Configure Upstream Resource Monitoring
For campus and branch deployments, Juniper Mist Edge provides a centralized data path for client traffic, while at the same time leveraging the benefits of the Juniper Mist cloud for control and management traffic. Advantages of the Mist cloud include access to Mist microservices, Service Level Expectations, and Marvis troubleshooting, which are not available when using a legacy wireless controller. Advantages of the centralized dataplane include access to upstream network services, micro-segmentation at the level of both devices and application, and macro-segmentation at the level of VLANs.
Architecture
On the Mist Edge, client traffic is tunneled. The tunnel can be split onto an upstream (network services) port and downstream (the APs and client traffic). The downstream port is connected to a trunk port of a core or aggregate switch that has all the VLANs configured to map to WLANs. Client traffic between the Mist Edge and the network services is secured via L2TPv3 tunnel. It is also bridged to the upstream port, which extends your VLANs to the WLANs on the Mist Access Point (AP). This has the further benefit of providing traffic separation on the basis of the connecting client's login credentials and allowed VLAN(s). Through Mist Edge, Mist APs can access the upstream network infrastructure, which can include services such as DHCP, NTP, and a RADIUS server.
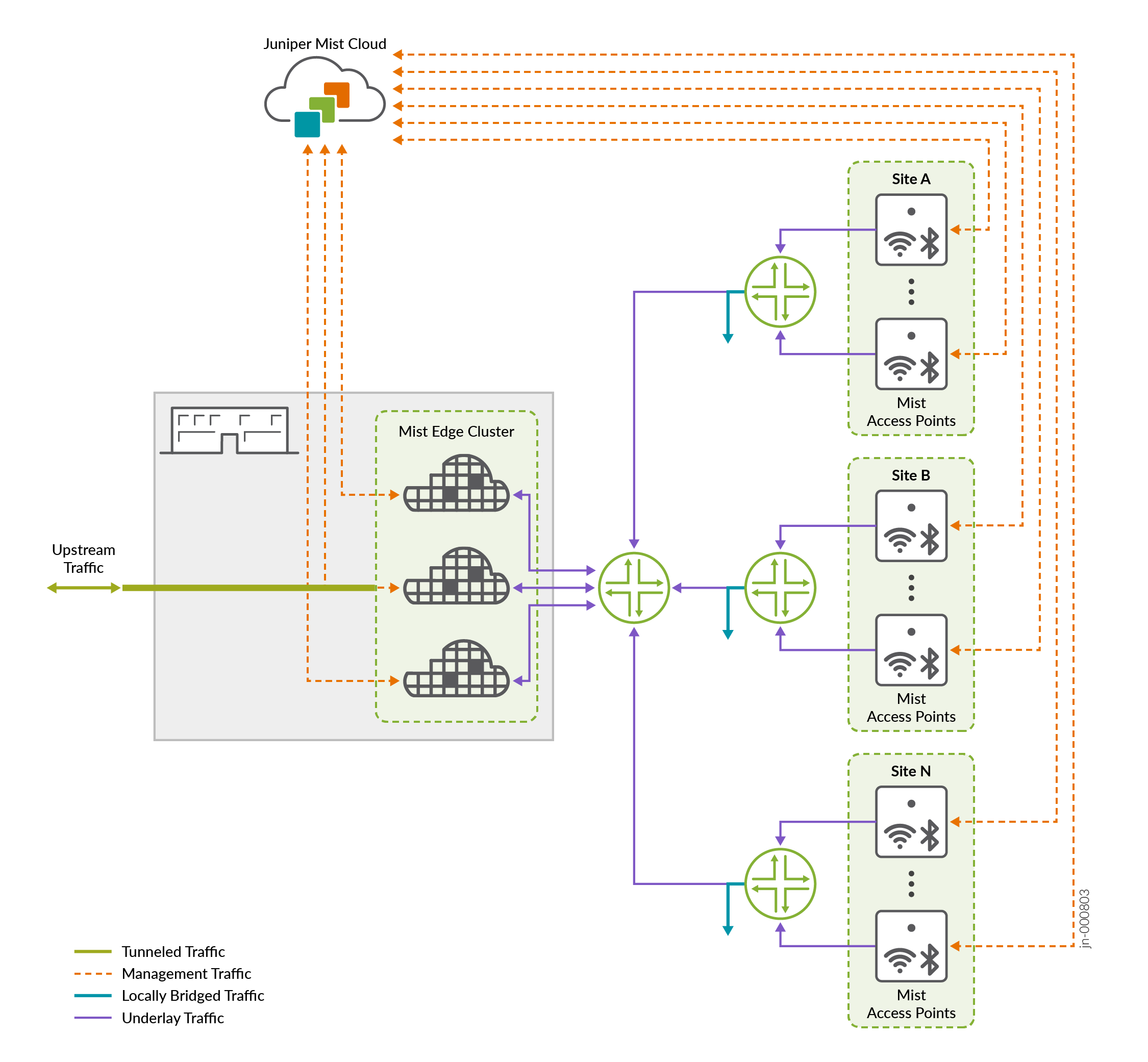
You can use the Mist Edge as a switch proxy to proxy data from a Juniper EX series switch to the Juniper Mist cloud, for example if the switch is behind an HTTP proxy or firewall. Mist Edge can act as a RADIUS proxy so that the Edge acts as the source of RADIUS access-request messages instead of the Mist APs. This allows you to use only a single IP Address, (the Mist Edge), instead of adding each Mist AP as an individual client. In other words, the Mist Edge, in its role of RADIUS proxy, acts as the RADIUS server toward the wireless AP RADIUS clients, and as a client toward the actual RADIUS server.
In the case of DHCP service, the Mist Edge acts as a DHCP relay to bridge requests. If a client logs on to a VLAN that doesn't have a DHCP server on the subnet, the Mist Edge can proxy the request to a VLAN that does to provide the client with an IP address for the given VLAN(s).
Redundancy
Because of the critical role Mist Edge can play in providing access to network services, we recommend that you deploy the Mist Edge in a cluster, for device redundancy, and configure fail-over timers for each tunnel to an AP to automatically leverage the redundancy when needed. You can also deploy Mist Edge clusters for high-availability and load balancing in either an active-active or active-passive configuration.
Upstream Resource Monitoring
For any given Mist Edge device or Mist Edge cluster, you can set up monitoring to detect any disruption in the upstream services and respond automatically by automatically triggering a fail-over. This feature is called upstream resource monitoring (URM, formerly called Critical Resource Monitoring, or CRM) and we recommend you configure it on the cluster. URM provides three ways to detect service interruption: ARP, PING, and TCP. You can configure any one, two, or all three so that if the service cannot be reached, the Mist Edge will automatically trigger a fail-over to the backup service, but we recommend that you only set up the one(s) than you need to avoid duplication.
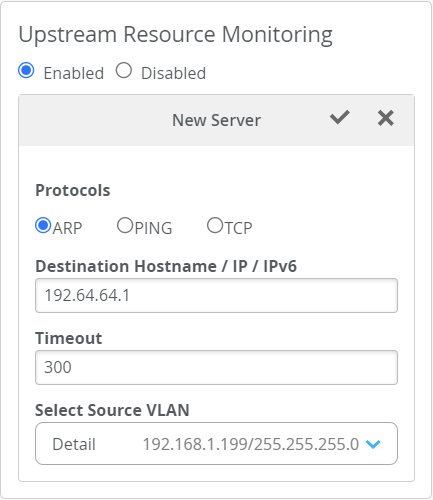
When creating a Mist Edge cluster from individual Mist Edge members, the cluster will inherit the URM configuration from the member. If you move a Mist Edge or claim it in a given site or organization, your URM settings will stay with the Mist Edge.
You can monitor upstream connections in the Monitor > Insights > Mist Edge | service dashboard, and by looking at the Mist Edge cluster configuration page under Upstream Resource Monitoring. A green icon indicates a healthy connection, and a red icon means the connection is down.
Source and Destination IP Addresses
When setting up URM to monitor a given service or device, you need to provide an IP address to act as the source address for the monitoring service (TCP, ARP, or PING). The IP address you use must be unique, and it must be valid (available) on VLAN from which it will be sent. The destination IP address is that of the device or service you are monitoring. For tunnel interfaces, the source VLAN is automatically assumed to be VLAN1.
By default, Mist Edge assumes that these source and destination IP addresses are on the same subnet. If they are not, you need to set up a next hop to resolve it. See below for instructions on configuring a next hop to bridge different source and destination subnets.
Out-of-Band Management
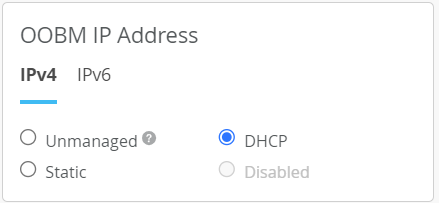
If you have configured out-of-band management (OOBM) for DHCP or Static IP addresses, Mist Edge can get the IP source address directly from the VLAN. On the other hand, if OOBM IP Address is Disabled or Unmanaged, you need to create a new VLAN and then specify a valid IP address that is available in that VLAN and use that as the source IP address.
To configure URM on a Mist Edge,
Setting Up A Next Hop for Different Subnets
If the source and destination are in different subnets, you'll need to set up a next hop to bridge them.
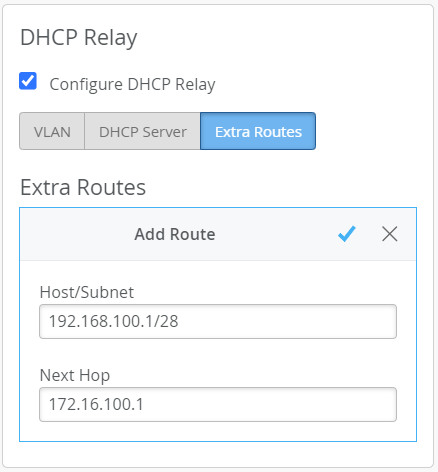
Under the DHCP relay section of the Mist Edge configuration page, select Configure DHCP Relay
.Click the Extra Routes tab and then Add Route.
In the Host/Subnet field that appears, specify the IP address and subnet for the network you are using as the source VLAN (that is, the client) in your URM configuration.
In the Next Hop field, specify the IP address of a gateway that can reach the destination service that you are monitoring (this is the service or device specified in the destination field of the URM configuration).
Click the check mark icon to keep your changes, and then click Save at the top of the page to save the new configuration.
