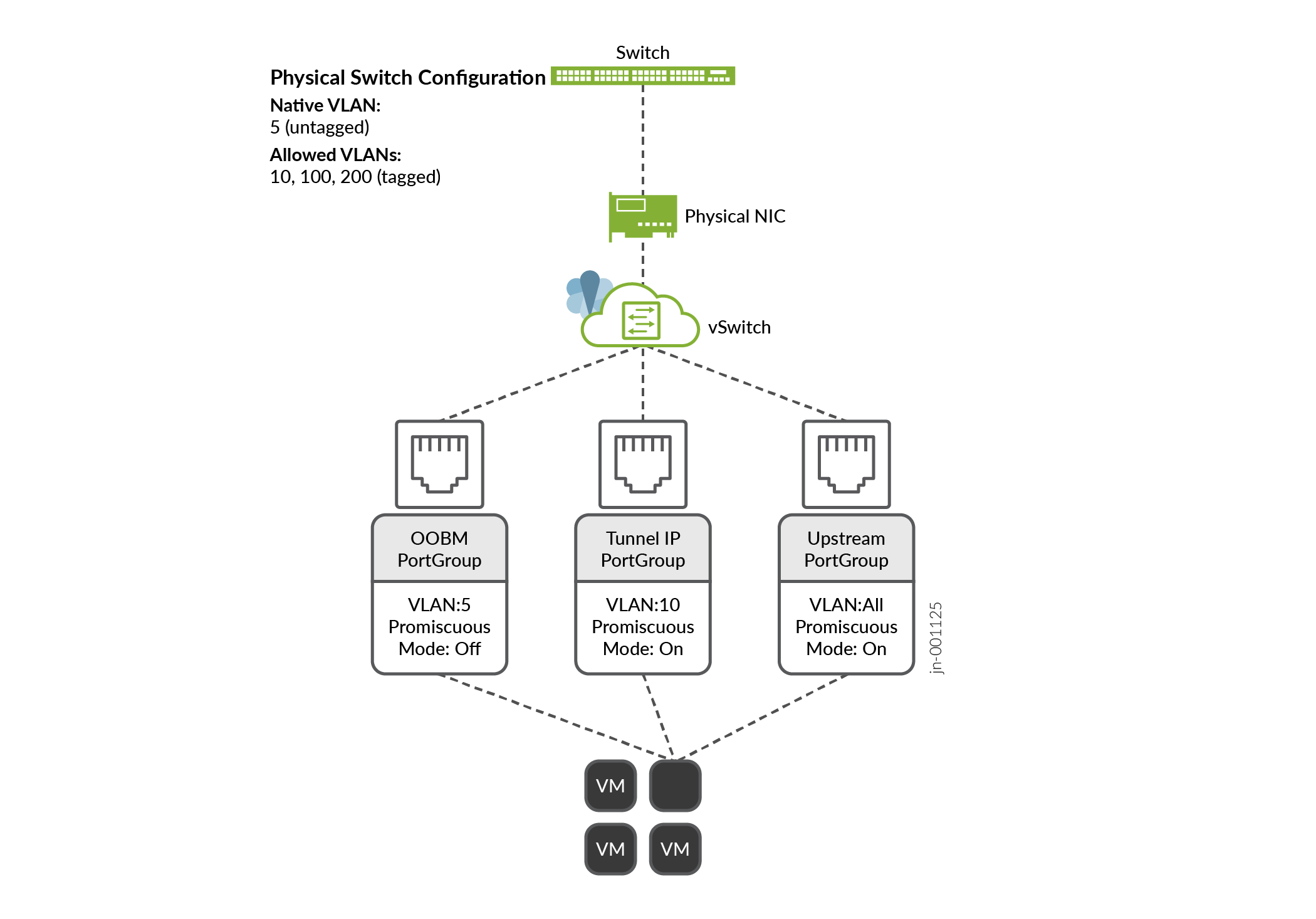
You can configure three port groups for Juniper Mist Edge on VMware. Actual binding of port groups to individual vSwitches or dvSwitches or to physical NICs does not matter. You can adapt the binding of port groups to individual vSwitches or dvSwitches or to physical NICs based on customer and network requirements.
The following image depicts the port groups for virtual Mist Edge:
Example: Mist Edge VM Deployment
This chapter describes how to deploy a Mist Edge VM.
- Configure a VMware Port Group
- Create a Juniper Mist Edge VM Using the VMWare ESXi Portal
- Deploy Juniper Mist Edge Using the Juniper Mist Portal
Configure a VMware Port Group
This topic provides information about a Juniper Mist port group configuration, with examples.
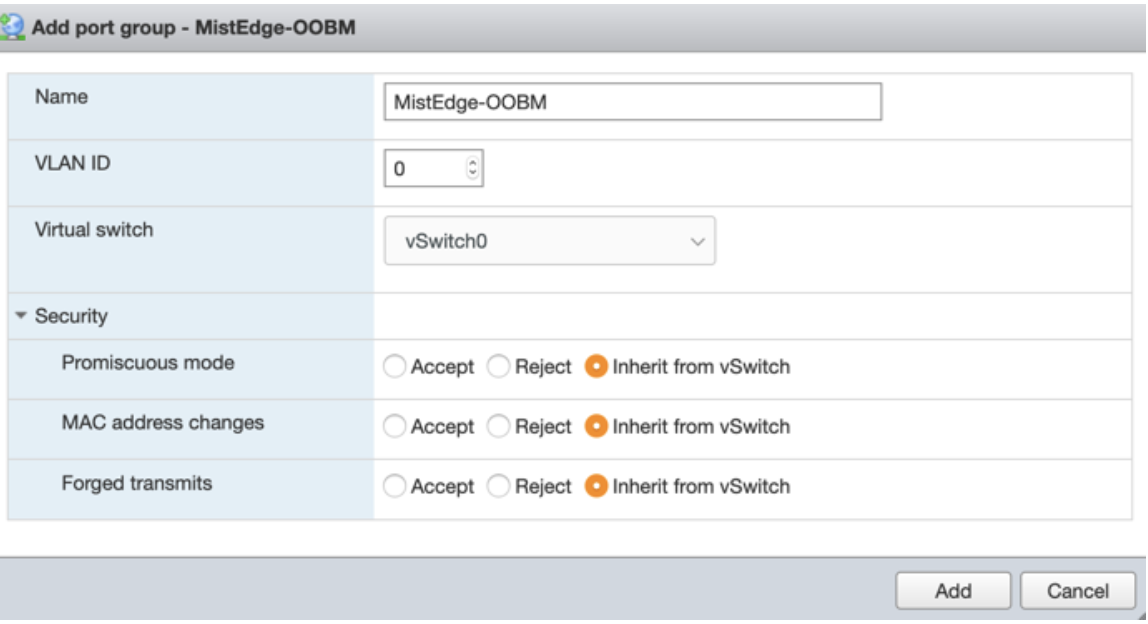
OOBM Port Group
In this example VLAN ID is set to 0 on the VMware side, while the actual untagged VLAN on the switchport is set to 5. .
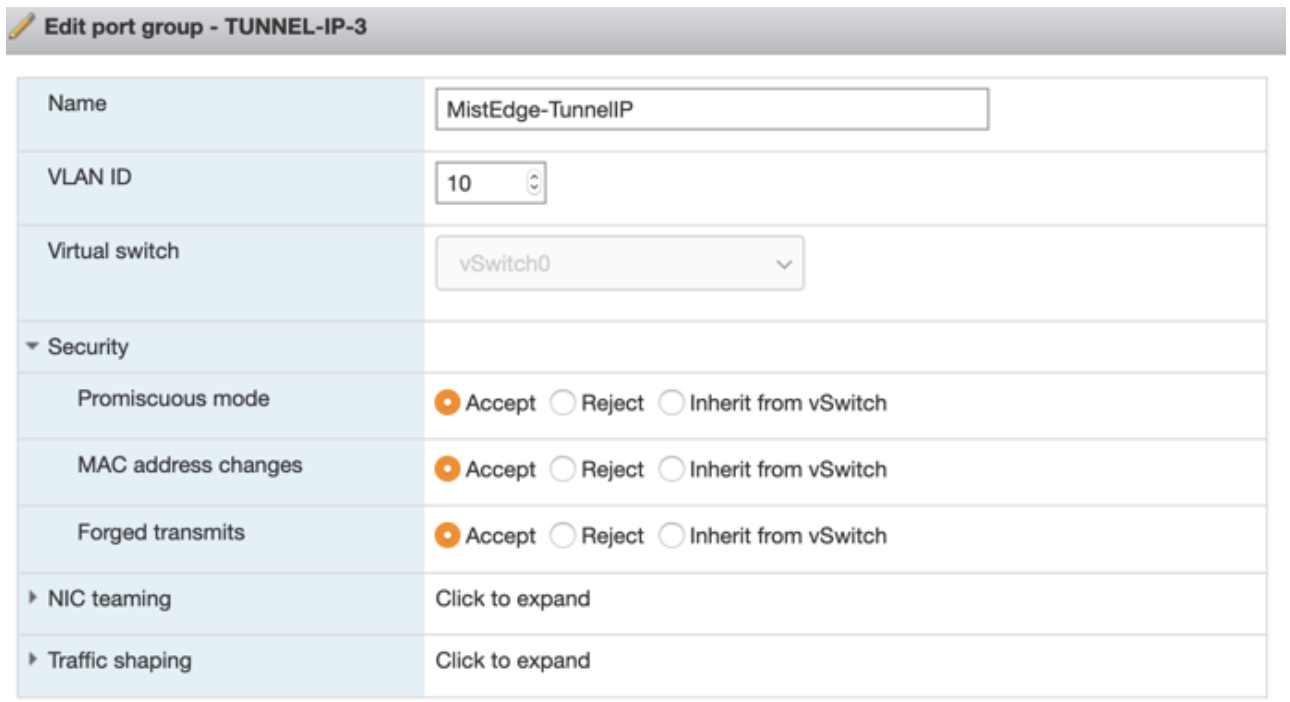
Tunnel IP Port Group
In this example, incoming tunnel connections from the access point (AP) land in this tunnel IP port group.
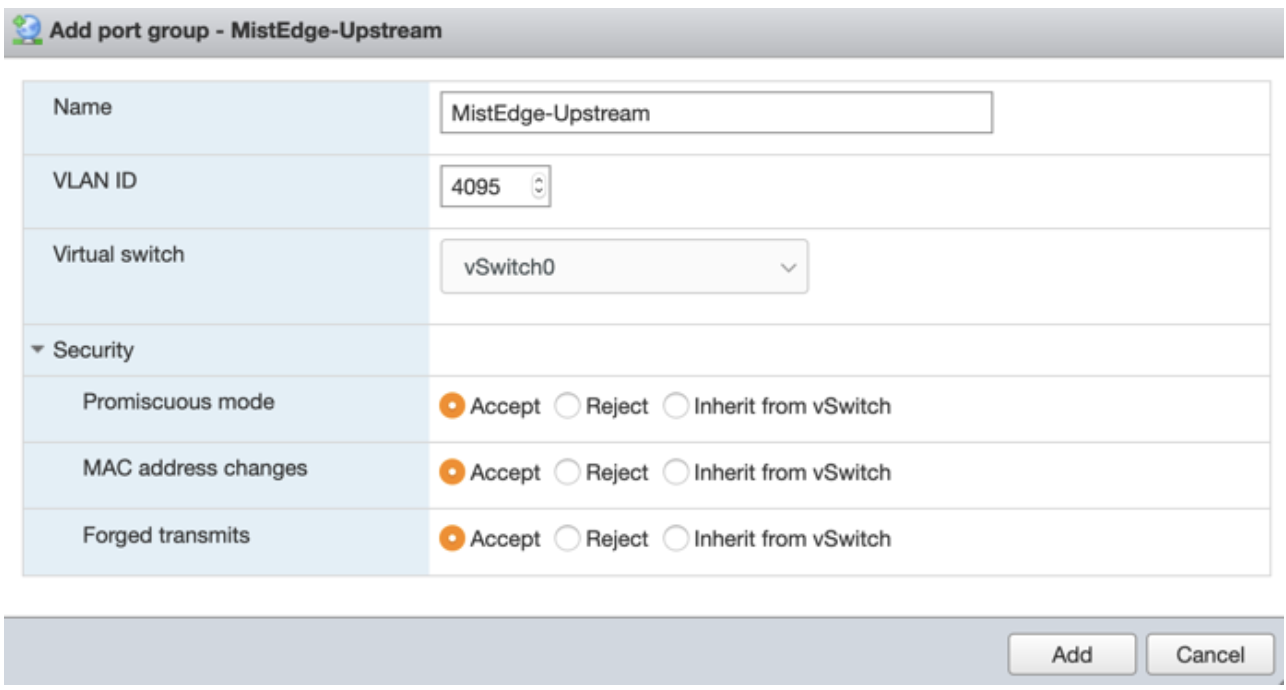
Upstream Port Group
You can configure the upstream port as trunk to tag all VLANs. The ESXi running a basic vSwitch has a 4095 VLAN ID that tags all VLANs automatically. The dvSwitch on a large-scale vCenter deployment enables you to configure VLAN range.
Multiple Uplinks and LAG Configuration
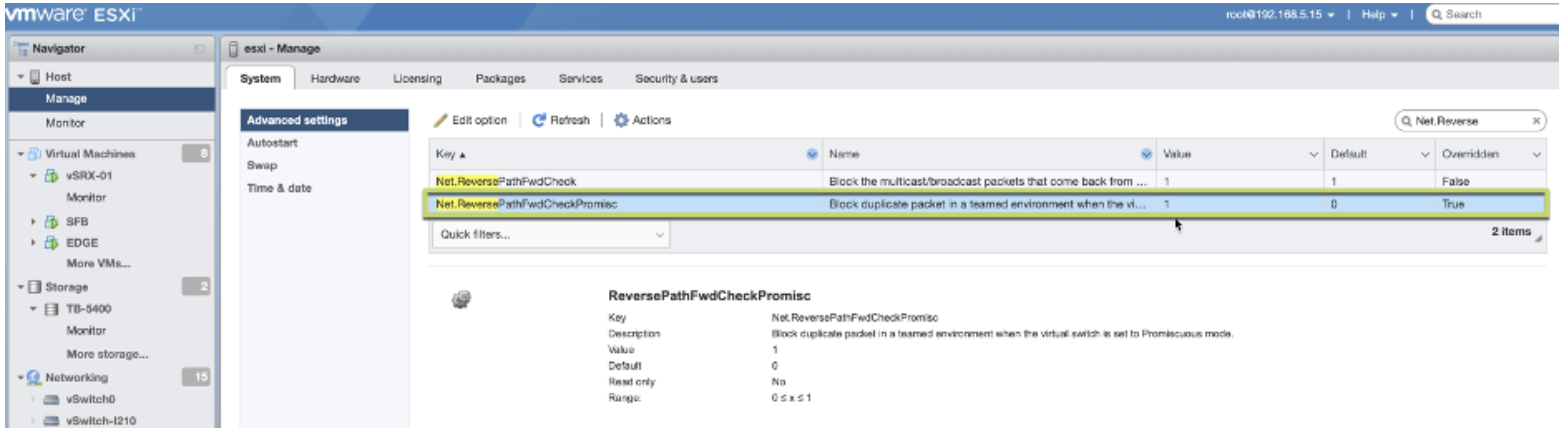
While VMware supports multiple uplinks with static or dynamic link aggregation, the default behavior for port groups in Promiscuous mode causes issues with any broadcast or Layer 2 (L2) multicast traffic.
By default, VMware vSwitch or dvSwitch copies any outgoing broadcast or multicast frame to all the uplinks, including the one it came in from. You must disable this behavior to allow client traffic to be tunneled without causing any loops on the network. This change is mandatory whenever using multiple uplinks with VMware (ESXi or vCenter).
For more information about disabling this behavior, see VMware KB article
Enabling ReversePathFwdCheckPromisc on VMware ESXi Portal
Create a Juniper Mist Edge VM Using the VMWare ESXi Portal
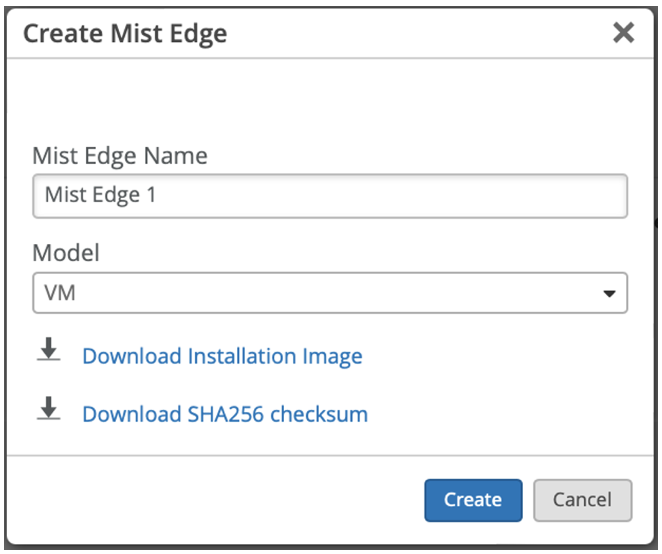
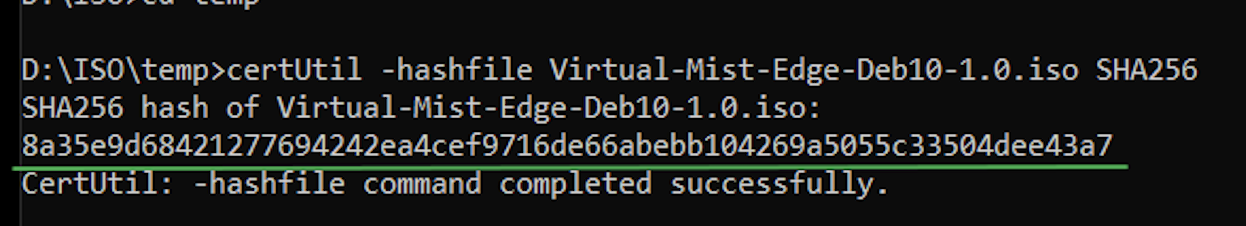
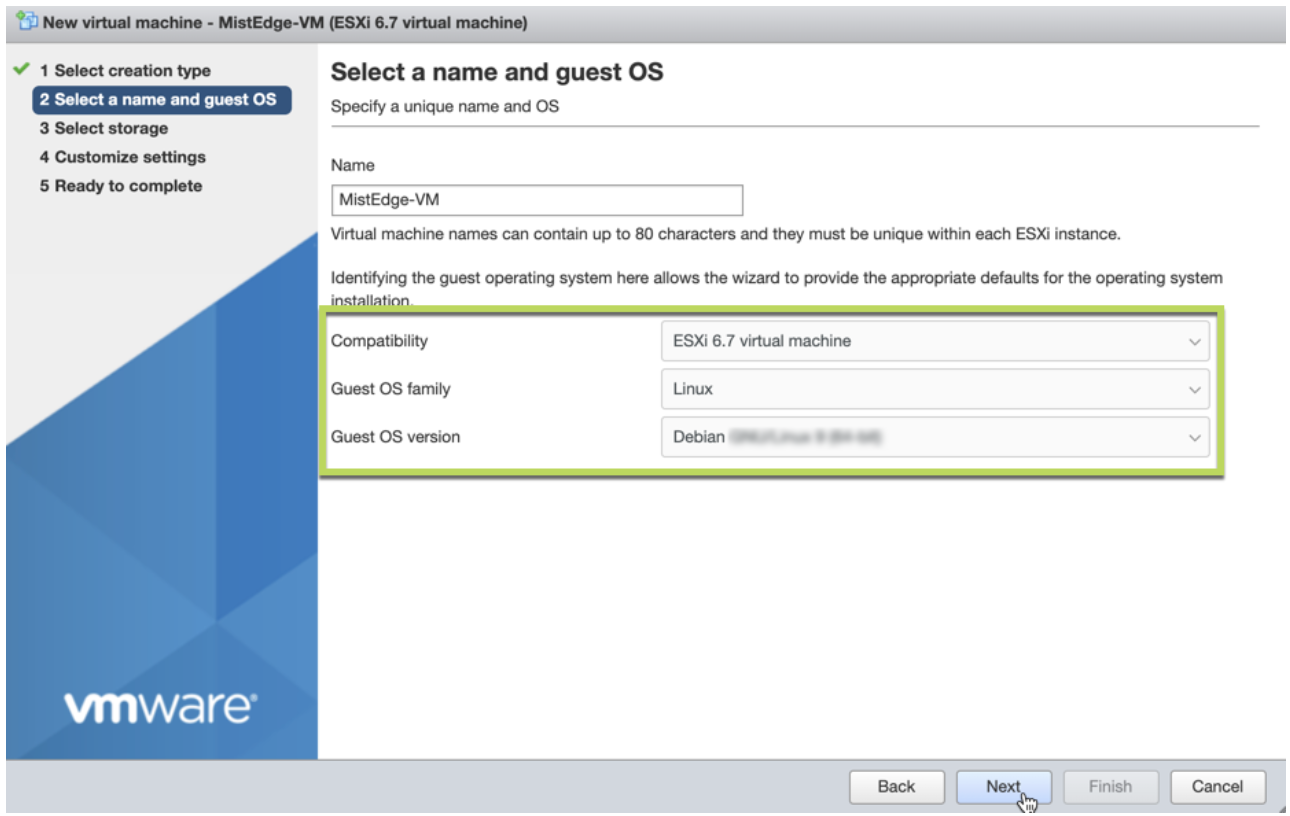
This topic describes how to download installation image from Juniper Mist portal and create a Juniper Mist Edge VM.
To download installation image and to create a Juniper Mist Edge VM:
Deploy Juniper Mist Edge Using the Juniper Mist Portal
This chapter provides information about the various tasks that you perform to deploy the Juniper Mist™ Edge.
- Create Juniper Mist Edge
- Provision the Virtual Mist Edge
- Create a Mist Cluster and Assign a Mist Edge
- Create Mist Tunnel (Organization Level)
- Create Mist Tunnel (Site Level)
- Configure WLAN Template
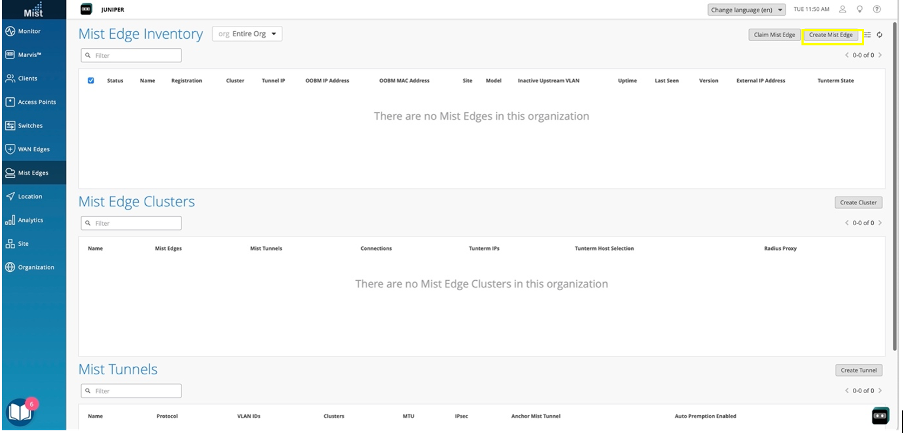
Create Juniper Mist Edge
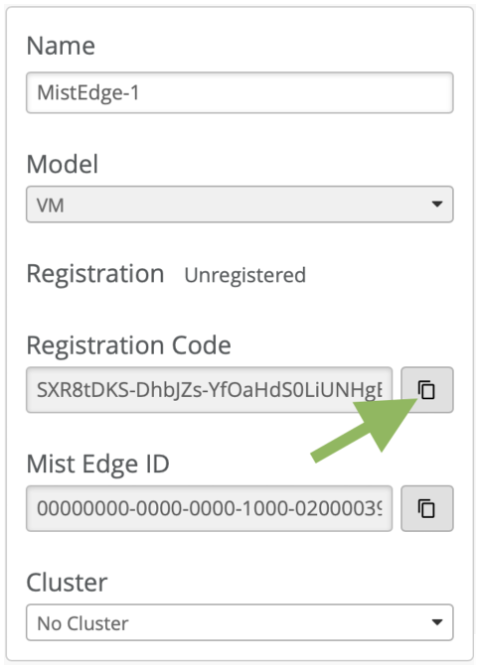
When you want to implement a virtual Mist Edge architecture using a Juniper Mist Edge appliance as the virtual machine (VM), you have to create a Juniper Mist Edge from the Juniper Mist Portal.
To create a Juniper Mist Edge from the Juniper Mist portal:
Provision the Virtual Mist Edge
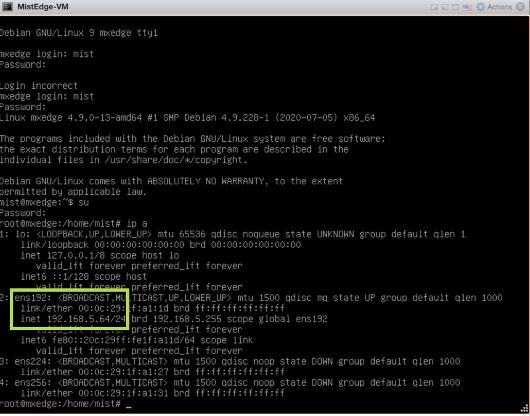
After you configure the Juniper Mist Edge on the Juniper Mist portal, you can connect to the console interface on the physical appliance using a terminal software and configure the OOBM IP address.
Once your Virtual Mist Edge boots up for the first time, login to the device using the following credentials:
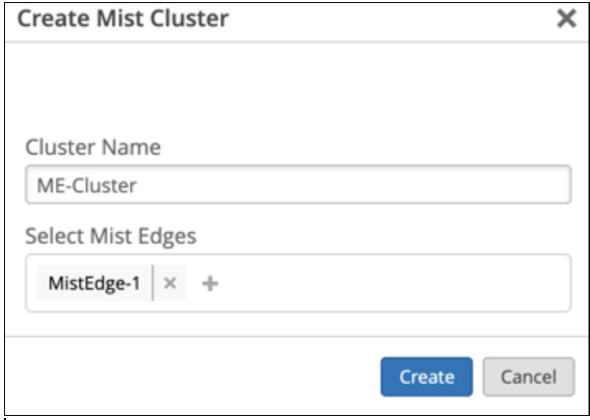
Create a Mist Cluster and Assign a Mist Edge
After you create a Juniper Mist Edge on the Juniper Mist portal, you must add the device to a Mist Cluster. A cluster can comprise a single edge device or multiple edge devices. You can skip this step for Mist Edges at Site level.
To create a cluster:
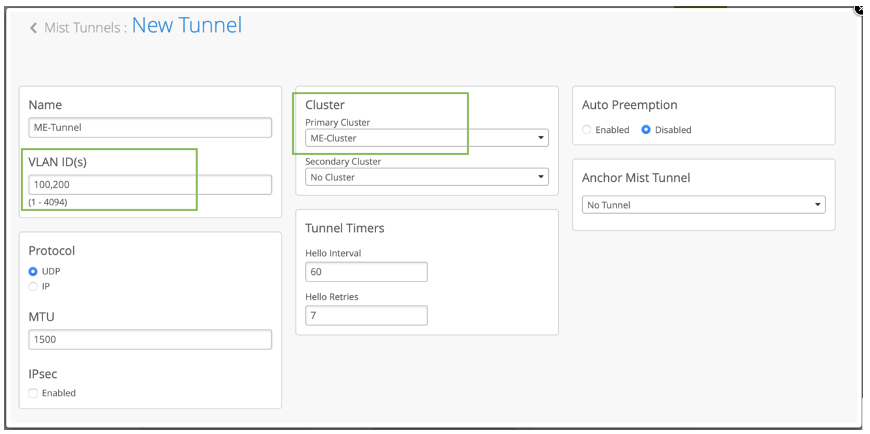
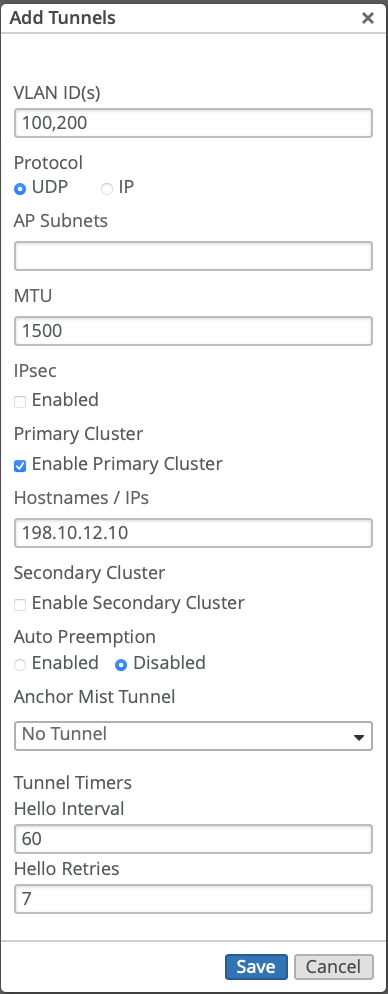
Create Mist Tunnel (Organization Level)
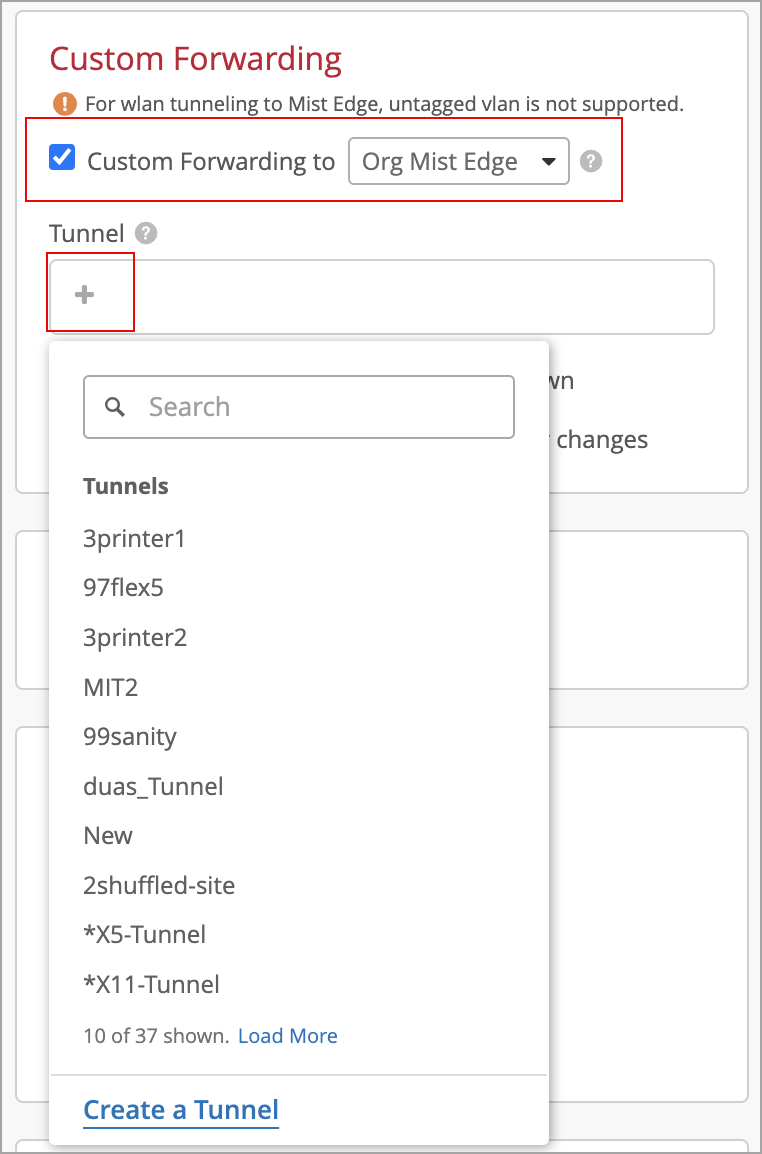
After you create a cluster, you must configure a tunnel and bind the tunnel to the cluster. Typically, the tunnel is where you list all your user VLANs (client VLANs) that you want to extend from your corporate network to the APs.
To create a Mist Tunnel at the organization level:
Configure Tunnel MTU Settings
When creating or configuring Mist tunnels, you can specify MTU settings to optimize tunnel performance. The Juniper Mist Edge tunnel uses two types of MTU settings:
-
Inner MTU: Defines the maximum transmission unit size for the payload within the tunnel.
-
Outer MTU: Defines the maximum transmission unit size for the entire encapsulated packet.
The system automatically includes a 50-byte pad in the MTU calculation to accommodate tunnel encapsulation overhead. You do not need to manually reduce your MTU settings to account for this padding.
You can edit only the outer MTU value, the inner MTU value is automatically calculated based on the outer MTU value.
To configure tunnel MTU settings:
Navigate to the Mist Tunnels page where you are creating or editing a tunnel.
In the MTU field, enter the MTU value.
The default MTU setting is 1500 bytes (which includes the 50-byte pad).
If you need to modify the MTU settings to accommodate specific network requirements:
-
Ensure that the MTU values are consistent across your network infrastructure.
-
Remember that the 50-byte pad is already included in the MTU value you configure.
-
Test connectivity after making MTU changes to ensure proper operation.
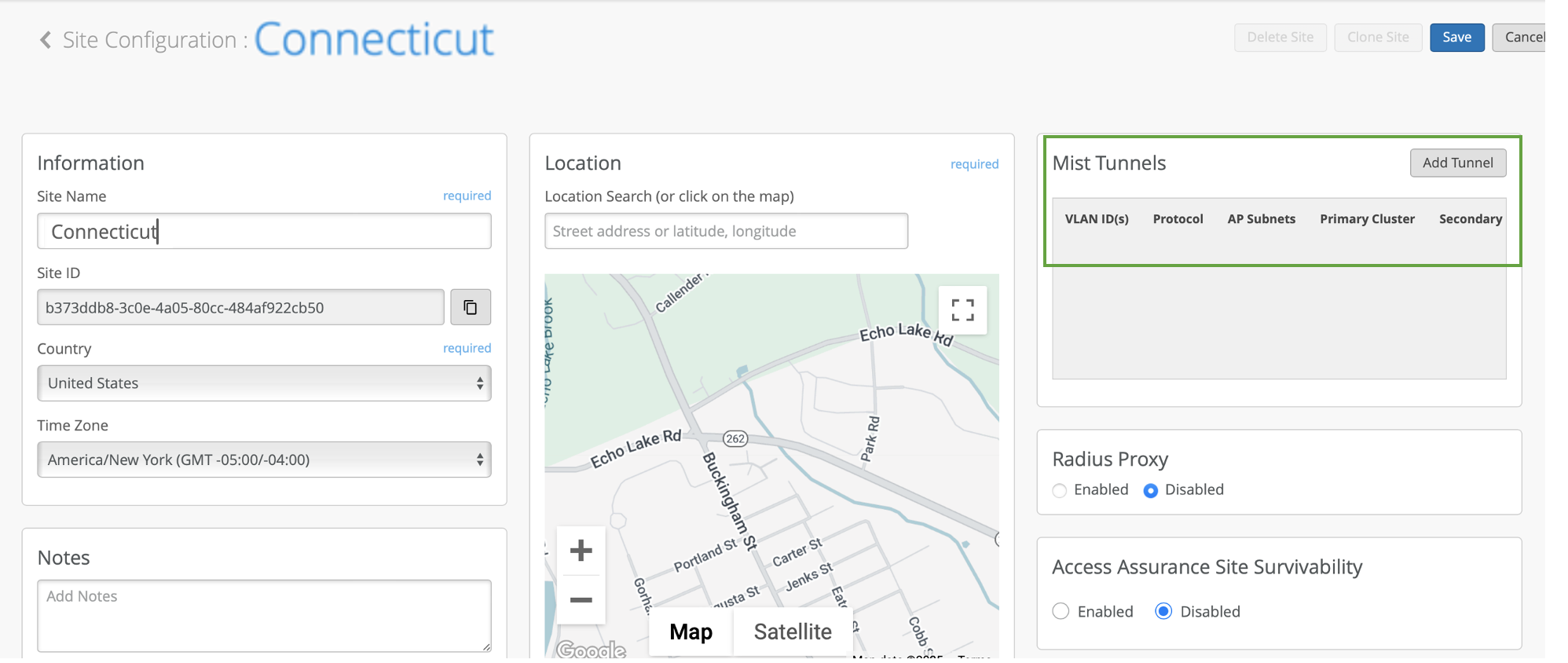
Create Mist Tunnel (Site Level)
After you claim the Juniper Mist Edge, you can assign it to a site.
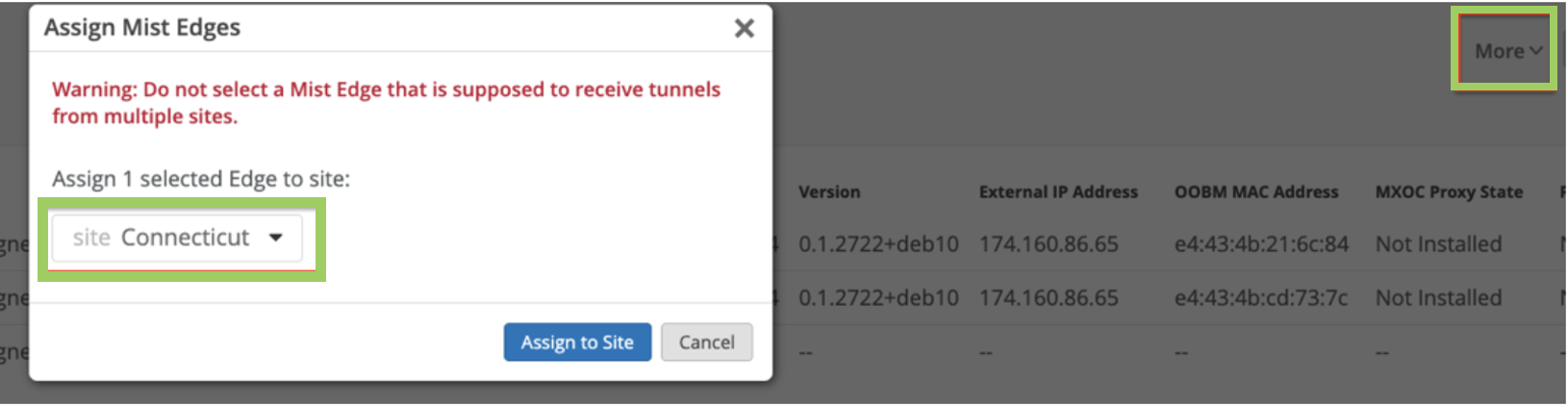
To create a Mist Tunnel at the site level:
Configure WLAN Template
A WLAN template is a collection of WLAN policies, tunneling policies and WxLAN policies. Instead of repeating a given configuration across multiple service set identifiers (SSIDs), with WLAN templates you can set it once and then attach APs to the template to automatically inherit the setting. Both the APs and WLAN must belong to the same site.
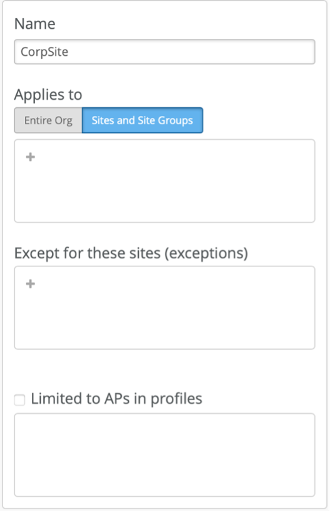
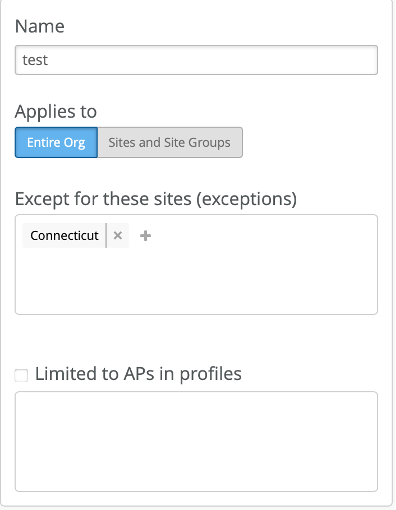
You must use the WLAN Templates to enable the corporate SSID. You can create a WLAN template and use the template assignment for:
-
Specific sites or a collection of individual sites that are mapped to a
Site-Group. -
Entire organization with actual office sites added as exceptions.
To configure a WLAN template: