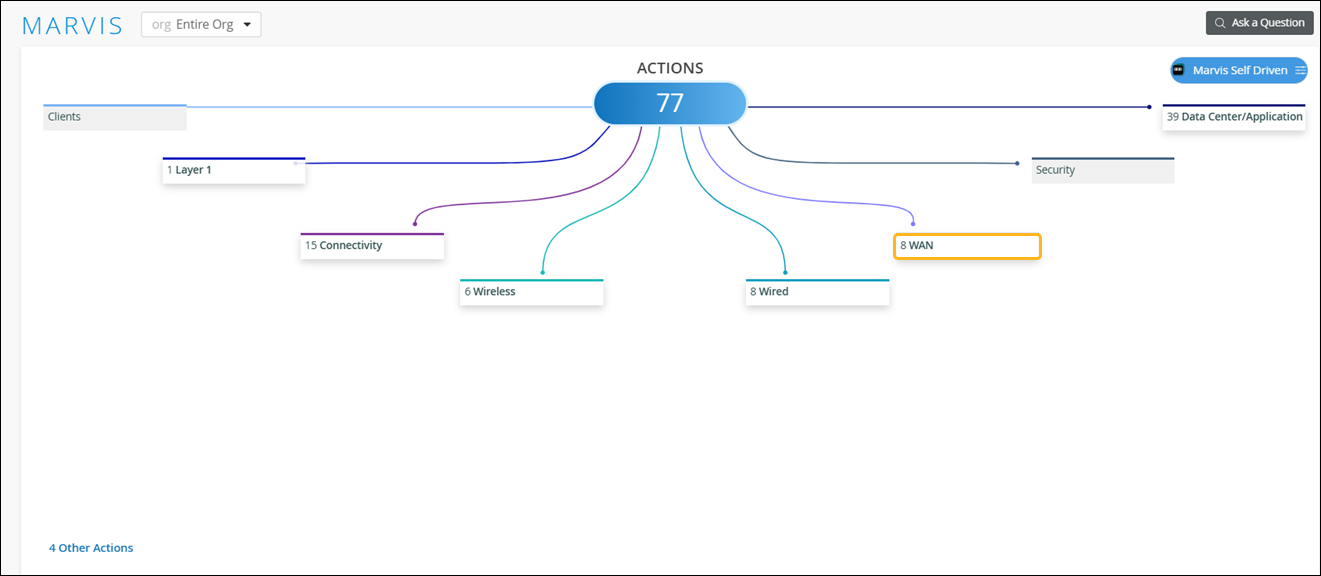
WAN Actions
Use the Actions dashboard to resolve issues affecting your WAN Edge devices.
When you click the WAN button on the Actions dashboard, you'll see a list of all available actions. You can then click an action to investigate further. Available actions are described later in this topic.
Your subscriptions determine the actions that you can see on the Actions dashboard. For more information, see Subscription Requirements for Marvis Actions.
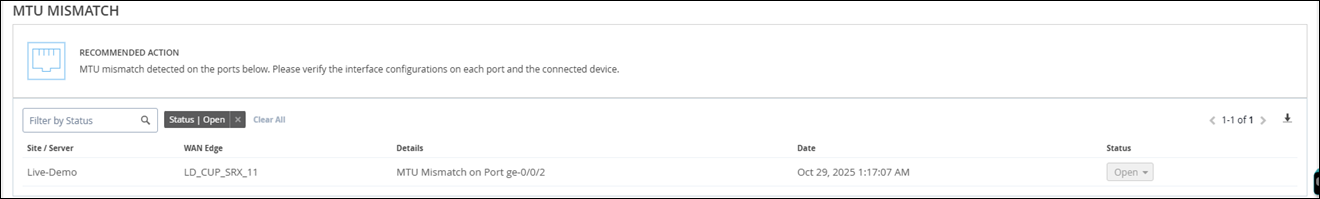
MTU Mismatch
Marvis detects MTU mismatches between a port on the WAN Edge device and a port on the directly connected device. All devices on the same Layer 2 (L2) network must have the same MTU size. When an MTU mismatch occurs, devices might either fragment packets resulting in a network overhead or discard packets. The Details column lists the port on which the mismatch occurs. You'll need to review the port configuration on the WAN edge device and the connected device to resolve the issue.
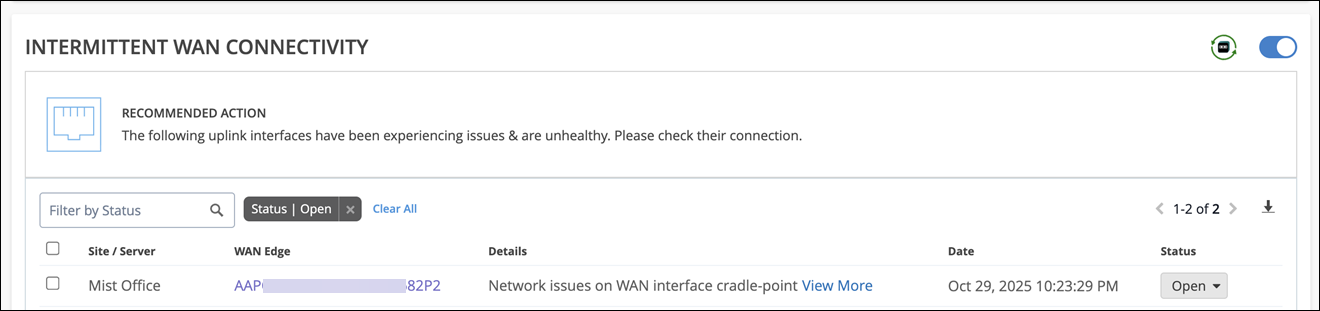
Intermittent WAN Connectivity
The Intermittent WAN Connectivity action identifies interface-related issues on WAN Edge devices such as uplink interface not receiving an IP address or the gateway ARP not being resolved for the uplink. These issues can cause poor user experience and result in an unhealthy WAN link. You might see errors in forming the overlay.
When you see an Intermittent WAN Connectivity action, we recommend that you check the uplink connection on your device to troubleshoot the issue. Marvis highlights the issue indicating the need to check the connection as shown in the following example:
An Intermittent WAN Connectivity action can be triggered when the ARP resolution for the ISP server's gateway IP address fails. The ISP ARP failure occurs when the WAN Edge device is unable to resolve the gateway's IP address to its corresponding MAC address. This issue can lead to network connectivity issues, as traffic cannot pass through the gateway, preventing the WAN Edge device from accessing external networks or Internet services.
Failure to obtain an IP address from the ISP can also trigger this action. In this case, the WAN Edge device is unable to connect to the Internet as it is unable to obtain an IP address from the ISP DHCP server.
The self-driving capability is enabled for the Intermittent WAN Connectivity action by default. When Marvis detects an ISP ARP or ISP DHCP failure, it initiates an automatic port bounce in an attempt to fix the issue. If the automatic port bounce fails to resolve the issue, Marvis lists it as an open action. For information about the self-driving capability, see Self-Driving Marvis Actions.
Bad WAN Uplink
The Bad WAN Uplink action identifies instances where the uplink interfaces on your Juniper Networks® SRX Series Firewall or Session Smart™ Router are experiencing issues due to poor LTE connectivity. For a bad LTE WAN link, Marvis shows a timeline of signal strength. This timeline view is like the Anomaly Detection view for connectivity failures. Marvis automatically finds and displays the worst signal strength metric during this time. Marvis displays any one of the following signal strength metrics:
-
Received signal strength indicator (RSSI)
-
Reference Signal Received Power (RSRP)
-
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)
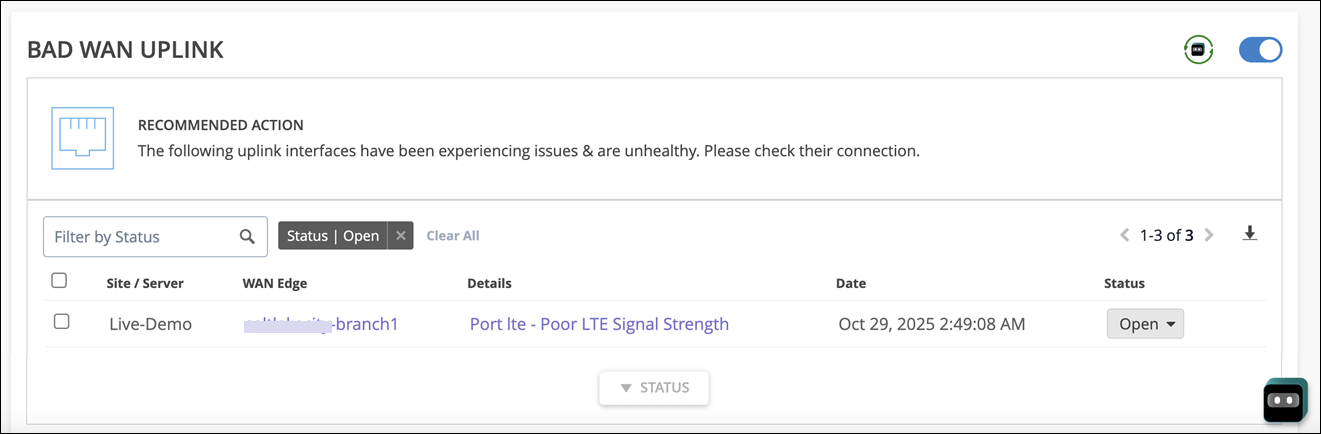
After you fix the issue in your network, Mist AI monitors the WAN link for a certain period of time to see if users are experiencing any issues. Hence, it might take up to 24 hours for the Bad WAN Uplink action to automatically resolve.
VPN Path Down
Marvis monitors the VPN paths that are associated with WAN edge nodes (Juniper Networks® SRX Series Firewall or Session Smart™ Router) in the overlay network. If VPN tunnels or peer paths toward a hub go down, Marvis displays the VPN Path Down action so that you can take immediate action. In the following example, Marvis reports that a hub gateway is down. Notice that Marvis provides detailed information such as the impacted sites, applications, and clients.
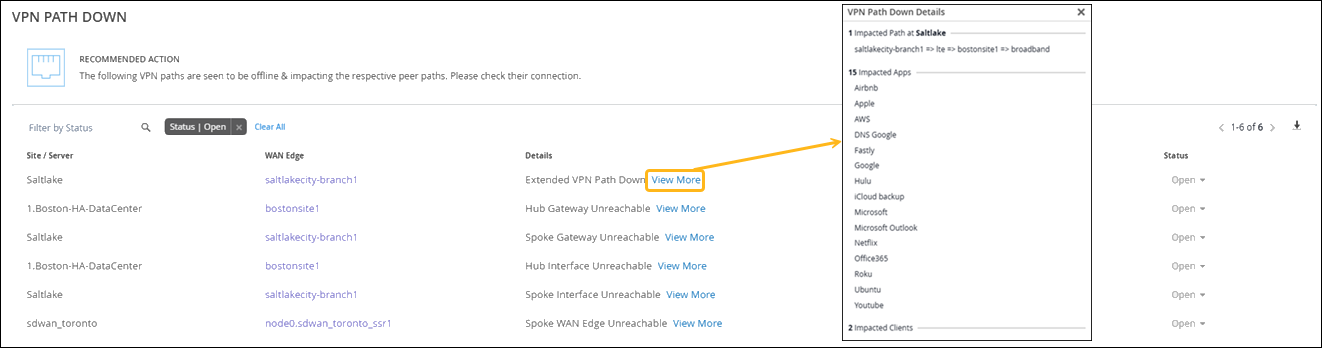
For SSR Series Routers, the VPN Path Down action lists the specific type of peer path that is down:
-
Spoke Interface Unreachable—All the peer paths originating from a spoke interface are down as the interface is down.
-
Spoke Gateway Unreachable—All the paths originating from a spoke are experiencing a peer path down issue.
-
Hub Gateway Unreachable—All the paths terminating at a hub are experiencing a peer path down issue.
-
Hub Interface Down—All the paths to a hub interface are down as the hub interface is down.
After you fix the issue in your network, Mist AI monitors the VPN path for a certain period of time to see if users are experiencing any issues. Hence, it might take up to 24 hours for the VPN Path Down action to automatically resolve.
Non-Compliant
Marvis monitors the Junos OS version running on the primary and backup partitions on SRX Series devices at a site. The Non-Compliant action flags an SRX device if the Junos OS version on the backup partition is different from the version running on the primary partition.
The following example shows the details for the Non-Compliant action. You can click the View More link to view the details.
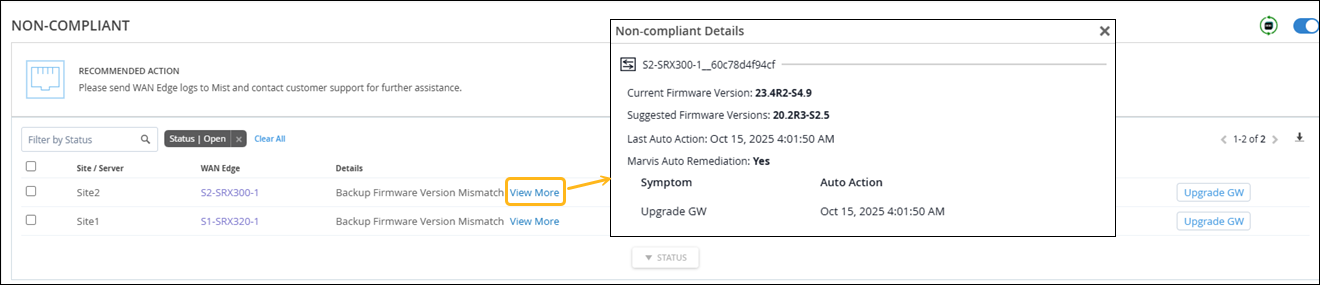
After you upgrade the backup partition on the SRX Series device to the proper version, the Non-Compliant action automatically resolves within 30 minutes.
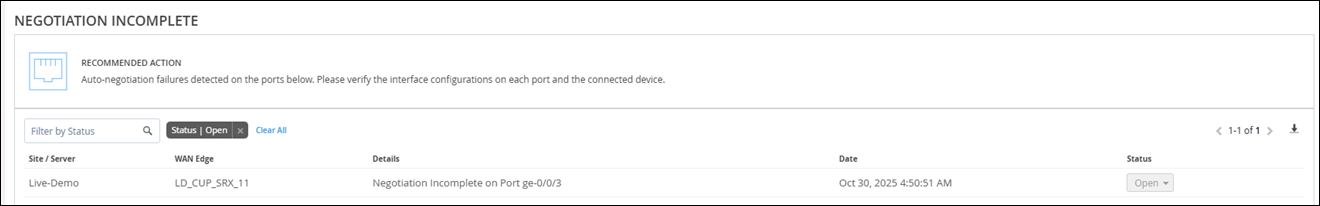
Negotiation Incomplete
The Negotiation Incomplete action for WAN Edges detects instances on the WAN Edge ports where autonegotiation failures occur. This issue can occur due to a duplex mismatch between the WAN Edge and the connected device due to the autonegotiation failing to set the correct duplex mode. Marvis provides details about the affected port. You can check the configuration on the port and the connected device to resolve the issue.