Results Summary and Analysis
The JVD team successfully validated comprehensive and multidimensional solutions for the Metro Ethernet Business Services reference architecture, encompassing over twenty service-delivery use cases across multi-domain and inter-AS seamless segment routing infrastructures. The network includes controller-less network lite-slicing solutions with flex-algo, transport classes, and service mapping. The validation features MX304, ACX7024, ACX7100-48L, ACX7100-32C and ACX7509 as primary DUTs with helper nodes including PTX10001-36MR, MX204, MX10003, ACX5448, ACX710, QFX5110 platforms. Over 300 test cases are executed for each DUT during validation on Junos OS and Junos OS Evolved Release 23.2R2.
A major objective of Juniper Validated Design is to create practical solutions with a multidimensional scale relevant to the domain-specific use case. Functional testing ensures services and protocols operate within expectations and network resiliency performance is measured and reported in the JVD.
The proposed network design delivers fast restoration with consistent sub-50ms convergence in expected segments with Segment Routing MPLS, Flex-Algo, and TI-LFA protection machinery. Additional mechanisms to improve failover and or load sharing include BGP multipath, ECMP fast-reroute, and VPN-unequal-cost for L3VPN services, Flow Aware Transport Label (FAT-PW), and enablement of all relevant hash-keys for extracting supported L2, L3, and MPLS fields. Color-aware services support the creation of TI-LFA backup paths over matching-colored paths, with both primary and backup following resolution scheme configurations.
The following tables summarize convergence reported during failure events, categorized by network segment. For additional information, contact your Juniper Networks representative.
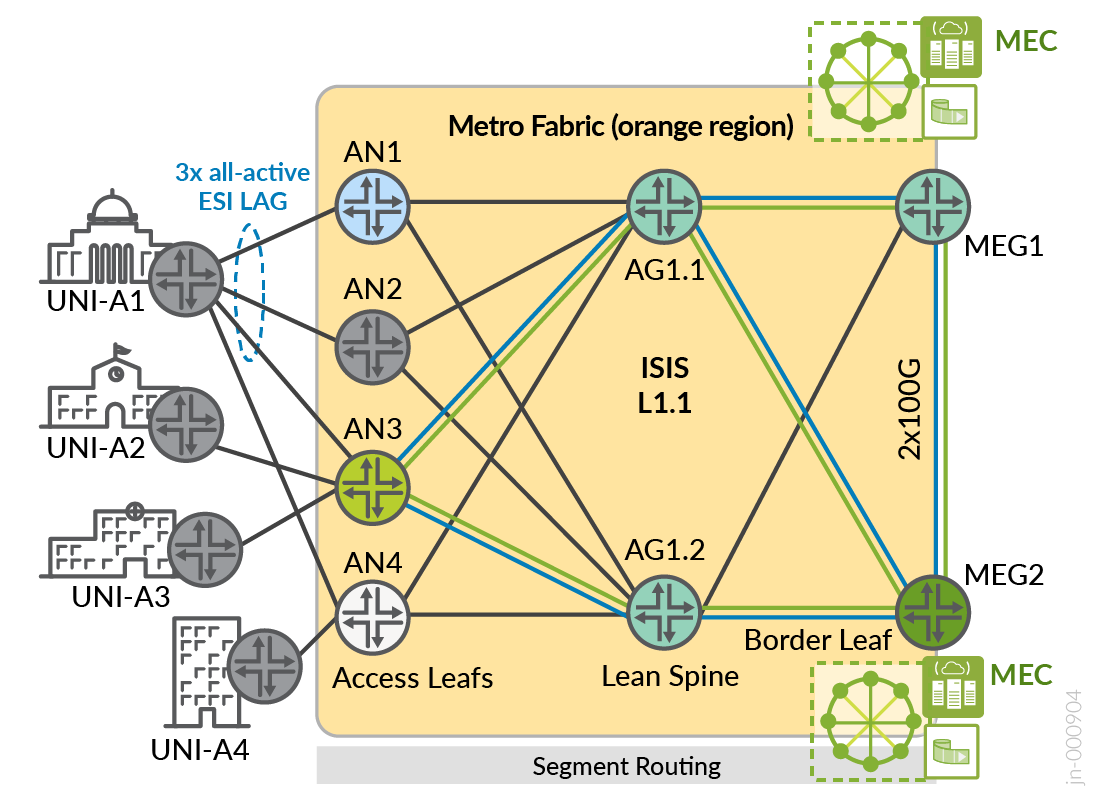
The table summarizes the convergence times for metro fabric services for a given failure event. The fabric design enables flow optimization for VPN services between AN-to-AN. Intra-AS Metro Fabric services include AN-to-AN (via spine AG1 nodes), AN-to-MEG single-homing, and AN-to-MEG1/MEG2 multi-homing. The Metro Edge Gateway (MEG) supports the connectivity into edge computing services. In the JVD, this connection handoff is supported with QFX5110 platforms.
| METRO FABRIC INTRA-AS (milliseconds) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVPN-VPWS | EVPN-ELAN | L2CIRCUIT | L3VPN | |||||
| EVENT | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC |
| AN3-AG1.1 link disable | 0 | 2.3 | 87 | 3 | 0 | 4.8 | 0 | 2.8 |
| AN3-AG1.1 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 |
| AN3-AG1.2 link disable | 0.3 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.3 |
| AN3-AG1.2 link enable | 0 | 0 | 46.6 | 0 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 |
| AG1.2-MEG2 link disable | 0.7 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0 | 0.6 |
| AG1.2-MEG2 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AG1.1-MEG1 link disable | 49.6 | 0.3 | 20.1 | 0.3 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AG1.1-MEG1 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| L2CKT Standby Failover 1 | - | - | - | - | 2939.8 1 | 2443 1 | - | - |
| L2CKT Standby Revert | - | - | - | - | 39 | 43 | - | - |
1 Results shown for L2Circuit failure events include link failures with TI-LFA fast reroute restoration while maintaining L2Circuit mastership. The standby failover convergence represents executing manual failover from CLI. There are control plan mechanisms to signal the reverse path on the remote backup neighbor to transition active/open. The implementation differs slightly from MX platforms, which maintain an open state for the standby path.
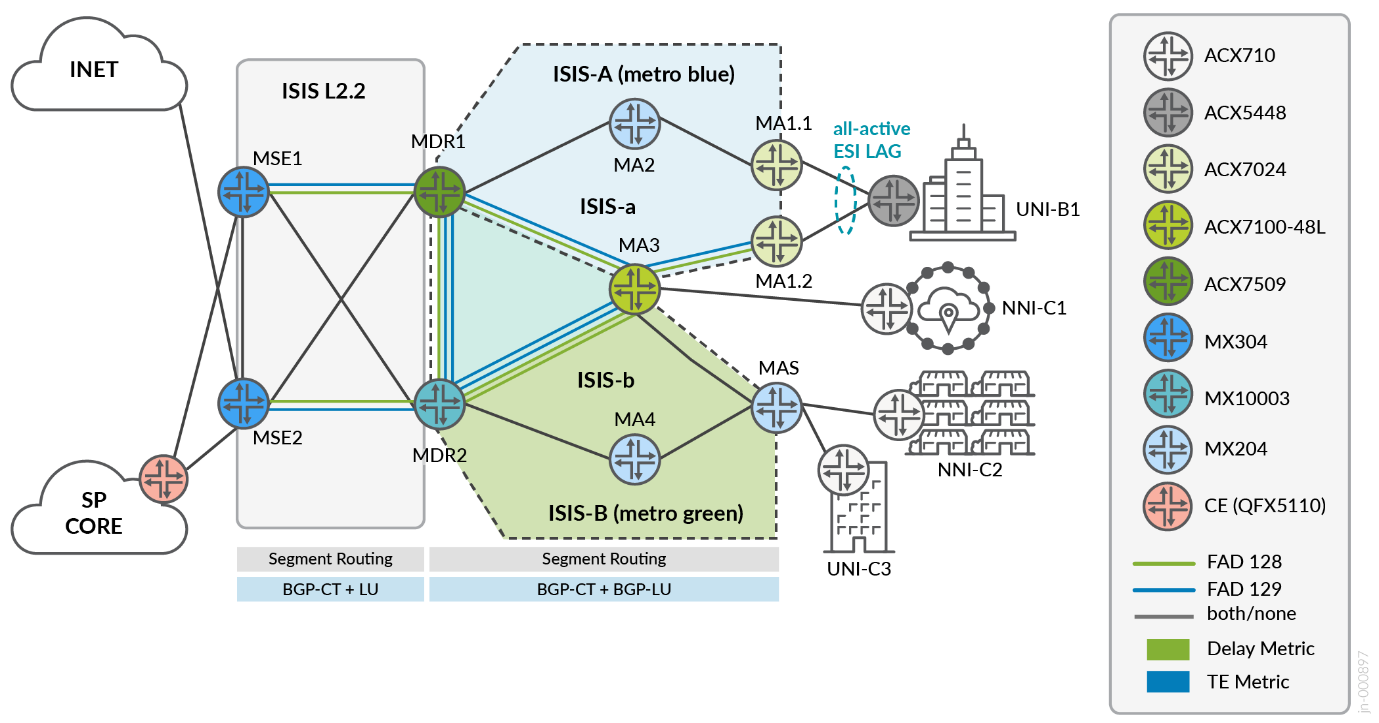
The next table summarizes convergence times for Metro multi-ring services for the given failure event. The multi-ring design enables flow optimization for MA-to-MA VPN services by leveraging MDR1/MDR2 as the deterministic point of leaking between ring domains (ISIS instances). Intra-AS Metro multi-ring services include traffic flows for MA-to-MA, MA-to-MSE single-homing, and MA-MSE1/MSE2 multi-homing. The multiservices edge routers support Internet-VRF and SP core connectivity, which enables services to be stitched into additional network domains.
| METRO MULTI-RING INTRA-AS (milliseconds) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BGP-VPLS | EVPN-TREE | FLOATING PW | L3VPN | |||||
| EVENT | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC |
| MDR1-MA2 link disable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR1-MA2 link enable | 17.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR1-MA3 link disable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 1 | 1 |
| MDR1-MA3 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA3 link disable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 37.2 | 29.4 | 0.4 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA3 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 | 6.3 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA4 link disable | 22.4 | 35.9 | 48.3 | 48.6 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| MDR2-MA4 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MA1.2-MA3 link disable | 115.3 | 178.3 | 0 | 0 | 67.4 | 18.4 | 0 | 0 |
| MA1.2-MA3 link enable | 12.6 | 12.8 | 0 | 0 | 6.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SP Core to MSE2 link disable1 | - | - | 28.1 | 131.7 | 8.8 | 6.6 | - | - |
| SP Core to MSE2 link enable1 | - | - | 32.4 | 31.7 | 84 | 412 | - | - |
1 SP Core to MSE2 represents a Q-in-Q segment handoff. The relationship here is more like a CE-facing link failure event and is measured with Dynamic List Next Hop (DLNH) and EVPN Egress Link Protection (ELP) support.
The final convergence table includes the end-to-end inter-AS services. This diagram displays the service instantiation points across the topology.
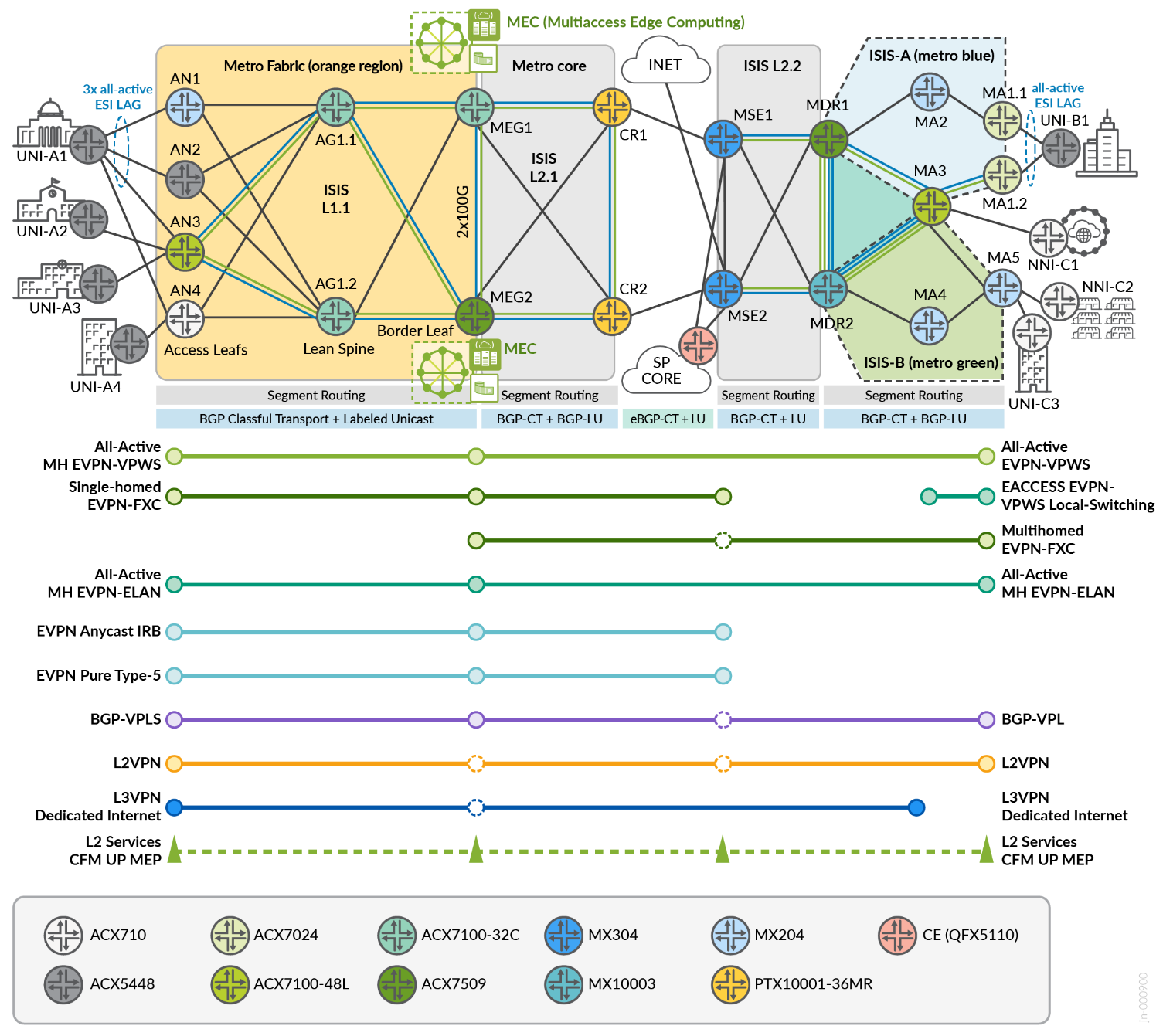
Flex Algo 128 include-any GREEN delay-metric
Flex Algo 129 include-any BLUE TE-metric
Transport Class 4000 maps to GOLD
Transport Class 6000 maps to BRONZE
Inter-AS services include:
- EVPN-ELAN Multihoming for VLAN-based services. All-Active ESI with 3xPE (AN1, AN2, AN3) to All-Active ESI with 2xPE (MA1.1, MA1.2) and All-Active ESI connectivity into MEC complex.
- EVPN-ELAN EP-LAN services between AN3 and MA1.2.
- EVPN-VPWS EPL services between AN3 and MA1.1.
- EVPN-VPWS Multi-homing All-Active ESI with 3xPE (AN1, AN2, AN3) to All-Active ESI with 2xPE (MA1.1, MA1.2).
- EVPN Flexible Cross-Connect VLAN Unaware between AN3 and MSE1.
- EVPN Flexible Cross-Connect VLAN Aware Multi-homing All-Active ESI with 2xPE (MA1.1, MA1.2) to All-Active ESI MEG1 and MEG2 for MEC connectivity.
- BGP-VPLS with multiple sites from AN3, MA1.2, MA5, and MEG1 or MEG2.
- L2VPN services between AN3 and MA5.
- L3 EVPN Route-Type 5 with multiple sites from AN3, MEG1. MEG2, MSE1, MSE2. Includes Internet Access through MSE2.
- L3 EVPN IRB Anycast with multiple sites from AN3, MEG1. MEG2, MSE1, MSE2. Includes Internet Access through MSE2.
- L3VPN with sites including AN3, MA4, MSE1. MSE2. L3VPN includes OSPF, BGPv4, and BGPv6 VRF services. Includes Internet Access through MSE2.
| METRO INTER-AS (milliseconds) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVPN-VPWS | EVPN-ELAN | L2VPN | VPLS | L3VPN | ||||||
| EVENT | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC | COLOR AWARE | COLOR AGNOSTIC |
| AN3-AG1.1 link disable | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 87 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AN3-AG1.1 link enable | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 1 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AN3-AG1.2 link disable | 0 | 0.8 | 0.18 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 |
| AN3-AG1.2 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AG1.2-MEG2 link disable | 0 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| AG1.2-MEG2 link enable | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AG1.1-MEG1 link disable | 0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AG1.1-MEG1 link enable | 0 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0 |
| MDR1-MA2 link disable | 1.9 | 3.4 | 0 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR1-MA2 link enable | 0.4 | 10.6 | 1.2 | 3.79 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR1-MA3 link disable | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR1-MA3 link enable | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3.9 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA3 link disable | 11.3 | 19 | 0.6 | 12.5 | 1.24 | 0.3 | 14.7 | 37.7 | 0.5 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA3 link enable | 0 | 26.9 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 38.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA4 link disable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 18.4 | 25.4 | 22.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDR2-MA4 link enable | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MA1.2-MA3 link disable | 54.9 | 9.6 | - | - | 0 | 0 | 18.4 | 61.9 | 0 | 0 |
| MA1.2-MA3 link enable | 11.6 | 0.4 | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 13.9 | 0 | 0 |
| AN3 ESI LAG disable | - | 2.2 | 1099.41 | 1075.61 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| AN3 ESI LAG enable | - | 1.8 | 38.1 | 38.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MEG-MEC link disable | 579.11 | 571.91 | 909.91 | 915.11 | - | - | - | - | - | 0 |
| MEG-MEC link enable | 144.81 | 232.81 | 14201 | 71.51 | - | - | - | - | - | 81.5 |
1 Current results show global repair because of CE-link failure. For fast failover, Dynamic List Next Hop (DLNH) and EVPN Egress Link Protection (ELP) are recommended and scheduled for Junos OS Evolved Release 24.3R1 on ACX7000 platforms. For comparative results demonstrating DLNH and ELP improvements supported by MX platforms, see Table 8.
Solution Gaps and Known Limitations
The solutions and services proposed by the JVD can be considered complete and supported with the following distinctions. Note that any target Junos OS/ Junos OS Evolved feature delivery references are not guaranteed and are subject to delay or cancellation without notice. Contact your Juniper Networks representative for status.
- Juniper recommends two additional optimization options for improving EVPN performance and reducing convergence time. For EVPN active-active multi-homing, the ESI route by default points to two next hops. A link failure event between PE and CE causes a new next-hop entry to be created, triggering mass MAC route withdrawals and additions. Juniper recommends Dynamic List Next Hop (DLNH) to enable silent removal of the affected next-hop entry without causing mass MAC withdrawals. EVPN Egress Link Protection (ELP) creates backup next hops on multi-homed PEs to support fast reroute (FRR). These features are currently supported on MX platforms. The ACX7000 family does not support these features in Junos OS Evolved Release 23.2R2 but support is planned for Junos OS Evolved Release 24.3R1.
- To avoid certain BGP-LU and BGP-CT inter-domain global repair events, Juniper recommends BGP-PIC machinery. In the presented solution, the functionality requires the preserve-nexthop-hierarchy knob, which is supported by MX platforms and included in the JVD. The ACX7000 family targets Junos OS Evolved Release 24.2R1 for these features. BGP-PIC for Seamless SR (BGP-LU and BGP-CT) is not included in the JVD for unsupported devices.
- BGP Classful Transport is included and validated on all featured DUTs running Junos OS Evolved Release 23.2R2 and 23.2R2. This feature enables seamless inter-domain color transport but is not required for the solution using only color-agnostic paths. Contact your Juniper Networks representative with questions or concerns.
- As of Junos OS Evolved Release 23.2R2, the ACX7000 family does not support simultaneous ECMP + FRR mechanisms. In general, TI-LFA fast reroute will provide optimal restoration and these are the results reported in the JVD. Support for the coexistence of ECMP+FRR is currently planned for Junos OS Evolved Release 24.1R1 and presents opportunities to further improve network resiliency and reduce convergence.
For additional JVD test information, contact your Juniper Networks representative.
