ES Tunnels for Layer 3 VPNs
Configuring an ES Tunnel Interface for Layer 3 VPNs
An ES tunnel interface allows you to configure an IP Security (IPsec) tunnel between the PE and CE routers of a Layer 3 VPN. The IPsec tunnel can include one or more hops.
The following sections explain how to configure an ES tunnel interface between the PE and CE routers of a Layer 3 VPN:
- Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on the PE Router
- Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on the CE Router
Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on the PE Router
To configure the ES tunnel interface on the PE router, include
the unit statement:
unit logical-unit-number {
tunnel {
source source-address;
destination destination-address;
}
family inet {
address address;
ipsec-sa security-association-name;
}
}
You can include this statement at the following hierarchy levels:
[edit interfaces interface-name][edit logical-systems logical-system-name interfaces interface-name]
By default, the tunnel destination address is assumed to be
in the default Internet routing table, inet.0. For IPsec tunnels using
manual security association (SA), if the tunnel destination address
is not in the default inet.0 routing table, you need to specify which
routing table to search for the tunnel destination address by configuring
the routing-instance statement. This is the case if
the tunnel encapsulating interface is also configured under the routing
instance.
unit logical-unit-number {
tunnel {
source address;
destination address;
routing-instance {
destination routing-instance-name;
}
family inet {
address address;
ipsec-sa security-association-name;
}
family mpls;
}
}
You can include these statements at the following hierarchy levels:
[edit interfaces interface-name][edit logical-systems logical-system-name interfaces interface-name]Note:For IPsec tunnels using dynamic SA, the tunnel destination address must be in the default Internet routing table, inet.0.
To complete the ES tunnel interface configuration, include the interface statement for the ES interface under the appropriate
routing instance:
interface interface-name;
You can include this statement at the following hierarchy levels:
[edit routing-instances routing-instance-name][edit logical-systems logical-system-name routing-instances routing-instance-name]
Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on the CE Router
To configure the ES tunnel interface on the CE router, include
the unit statement:
unit 0 {
tunnel {
source address;
destination address;
}
family inet {
address address;
ipsec-sa security-association-name;
}
}
You can include this statement at the following hierarchy levels:
[edit interfaces interface-name][edit logical-systems logical-system-name interfaces interface-name]
Configuring an ES Tunnel Interface Between a PE and CE Router
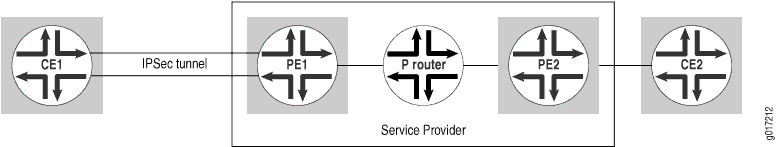
This example shows how to configure an ES tunnel interface between a PE router and a CE router in a Layer 3 VPN. The network topology used in this example is shown in Figure 1.
To configure this example, you perform the steps in the following sections:
- Configuring IPsec on Router PE1
- Configuring the Routing Instance Without the Encapsulating Interface
- Configuring the Routing Instance with the Encapsulating Interface
- Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on Router CE1
- Configuring IPsec on Router CE1
Configuring IPsec on Router PE1
Configure IP Security (IPsec) on Router PE1:
[edit security]
ipsec {
security-association sa-esp-manual {
mode tunnel;
manual {
direction bidirectional {
protocol esp;
spi 16000;
authentication {
algorithm hmac-md5-96;
key ascii-text "$9$ABULt1heK87dsWLDk.P3nrevM7V24ZHkPaZ/tp0cSvWLNwgZUH";
}
encryption {
algorithm des-cbc;
key ascii-text "$9$/H8Q90IyrvL7VKMZjHqQzcyleLN";
}
}
}
}
}
Configuring the Routing Instance Without the Encapsulating Interface
You can configure the routing instance on Router PE1 with or
without the encapsulating interface (t3-0/1/3 in this example).
The following sections explain how to configure the routing instance
without it:
- Configuring the Routing Instance on Router PE1
- Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on Router PE1
- Configuring the Encapsulating Interface for the ES Tunnel
Configuring the Routing Instance on Router PE1
Configure the routing instance on Router PE1:
[edit routing-instances]
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface es-1/2/0.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.174:1;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpna {
type external;
peer-as 100;
as-override;
neighbor 10.49.2.1;
}
}
}
}
Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on Router PE1
Configure the ES tunnel interface on Router PE1:
[edit interfaces es-1/2/0]
unit 0 {
tunnel {
source 192.168.197.249;
destination 192.168.197.250;
}
family inet {
address 10.49.2.2/30;
ipsec-sa sa-esp-manual;
}
}
Configuring the Encapsulating Interface for the ES Tunnel
For this example, interface t3-0/1/3 is the encapsulating
interface for the ES tunnel. Configure interface t3-0/1/3:
[edit interfaces t3-0/1/3]
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.197.249/30;
}
}
Configuring the Routing Instance with the Encapsulating Interface
If the tunnel-encapsulating interface, t3-0/1/3,
is also configured under the routing instance, you need to specify
the routing instance name under the interface definition. The system
uses this routing instance to search for the tunnel destination address
for the IPsec tunnel using manual security association.
The following sections explain how to configure the routing instance with the encapsulating interface:
- Configuring the Routing Instance on Router PE1
- Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on Router PE1
- Configuring the Encapsulating Interface on Router PE1
Configuring the Routing Instance on Router PE1
Configure the routing instance on Router PE1 (including the tunnel encapsulating interface):
[edit routing-instances]
vpna {
instance-type vrf;
interface es-1/2/0.0;
interface t3-0/1/3.0;
route-distinguisher 10.255.14.174:1;
vrf-import vpna-import;
vrf-export vpna-export;
protocols {
bgp {
group vpna {
type external;
peer-as 100;
as-override;
neighbor 10.49.2.1;
}
}
}
}
Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on Router PE1
Configure the ES tunnel interface on Router PE1:
[edit interfaces es-1/2/0]
unit 0 {
tunnel {
source 192.168.197.249;
destination 192.168.197.250;
routing-instance {
destination vpna;
}
}
family inet {
address 10.49.2.2/30;
ipsec-sa sa-esp-manual;
}
}
Configuring the Encapsulating Interface on Router PE1
Configure the encapsulating interface on Router PE1:
[edit interfaces t3-0/1/3]
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.197.249/30;
}
}
Configuring the ES Tunnel Interface on Router CE1
Configure the ES tunnel interface on Router CE1:
[edit interfaces es-1/2/0]
unit 0 {
tunnel {
source 192.168.197.250;
destination 192.168.197.249;
}
family inet {
address 10.49.2.1/30;
ipsec-sa sa-esp-manual;
}
}
Configuring IPsec on Router CE1
Configure IPsec on Router CE1:
[edit security]
ipsec {
security-association sa-esp-manual {
mode tunnel;
manual {
direction bidirectional {
protocol esp;
spi 16000;
authentication {
algorithm hmac-md5-96;
key ascii-text "$9$ABULt1heK87dsWLDk.P3nrevM7V24ZHkPaZ/tp0cSvWLNwgZUH";
}
encryption {
algorithm des-cbc;
key ascii-text "$9$/H8Q90IyrvL7VKMZjHqQzcyleLN";
}
}
}
}
}
