Use Case and Reference Architecture
A big enterprise network can include multiple campus and branch locations. These remote locations connect to the enterprise WAN (EWAN) private backbone/core network to access various business-critical applications and to communicate with each other. The remote campus and branch locations use L2/L3 VPN services to communicate with each other. The remote users also connect to public cloud providers to access applications such as Office365 and Microsoft Teams. Enterprises such as educational institutions or hospitals have multiple surveillance cameras installed that stream multicast video to one or more remote monitoring centers. The EWAN backbone or core network, which interconnects the different campus and branch networks must be resilient and reliable.
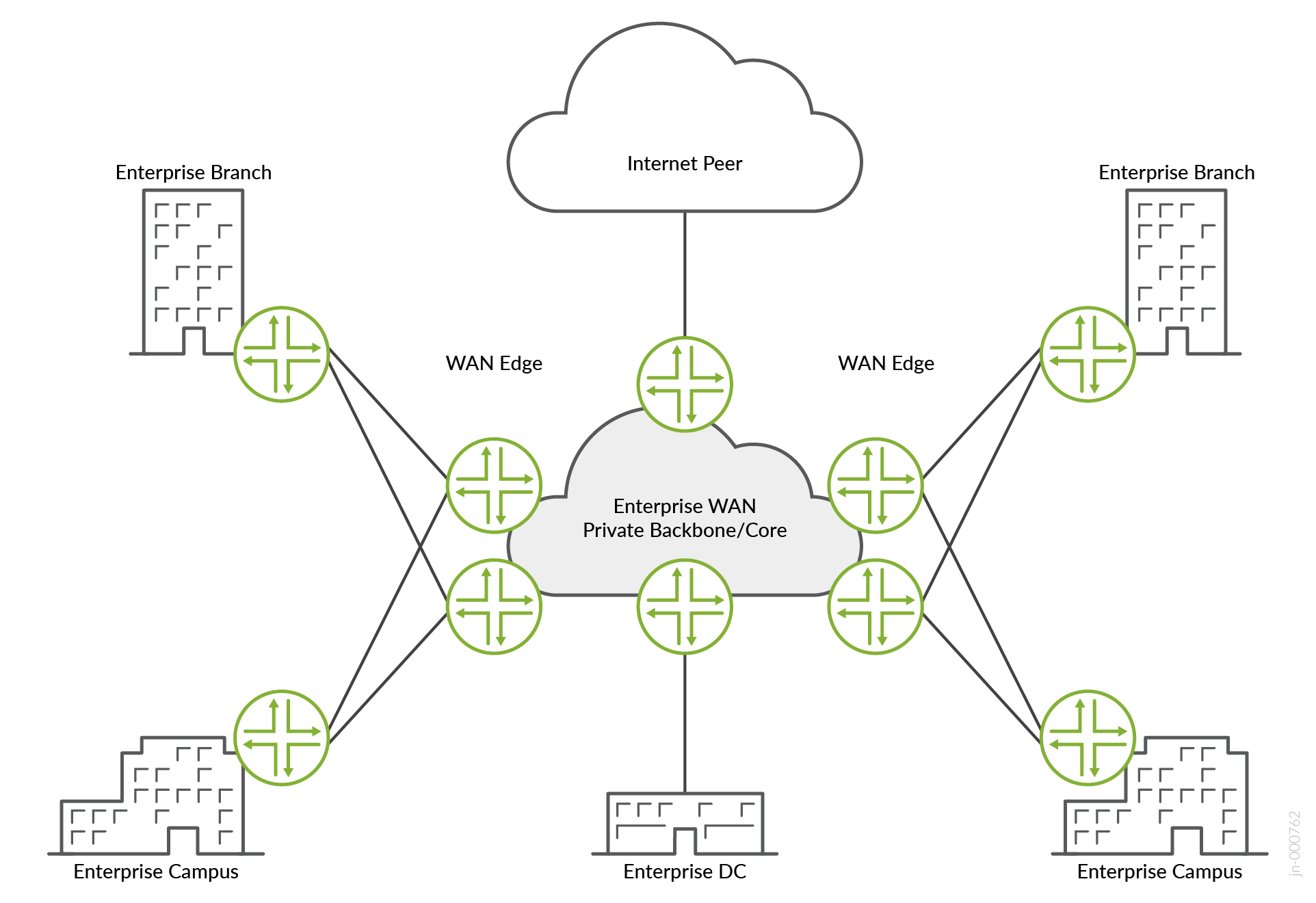
The remote campus and branch locations use L2/L3 VPN services to access the business-critical applications running in the enterprise private data center, and to communicate with each other. The remote users can also connect to public cloud providers and access applications such as Office365 and Microsoft Teams. The connection to the enterprise data center network that runs the business-critical applications must be resilient and reliable. This document validates multiple connection models that EWAN administrators can use. This document also validates a scenario where enterprises such as educational institutions or hospitals have multiple surveillance cameras installed that stream multicast video to one or more remote monitoring centers. The multicast traffic is transported inside of NGMVPN tunnels.
Remote campus and branch networks can connect to the headquarters network using Virtual Private LAN services (VPLS), Layer 2 Circuits (L2CKT), or L3VPN services. The VPN connections can use a hub-spoke design, where traffic from the campus and branch networks passes through a central HQ device that acts as a hub. The VPN connections can be single-homed, or multihomed to avoid single points of failure. The WAN edge devices use QoS to control bandwidth and WAN traffic is transported using MPLS.
