Use Case and Reference Architecture
The modern service provider networks have two main segments referred to as core and edge ( Figure 1 ). The solution uses a reference design that implements core and edge segments within a single flat IS-IS Level 2 domain, using the default IS-IS instance. Additionally, the Multi-Service Edge (MSE) service complex is placed in a separate domain, with BGP-only reachability.
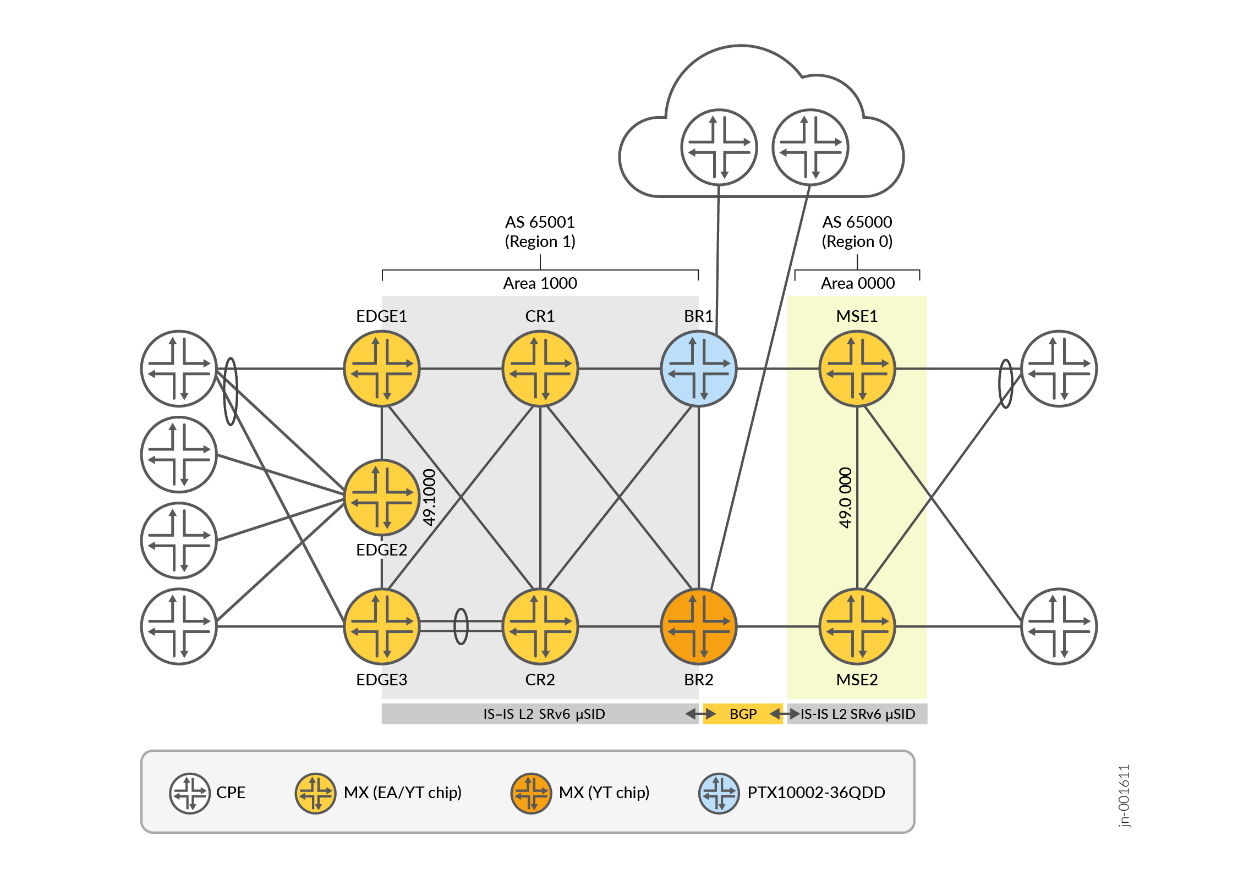
Appropriate redistribution policies, with or without summarization, are provisioned between an IS-IS and a BGP domain to provide end-to-end IPv6 connectivity between loopbacks and locators.
The reference architecture deploys an infrastructure designed to support traditional service provider topologies with edge services termination.
The major components under consideration include:
- SP reference architectures
- Seamless Segment Routing across SP edge and core domains (Inter-AS BGP + SRv6 locator redistribution/summarization between domains)
- Fast failover and detection TI-LFA, MLA, BFD, ECMP, and so on.
- SRv6 SID with IS-IS
- Flex-Algo Application Specific Link Attribute (ASLA) TE and Delay metrics
- Flex-Algo Prefix Metric (FAPM)
- Transport Classes
- Strict and Cascade Transport Class Resolution schemes Inter-AS BGP Transport
- VPN Service Mapping to transport Flex-Algo
- Redundant Route Reflectors
- EVPN-VPWS with A/A and A/S Multihoming
- Inter-AS Option C
- TWAMP light for delay measurement
Baseline Features
The baseline features required for this JVD include:
- SRv6 SID IS-IS, Flex-Algo (with dynamically measured delay metrics) IS-IS
- TI-LFA (link/node) IS-IS, MLA (micro-loop avoidance) IS-IS
- SRv6 mSID locator summarization IS-IS
- L3VPN (mDT4, mDT6, mDT46), EVPN-VPWS (mDX2)
- BGP, BFD, Community-based Routing Policy, Route Reflection, IPv4, IPv6
- LACP, AE, VLAN (802.1q)
