Integrate with Microsoft Intune
Follow these steps to understand Intune integrations, link your Intune account to your Juniper Mist organization, create policy rules, and view client events.
Overview
Microsoft Intune Endpoint Management uses Device Compliance Policies to check for the presence of an antivirus software, account for firewall rules, check clients for the latest security patches, and so on. Juniper Mist™ Access Assurance can leverage the compliance state of Intune-managed device for additional posture assessment according to the Auth Policies you create.
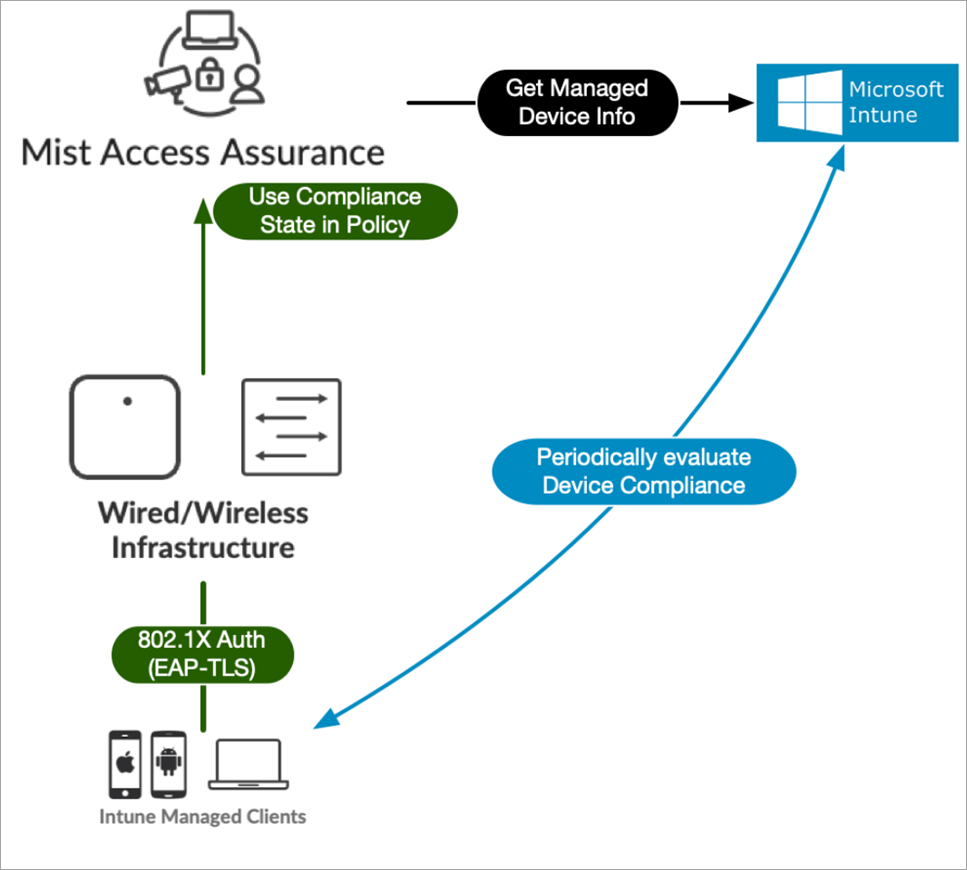
You can integrate Access Assurance with the Intune for use in the Mist portal. For example, you can use the integration to create a client authorization policy in Mist that segregates non-compliant clients to a quarantine VLAN while letting compliant ones access the corporate network. To do so, you need to be running firmware version 0.14 or later on the Juniper Mist APs, and have an administrator account on Microsoft Entra ID (this is to grant read privileges to Mist Access Assurance to get the Intune device data).
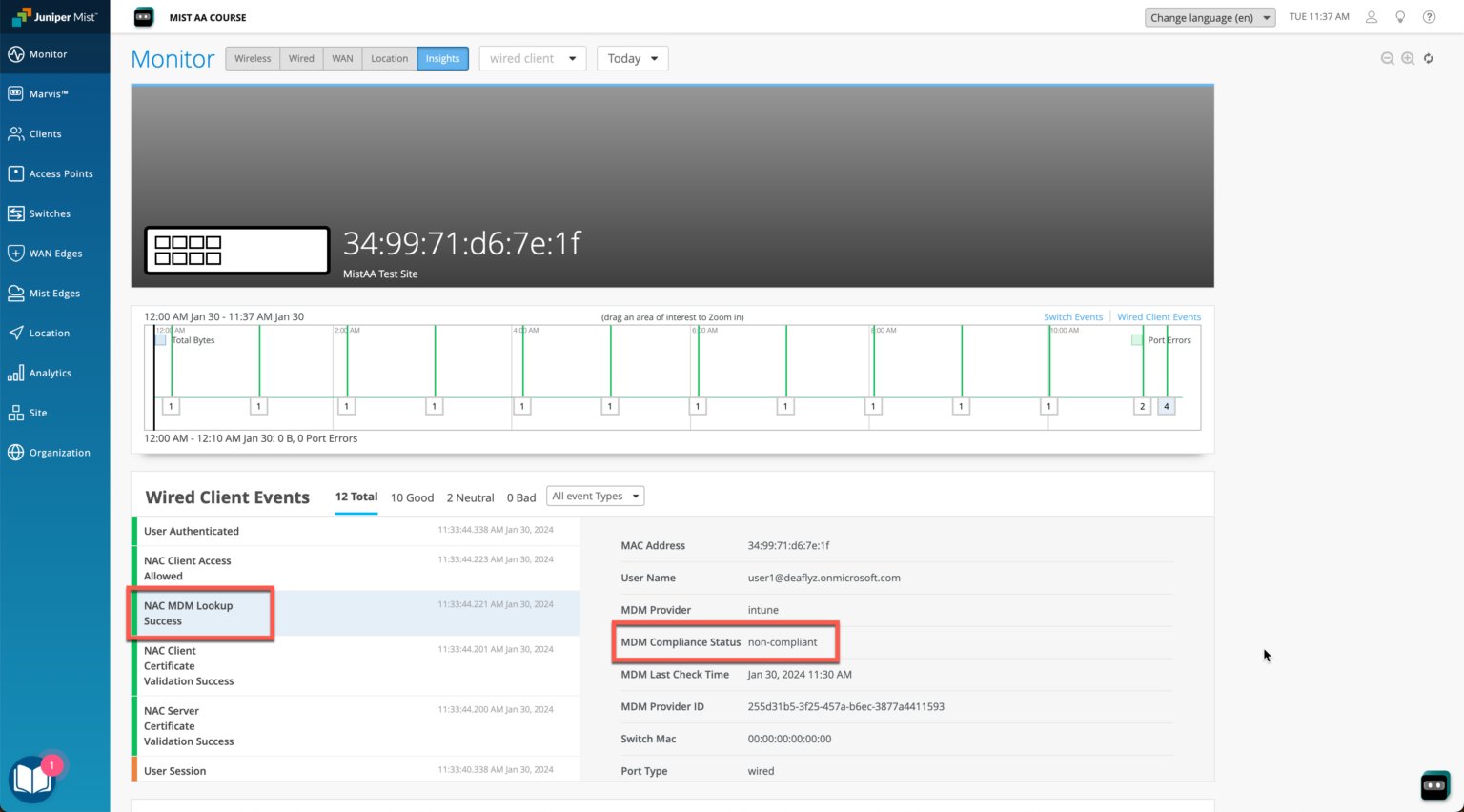
As wireless clients log on and are authorized on a Juniper Mist AP, the cloud-based Mist Access Assurance service learns the client's security compliance status from Intune. It then uses that information in an authentication policy to connect the client to a selected VLAN based on the results. In the figure above, which shows the Insights tab on the Monitor portal page, Intune has classified one of the clients as non-compliant.
Some of the screenshots included in this document are sourced from third-party applications. Be aware that these screenshots may change over time and may not always match the current version of the applications.
How it Works
The Access Assurance API polls Microsoft Intune every two hours for a list of authenticated Intune-managed clients, and makes any necessary updates. The default polling interval for Microsoft Intune to its managed devices is every eight hours. Mist Access Assurance caches the retrieved compliance state data to optimize retrieval times.
Whenever a device if found to be out of compliance, Mist Access Assurance issues a Change Of Authorization command and re-runs the policy. The policy then triggers the required corrective actions, as needed, to bring the device back in to compliance.
The communication flow between the two services is shown in Figure 2.
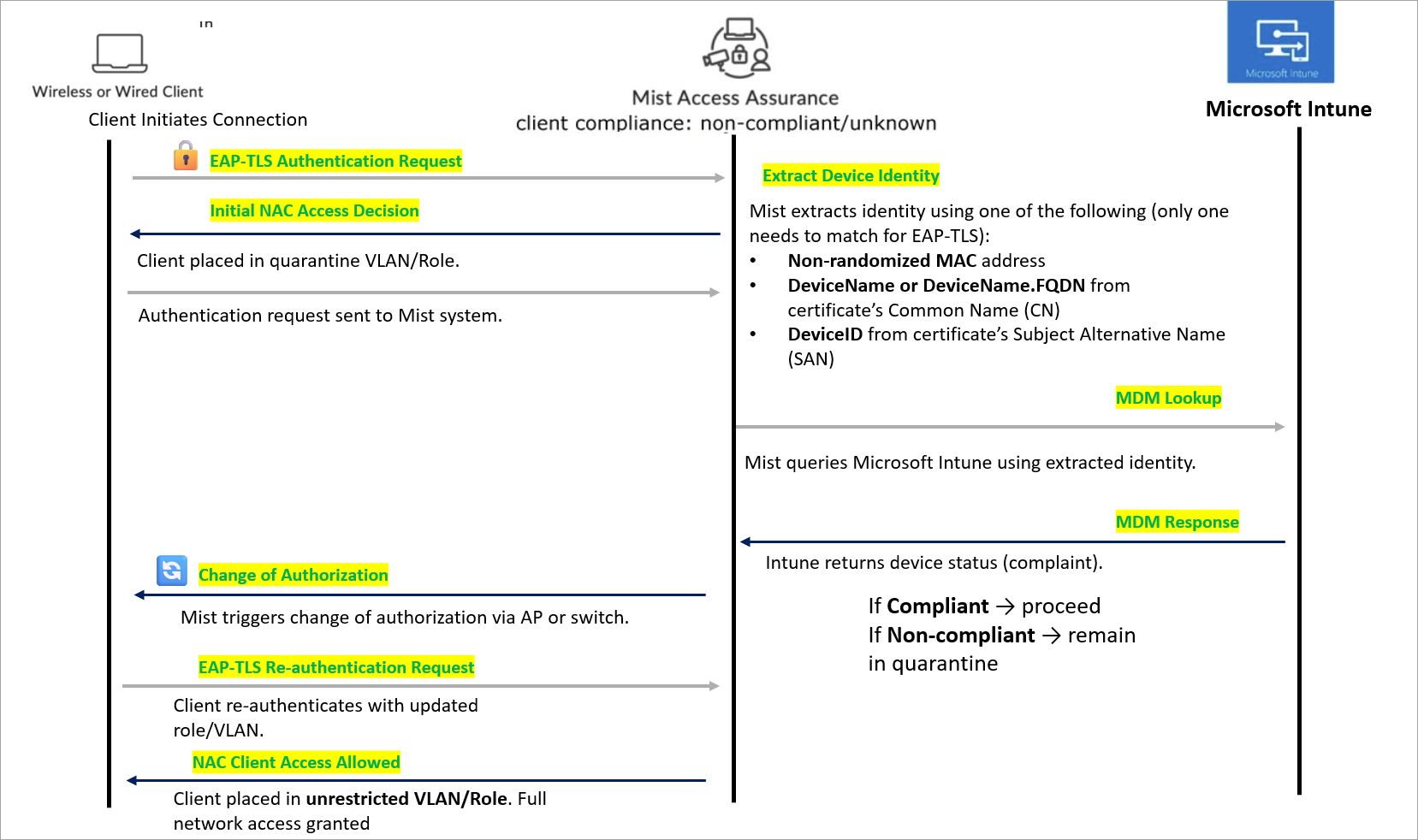
Client onboarding sequence includes:
- EAP-TLS Authentication—Client initiates a connection (wired or wireless) and authentication request is sent to the Mist system.
- Initial NAC Access Decision—Client is placed in a quarantine VLAN/Role. Restricted access is provided until device compliance is verified.
- Device Identity Extraction—Mist uses the following information during client
authentication to match a client with a device record in Microsoft Intune (in order of
lookup):
- Non-randomized MAC address
- DeviceName or DeviceName.FQDN from the certificate’s Common Name (CN) field
- DeviceID from the certificate’s Subject Alternative Name (SAN) as a DNS entry
For EAP-TLS authentication, a match is successful if any one of these identifiers is found.
For EAP-TTLS authentication, Mist Access Assurance uses only the non-randomized MAC address to match with Intune device records.
- MDM Lookup—Mist queries Microsoft Intune using the extracted identity.Retrieve the device’s compliance status.
- MDM Response- Intune returns the device status.
If the client device is found compliant, access is provided.
If the client device is non-compliant, it remains in quarantine.
- Change of Authorization (CoA)—Mist triggers CoA via the AP or switch. Client session is refreshed with updated access rights.
- EAP-TLS Re-Authentication—Client re-authenticates with the updated VLAN/Role.
- Final NAC Access Decision—Client is placed in an unrestricted VLAN/Role. Full network access is granted.
The device lookup process via Microsoft Intune can time depending on system load and response intervals. To ensure a seamless onboarding experience, we recommend configuring an authentication policy that permits initial access for the client device.
Configure the policy in accordance with your organization's security standards and access control policies to establish appropriate safeguards during the initial connection.
Once the MDM lookup succeeds and the device record is added to the Dynamic Device Database (DDB), the Mist MDM service automatically sends a Change of Authorization (CoA) message to the associated AP or switch. This prompts the client to reconnect.
Upon reconnection, the client is evaluated against the MDM Authentication policy, which determines access based on the device’s compliance status—either Compliant or Non-compliant.
Following sections provide more details about the identifiers.
Non-Randomized MAC Address
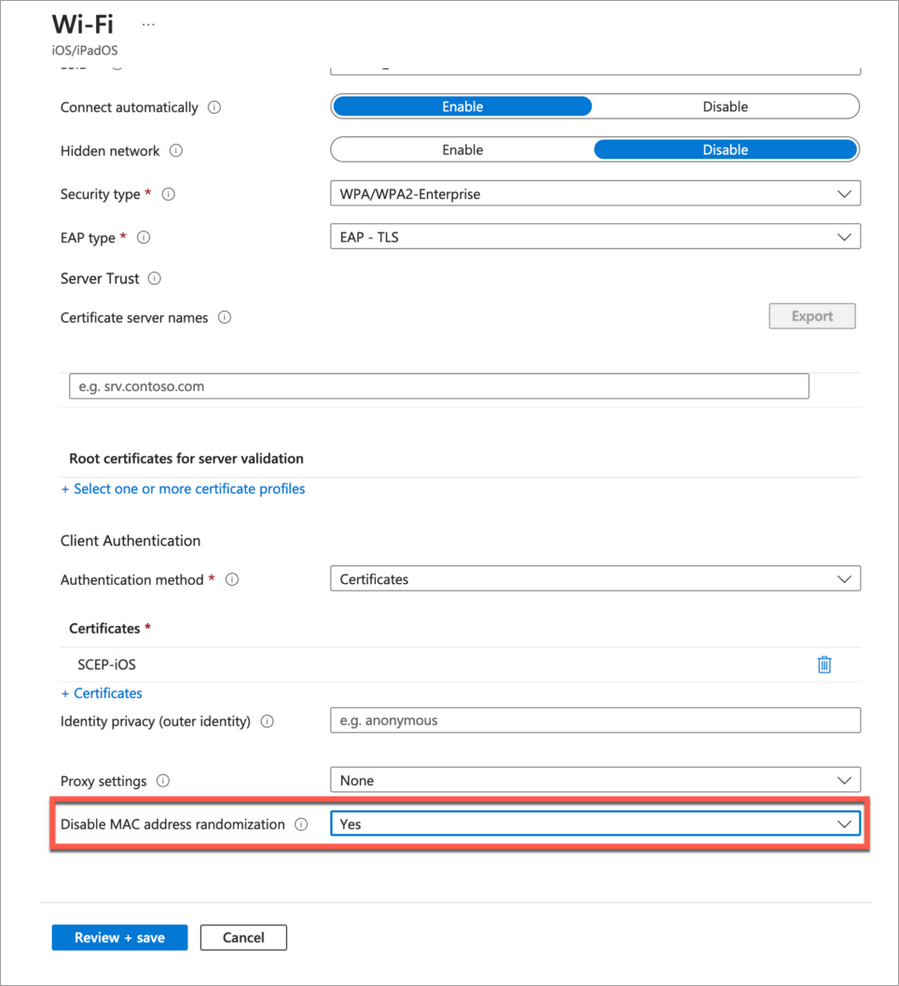
If you want to show non-randomized MAC addresses under Client Events, you need to disable MAC randomization in the Intune Wi-Fi settings. This display supports both EAP-TTLS and EAP-TLS authentication, and uses the client MAC address from Intune.
The screenshots from third-party applications are correct at the time of publishing. We have no way to know when or if the screenshots will be accurate at any future time. Please refer to the third-party website for guidance about changes to these screens or the workflows involved.
DeviceName or DeviceName.FQDN
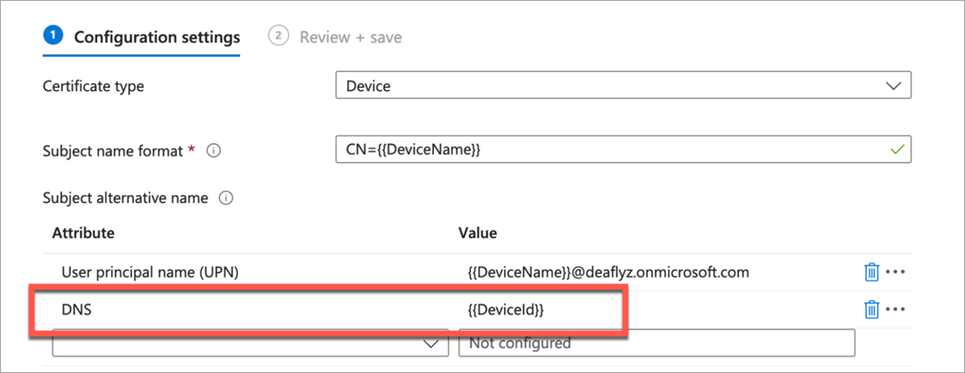
Under Client Events, the name shown for Certificate CN comes from the Intune SCEP certificate configuration (it's the Subject name format field). The Client Events name shown for Certificate SAN (DNS Name) comes from the Intune SCEP profile variable used to encode the Intune Device ID in the SAN:DNS certificate field
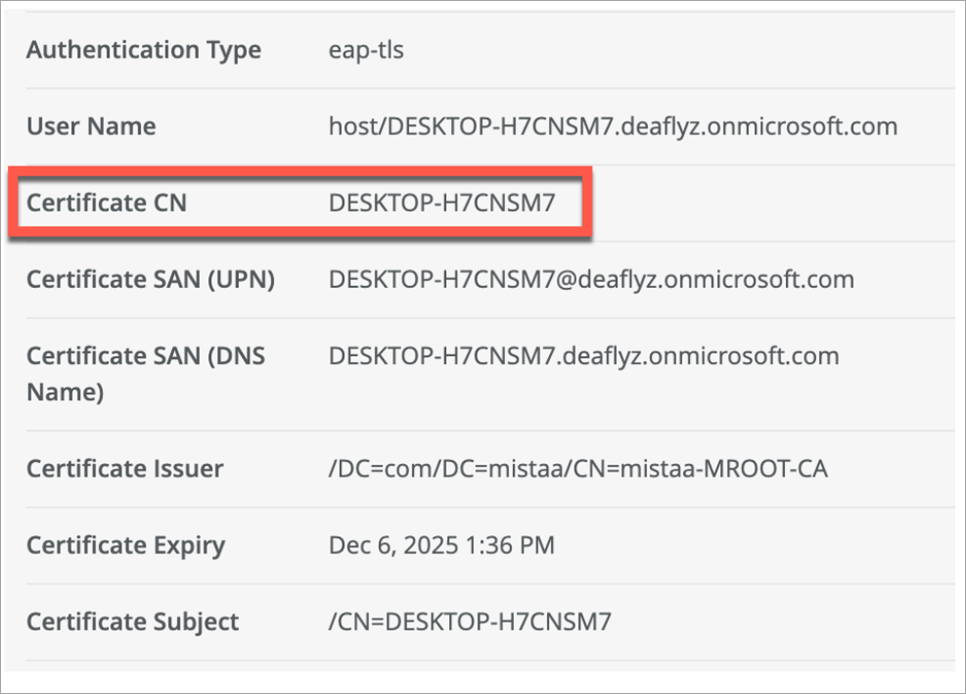
In Intune SCEP profile, use the variables to create this certificate.
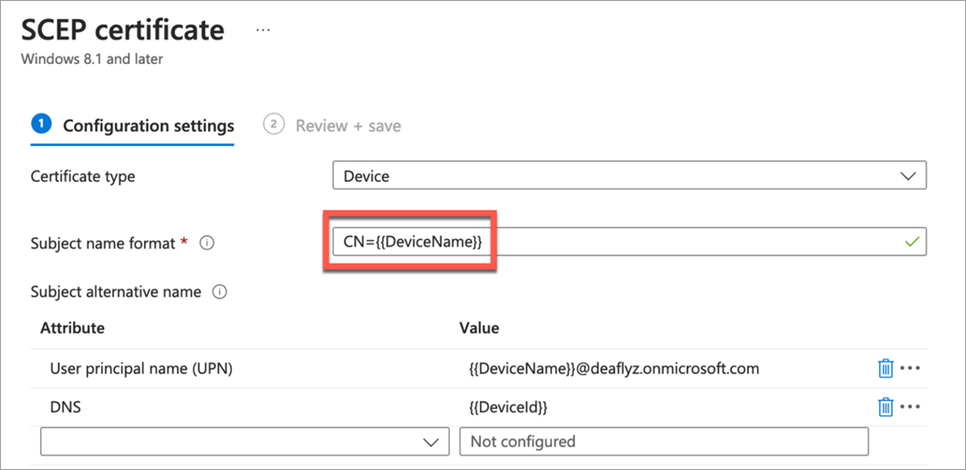
DeviceID in Certificate's SAN:DNS
Intune Device ID encoded in SAN:DNS certificate attribute in Juniper Mist portal client events as shown in the following illustration.
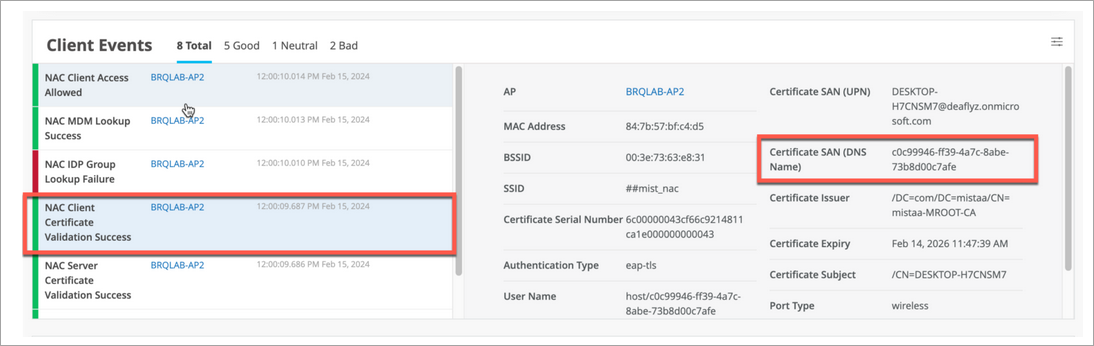
In Intune SCEP profile, use the variable to encode Intune Device ID in the SAN:DNS certificate field.
Adding Intune to the Mist Portal
To add Microsoft Intune to the Mist Access Assurance portal:
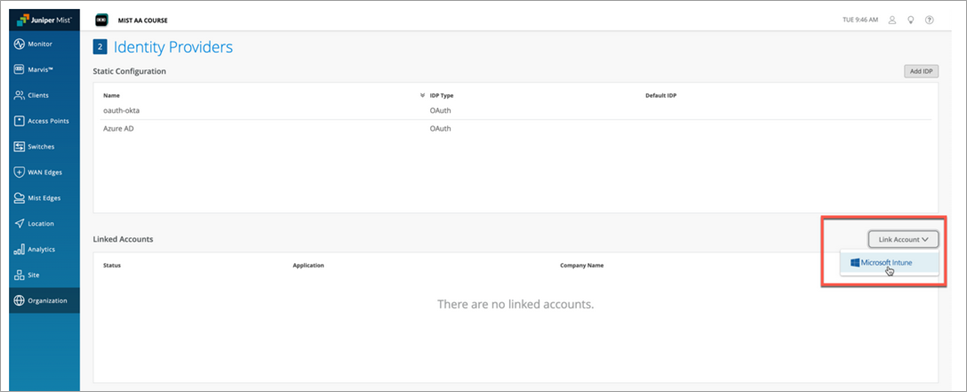
- From the left menu of the Juniper Mist portal, select Organization | Access > Identity Providers
- In the Linked Accounts section, click Link Account .
- Select Microsoft Intune.
You will be redirected to Microsoft Entra ID / Intune for the Single Sign On (SSO) login, and then prompted to grant permission for the Mist Access Assurance portal to read Microsoft Intune device data.
Figure 5: Permissions for Intune Integration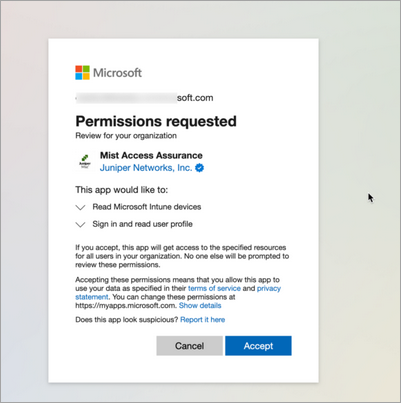
After linking the Intune account, connected Intune account status is displayed on the Identity Providers page.
Figure 6: Linked Intune Account Status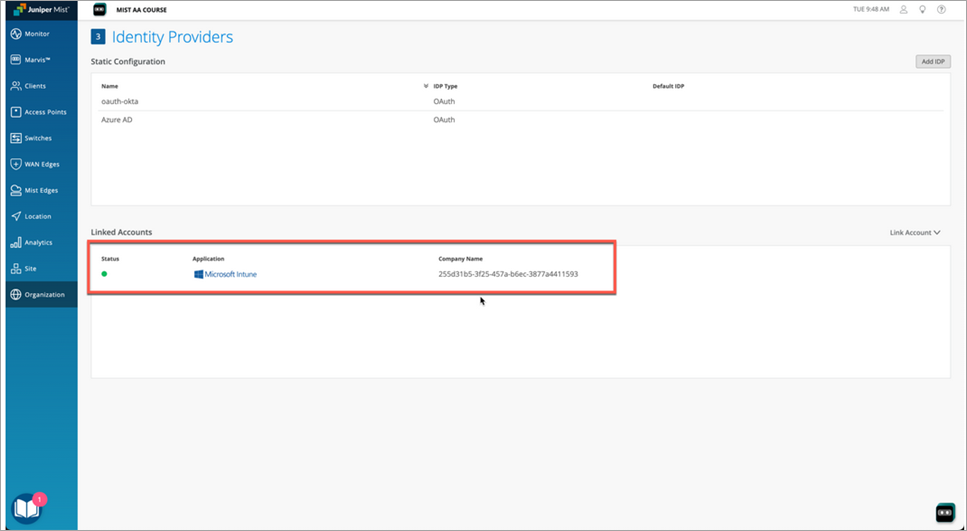 Figure 7: Linked Intune Account Details
Figure 7: Linked Intune Account Details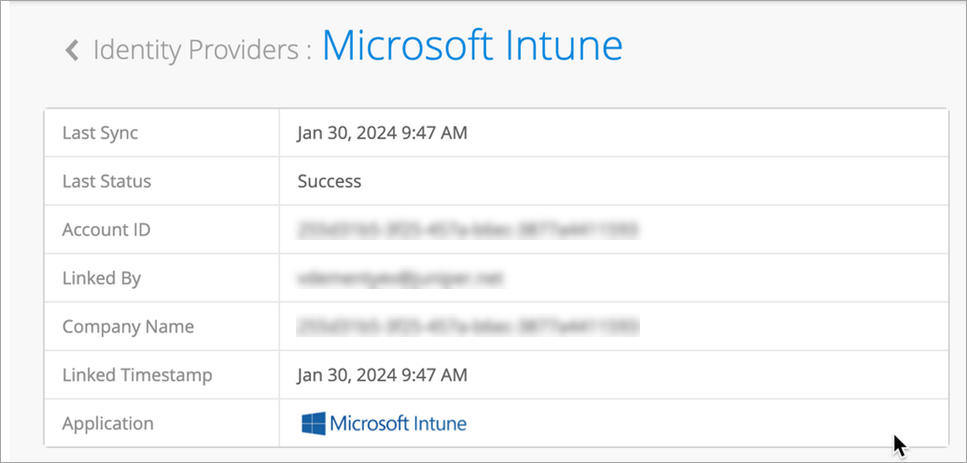
- (Optional) After linking the Intune account, you can see the Intune account status on the Identity Providers page: Organization | Access > Identity Providers.
Creating Policy Rules
With the Intune account linked to Mist, you can leverage managed the device compliance status in your Mist Auth Policies. For example, you can put non-compliant clients into a quarantine VLAN, while allowing compliant devices to connect to the corporate VLAN. You do this by creating a pair of labels for compliance and non-compliance, and another pair for corp and quarantine VLANs. Then you use these labels in a pair of Auth Policy rules to automatically govern network access.
Create compliance and quarantine labels:
- From the left menu of the Juniper Mist portal, select Organization > Access > Auth Policies.
- Click the Create Label button and give the label a name, for example, Intune-Compliant.
- Under Label Type, choose MDM Compliance.
- Under Label Values, select Compliant.
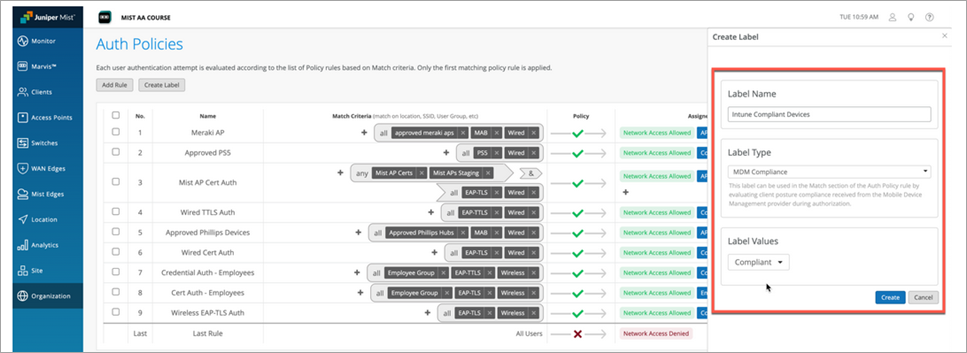
Click the Create button.
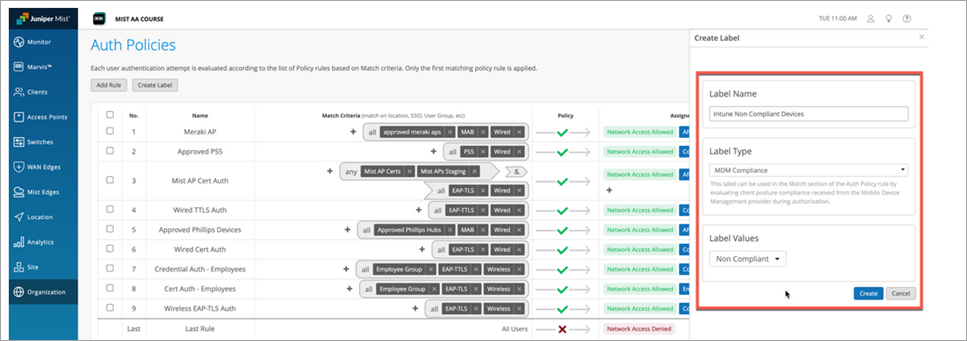
Repeat these steps to create the remaining labels, as shown here:
Label Name: Intune-Non-Compliant, Label Type: MDM Compliance, Label Value: Non Compliant
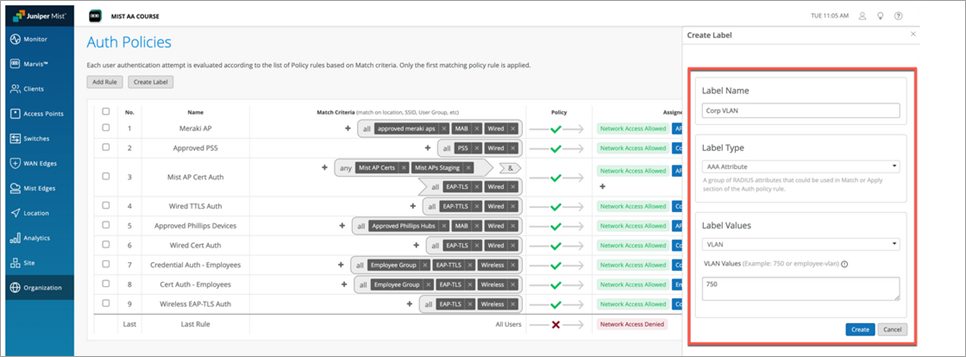
- Label Name: Quarantine, Label Type: AAA, Label Value: VLAN, 1
Label Name: Corp VLAN, Label Type: AAA, Label Value: VLAN, 750
Create Auth Policy Rules:
- Click the Add Rule button and give the rule a name, for example, Corp Compliant.
- In the Match Criteria column, click the + icon and then select Intune-Compliant from the list that appears.
- In the Policy column, select Allow.
- In the Assigned Policies column, click the + icon and then select Corp
VLAN. Figure 8: Compliance Rules Based on Intune
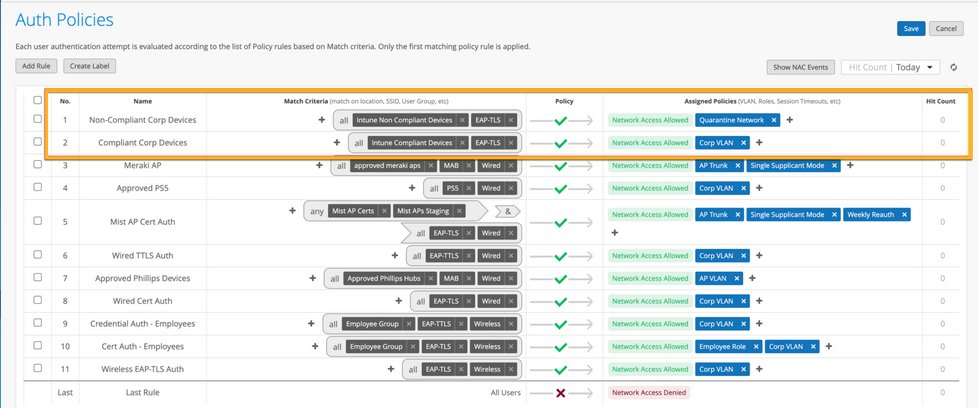
Repeat these steps to create the quarantine rule.
When finished, click Save.
Viewing Client Events
As shown in the following illustration, in the Client Events section on the Insights tab of the Monitor portal page, the values show for some parameters depend on how you have configured Microsoft.