Storage Backend Fabric
The Storage Backend fabric provides the connectivity infrastructure for storage devices to be accessible from the GPU servers.
The performance of the storage infrastructure significantly impacts the efficiency of AI workflows. A storage system that provides quick access to data can significantly reduce the amount of time for training AI models. Similarly, a storage system that supports efficient data querying and indexing can minimize the completion time of preprocessing and feature extraction in an AI workflow.
The Storage Backend fabric design in the JVD also follows a 3-stage IP clos architecture as shown in Figure 16. There is no concept of rail-optimization in a storage cluster. Each GPU server has a single connection to the leaf nodes, instead of 8.
Figure 16: Storage Backend Fabric Architecture
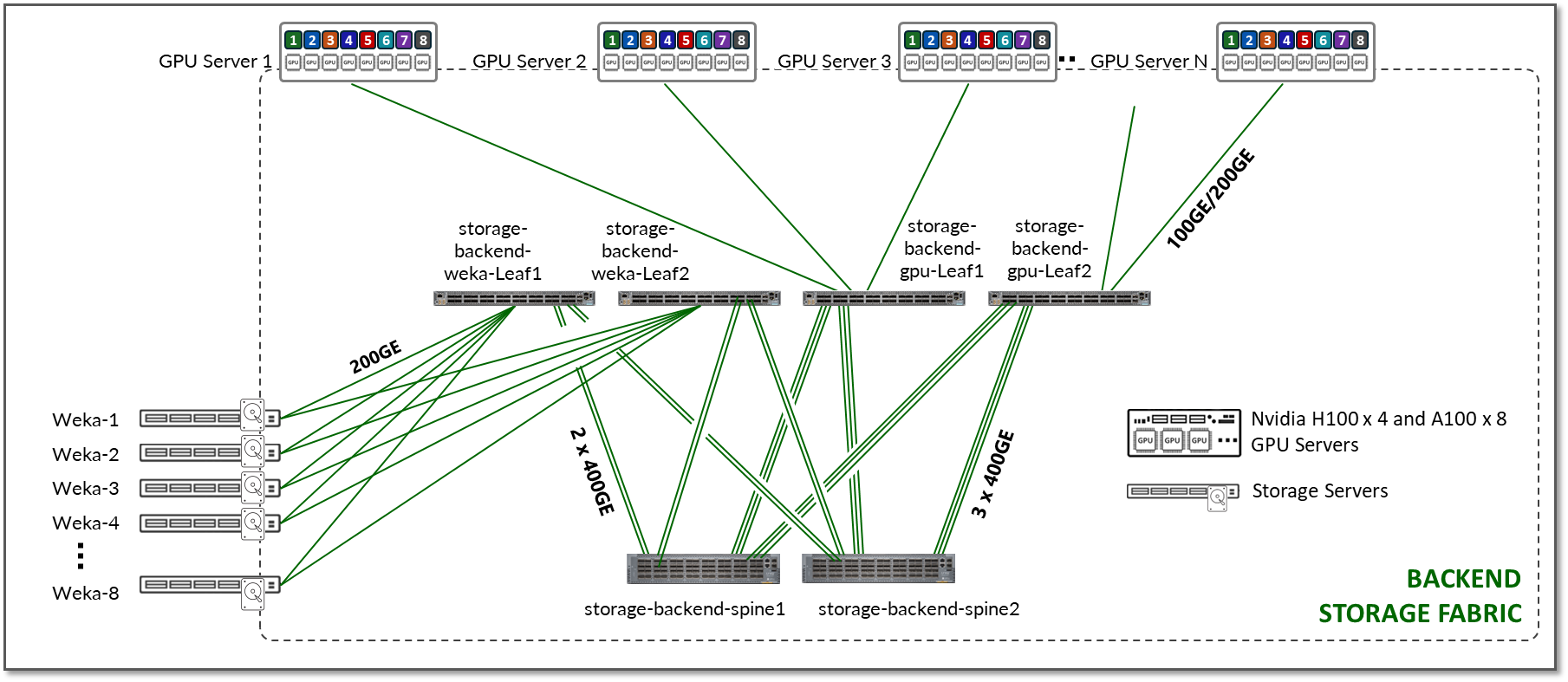
The Storage Backend devices included in this fabric, and the connections between them, are summarized in the following table:
Table 16: Storage Backend devices
| Nvidia DGX GPU Servers | Weka Storage Servers |
Storage Backend Leaf Nodes switch model (storage-backend-gpu-leaf & storage-backend-weka-leaf) |
Storage Backend Spine Nodes switch model (storage-backend-spine#) |
|
A100 x 8 H100 x 4 |
Weka storage server x 8 |
QFX5130-32CD x 4 (2 storage-backend-gpu-leaf nodes, and 2 storage-backend-weka-leaf nodes) |
QFX5130-32CD x 2 |
QFX5230 and QFX5240 were also validated for the Storage Backend Leaf and Spine roles.
Table 17: Connections between servers, leaf and spine nodes in the Storage Backend
|
GPU Servers <=> Storage Backend GPU Leaf Nodes |
Weka Storage Servers <=> Storage Backend Weka Leaf Nodes |
Storage Backend Spine Nodes <=> Storage Backend Leaf nodes |
|
1 x 100GE links between each H100 server and the storage-backend-gpu-leaf switch 1 x 200GE links between each A100 server and the storage-backend-gpu-leaf switch |
1 x 100GE links between each storage server (weka-1 to weka-8) and the storage-backend-weka-leaf switch |
2 x 400GE links between each leaf and spine nodes and the storage-backend-weka-leaf switch 3 x 400GE links between each leaf and spine nodes and the storage-backend-gpu-leaf switch |
The NVIDIA servers hosting the GPUs have dedicated storage network adapters (NVIDIA ConnectX) that support both the Ethernet and InfiniBand protocols and provide connectivity to external storage arrays.
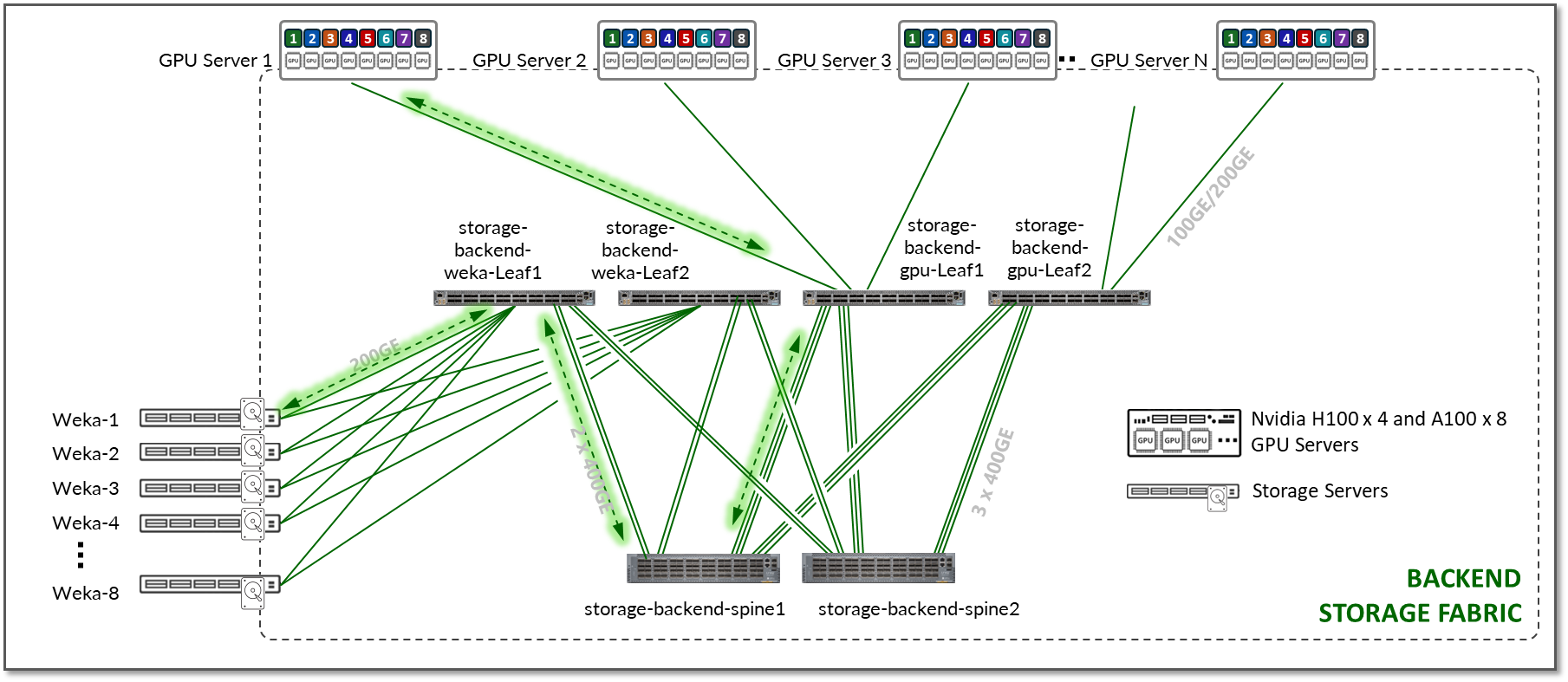
Communications between GPUs and the storage devices leverage the WEKA distributed POSIX client which enables multiple data paths for transfer of stored data from the WEKA nodes to the GPU client servers. The WEKA client leverages the Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) to offload TCP packet processing from the Operating System Kernel to achieve higher throughput.
This communication is supported by the Storage Backend fabric described in the previous section and exemplified in Figure 17.
Figure 17: GPU Backend to Storage Backend Communication
WEKA Storage Solution
In small clusters, it may be sufficient to use the local storage on each GPU server, or to aggregate this storage together using open-source or commercial software. In larger clusters with heavier workloads, an external dedicated storage system is required to provide dataset staging for ingest, and for cluster checkpointing during training. This JVD describes the infrastructure for dedicated storage using WEKA storage.
WEKA is a distributed data platform that allows high performance and concurrent access and allows all GPU Servers in the cluster to efficiently utilize a shared storage resource. With extreme I/O capabilities, the WEKA system can service the needs of all servers and scale to support hundreds or even thousands of GPUs.
Toward the end of this document, you can find more details on the WEKA storage system, including configuration settings, driver details, and more.
