ON THIS PAGE
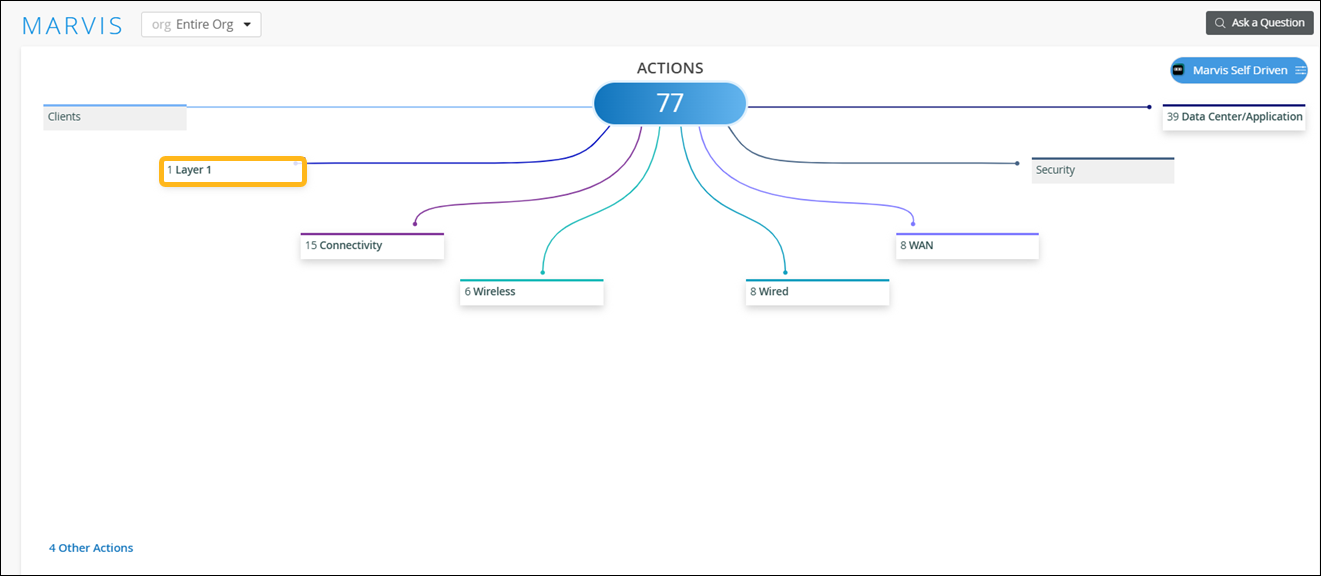
Layer 1 Actions
Use the Actions dashboard to resolve Layer 1 issues.
When you click the Layer 1 button on the Action dashboard, all available Layer 1 actions appear. This category currently contains two actions: Bad Cable and Bad Fiber Optics.
Your subscriptions determine the actions that you can see on the Actions dashboard. For more information, see Subscription Requirements for Marvis Actions.
Bad Cable
Marvis can detect a faulty cable that is connected to an access point (AP), a switch, or a WAN Edge device.
A faulty cable is one of the root causes of network issues, which manifest as user experience issues. It is a difficult and time-consuming task to manually identify a faulty cable. Marvis can detect bad cables easily by using cable data such as frame errors, link statistics, link errors, and traffic patterns.
A bad cable action indicates cable issues that APs, Switches, and WAN edge devices detect at a site. The details section indicates if a switch, an AP, or a WAN edge device detected the issue.
Marvis monitors APs that reboot frequently to determine if the cause for the reboot is a bad cable. For example, if one AP reboots frequently while other APs connected to the same switch do not reboot, then it might indicate a faulty cable.
For a WAN Edge detected issue, you'll need to perform the following steps:
-
Ensure that the duplex setting is full duplex on both sides of the link.
-
Change the cable to rule out issues due to a defective cable.
-
Change the SFP and check the status.
-
Change the port to rule out any NIC card issues.
-
Change the Layer2 device (modem or router).
The following sample illustrates the issue:
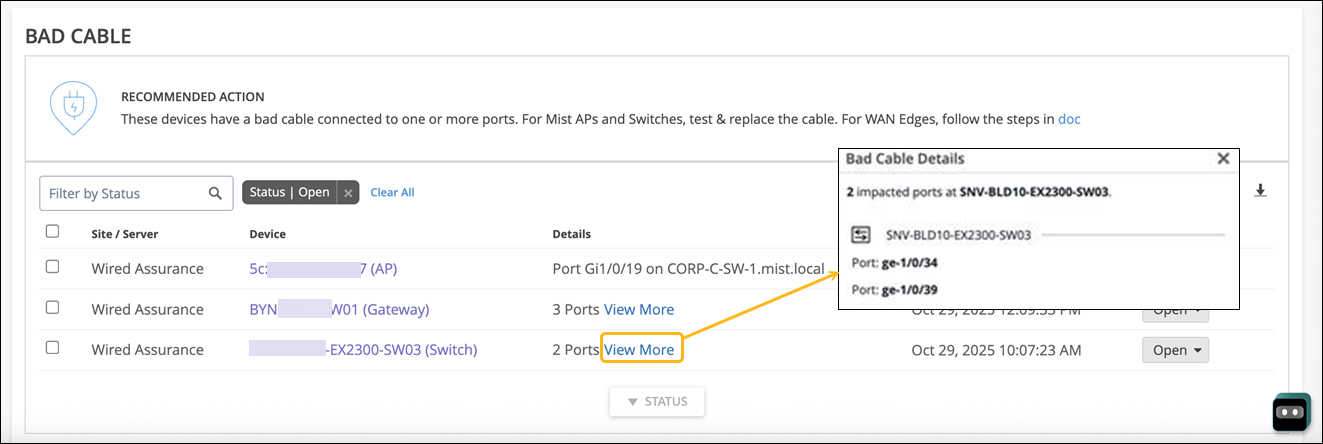
After you fix the issue, Mist AI monitors the AP, switch, or WAN edge for a certain period and ensures that the cable issue is indeed resolved. Hence, it might take up to 24 hours for the Bad Cable action to automatically resolve.
The next one in the list is under layer one called Bad Cable. This is specific to a cable to which an AP is connected to and thus is applicable for any and every 3rd party switch as well. What we are seeing here is this AP having a bad cable along with the port information on which it's connected to, and finally the switch as well. The uniqueness of this action is no net new traffic or active tests are run to determine a bad cable, and this is purely based on baselining and monitoring the AP health and the AP behavior since the time it came online.
Bad Fiber Optics
Fiber optic cables and transceivers that are damaged, degraded, or not functioning properly can significantly affect the network performance, speed, and scalability. Issues such as physical damage, wear and tear, using the wrong transceiver, or improper installation can lead to fiber optic failures. Regular inspections are crucial to detect and fix faulty fiber optics promptly. By utilizing switch reported events and network statistics, Marvis can help in the early detection of faulty fiber optics, enabling quick resolution and minimizing network disruptions.
Marvis identifies the following two types of issues:
-
Cable related issues, which include CRC errors, link flaps, and packet mismatches
-
Fiber optics hardware issues indicated by low-light alarms
The Bad Fiber Optics Marvis action is generated only when both the above issues occur on the same switch port within a 2-hour window.
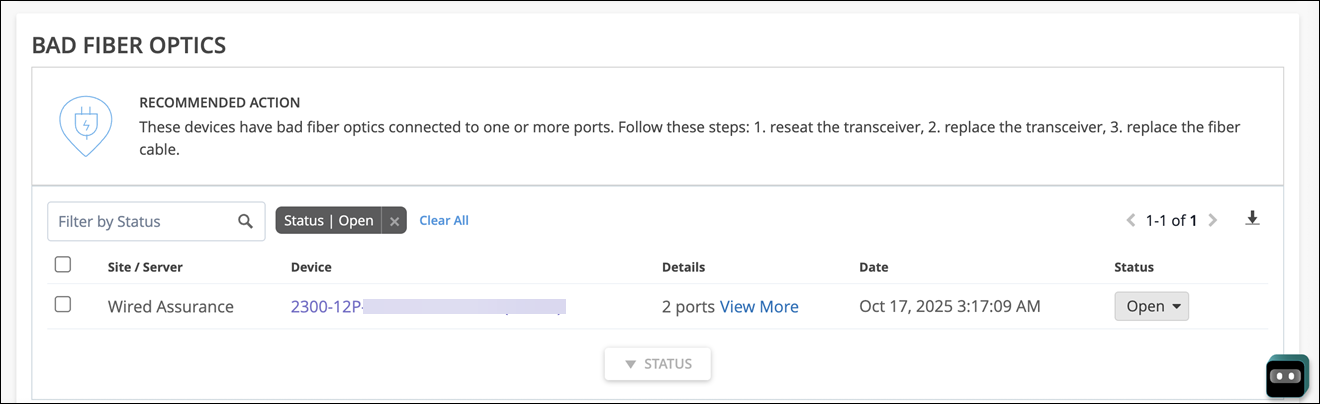
The View More link provides more details about the issue:
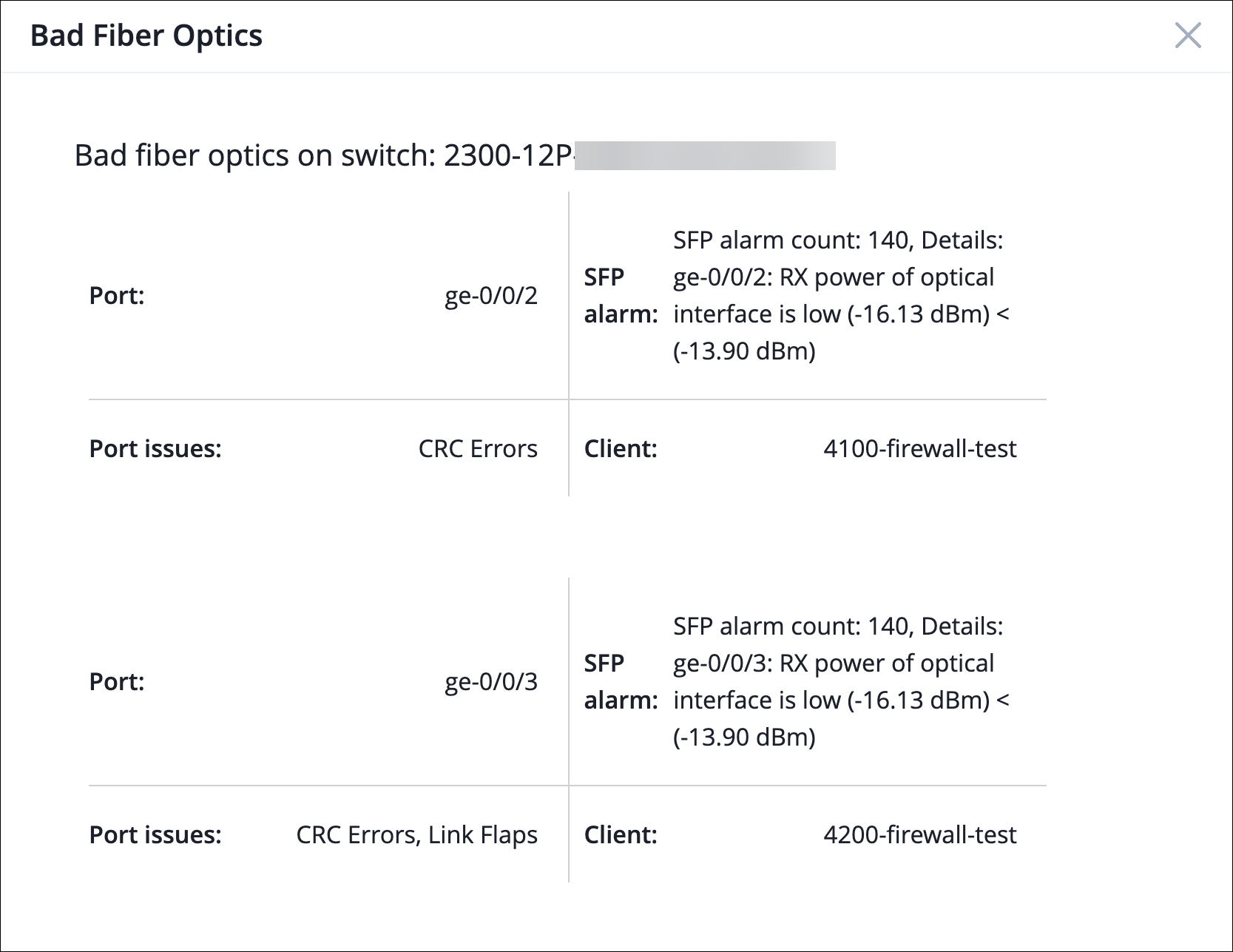
When you see a bad fiber optics Marvis action listed, follow these steps:
-
Reseat the transceiver—This procedure involves physically removing the transceiver from its port and then reinserting it. It’s a quick and effective diagnostic step to address connection problems caused by an improperly seated transceiver.
-
Replace the transceiver—If reseating does not resolve the issue, then evaluate whether the transceiver needs to be replaced.
-
Replace the fiber cable—Sometimes the issue might stem from a damaged fiber cable warranting its replacement.
