Solution Benefits
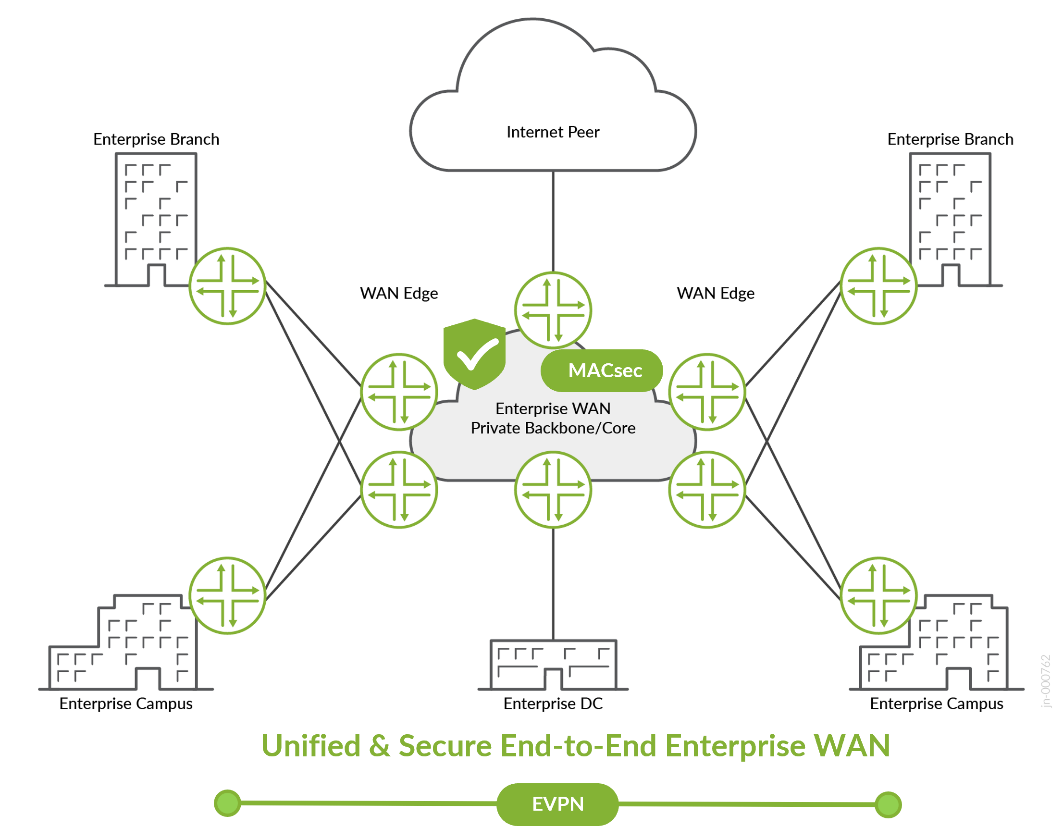
In the age of AI and Cloud Services, a private enterprise WAN remains an essential component of enterprise IT infrastructure. A big enterprise network can include multiple campus and branch locations. EWAN connects multiple sites within an organization such as universities, utilities, hospitals, banks, and railways. It enables end-to-end data communication and information transfer between different locations, such as campus and branch offices, data centers, and remote sites.
EWANs are designed to provide secure and reliable connectivity across diverse locations, allowing access to centralized resources, sharing data, and collaborating effectively. Enterprises typically utilize a combination of private and public networks, including leased lines, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), legacy and advanced Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and the Internet to connect to their headquarter network.
This JVD provides a validated solution for a unified and secure enterprise WAN Edge and Core infrastructure, which is based on the following five critical functional aspects:
- Connectivity: Enterprise WANs establish a network infrastructure to connect geographically dispersed locations, enabling seamless communication and resource sharing.
- Scalability: Enterprise WANs is designed to accommodate the growth and expansion of an organization, allowing new sites to be easily added to the network.
- Performance: WANs prioritize data traffic and apply Class of Service (CoS) mechanisms to ensure efficient utilization of network resources and optimize performance for critical applications.
- Security: Enterprise WANs implement various security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect sensitive data transmitted across the network.
- Reliability: Enterprise WANs implement redundant, and failover mechanisms are implemented to ensure high availability and minimize downtime in case of network failures.
Through multiple evolutionary cycles, the complexity of EWAN networks increases over time and often exceeds the complexity of certain tier 2 or tier 3 service providers. To simplify network operations and reduce associated costs, IT departments are actively seeking network simplification methods such as migrating to new, advanced protocols. Two protocols—Ethernet virtual private network (EVPN) and Segment Routing (SR)—generally allow for the reduction of the network complexity. These two protocols are sufficient to:
- Enable Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN connectivity,
- Enable a new level of reliability with built-in high availability mechanisms,
- Improve network stability, and
- Facilitate seamless stitching between campus and data center deployments.
EVPN and SR also often leverage EVPN VXLAN protocols.
In this JVD, network designs are validated that cover migration scenarios from legacy L2/L3 services to advanced VPN services based on an EVPN and SR underlay infrastructure. This JVD takes into consideration cases where SR and MPLS Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) transports are used simultaneously in different parts of the network and showcases the interoperability between the two protocols. Essentially, EVPN over MPLS is used as a universal method to enable L2 and Layer 3 multipoint-to-multipoint and L2 point-to-point circuits, which replaces a range of traditionally used L3VPN, L2VPN, Martini L2 circuits, and Virtual Private LAN service (VPLS) offerings.
On top of the network transport and service infrastructure, the solution provides advanced class-of-service (CoS) capabilities through hierarchical CoS to prioritize or guarantee bandwidth for specific applications or corporate VPN services across the network transport and service infrastructure.
Ensuring network security and data integrity is crucial for this solution. Network security encompasses a wide range of techniques that safeguard against various threats, typically requiring a dedicated framework of both hardware and software. However, can the network routing gears enhance the security of the WAN infrastructure and safeguard the transfer of information, beyond the application of access lists and securing management access to its components? The presented solution provides a positive response to the aforementioned question, emphasizing the utilization of the latest Juniper Networks products, which feature embedded MACsec functionality. This technology can be seamlessly enabled across the portfolio between MX, PTX, ACX platforms at the core and edge of the enterprise WAN.
Static ACLs (stateless firewall filters in Junos OS terminology) are essential mechanisms that can efficiently control network flows and prevent malicious attacks. Enterprises can enhance network stability under attack by activating DDoS protection at the edge routers. Through this solution, edge routers communicate with peripheral security devices using BGP flowspec protocol, dynamically installing filters for specific source/destination port/IP-address flows into the routers to block malicious attacks, such as ICMP flood attacks. Suspicious flows can also be redirected towards advanced traffic screening network security complexes enabled by this solution.
