ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configuring BFD for VCCV for Layer 2 Circuits
This example shows how to configure BFD for VCCV for Layer 2 circuits which enables faster detection of failure in the data path.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
Two MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platforms
Junos OS Release 12.1 or later running on all devices
Overview
Starting with Junos OS Release 12.1, Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) support for virtual circuit connection verification (VCCV) allows you to configure a control channel for a pseudowire, in addition to the corresponding operations and management functions to be used over that control channel. BFD provides a low resource mechanism for the continuous monitoring of the pseudowire data path and for detecting data plane failures. This feature provides support for asynchronous mode BFD for VCCV as described in RFC 5885, Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for the Pseudowire Virtual Circuit Connectivity Verification (VCCV). You can also use a ping to detect pseudowire failures. However, the processing resources required for a ping are greater than what is needed for BFD. In addition, BFD is capable of detecting data plane failure faster than VCCV ping. BFD for pseudowires is supported for Layer 2 circuits (LDP-based).
To configure BFD for VCCV for Layer 2 circuits, configure the oam configuration statement at the [edit protocols l2circuit
neighbor address interface interface-name] hierarchy level. The control-channel configuration
statement at the [edit routing-instances routing-instance-name protocols l2vpn oam] hierarchy level does not apply to Layer
2 circuit configurations.
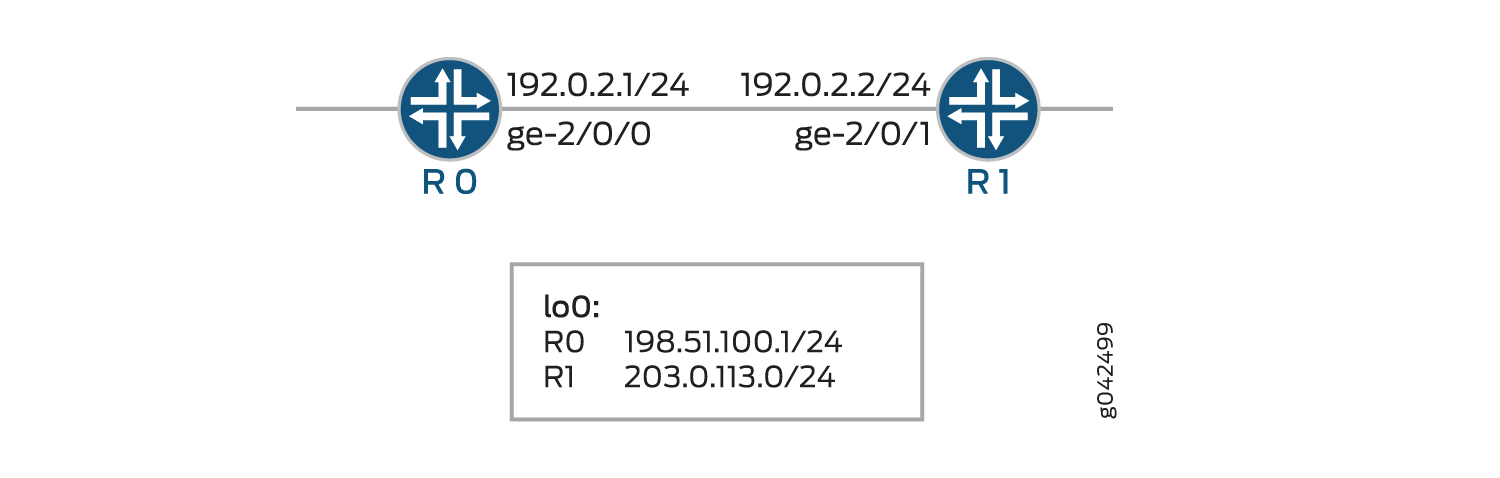
Topology
In the topology, BFD for VCCV for Layer 2 circuits is configured on Device R0.
Configuration
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure this example, copy the
following commands, paste them into a text file, remove any line breaks,
change any details necessary to match your network configuration,
copy and paste the commands into the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy
level, and then enter commit from configuration mode.
R0
set chassis redundancy graceful-switchover set interfaces ge-1/1/9 vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-1/1/9 encapsulation vlan-ccc set interfaces ge-1/1/9 unit 0 encapsulation vlan-ccc set interfaces ge-1/1/9 unit 0 vlan-id 512 set interfaces ge-2/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.1/24 set interfaces ge-2/0/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.0/24 set routing-options nonstop-routing set routing-options static route 203.0.113.0/24 next-hop 192.0.2.2 set routing-options router-id 198.51.100.0 set protocols rsvp interface ge-2/0/0.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path lsp1 to 203.0.113.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-2/0/0.0 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/0.0 set protocols ldp interface all set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 virtual-circuit-id 1 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection minimum-interval 300 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection minimum-receive-interval 10 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection multiplier 3 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval minimum-interval 5 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval threshold 30 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection detection-time threshold 40
R1
set interfaces ge-1/1/9 vlan-tagging set interfaces ge-1/1/9 encapsulation vlan-ccc set interfaces ge-1/1/9 unit 0 encapsulation vlan-ccc set interfaces ge-1/1/9 unit 0 vlan-id 512 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.2/24 set interfaces ge-2/0/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 203.0.113.0/24 set routing-options static route 198.51.100.0/24 next-hop 192.0.2.1 set routing-options router-id 203.0.113.0 set protocols rsvp interface ge-2/0/1.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path lsp2 to 198.51.100.0 set protocols mpls interface ge-2/0/1.0 set protocols ospf traffic-engineering set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/1.0 set protocols ldp interface all set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 virtual-circuit-id 1 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection minimum-interval 300 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection minimum-receive-interval 10 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection multiplier 3 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval minimum-interval 5 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval threshold 30 set protocols l2circuit neighbor 198.51.100.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection detection-time threshold 40
Configuring Device R0
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To configure Device R0:
Repeat this procedure for Device R1 after modifying the appropriate interface names, addresses, and any other parameters for the device.
Configure graceful switchover redundancy.
[edit chassis] user@R0# set redundancy graceful-switchover
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@R0# set ge-1/1/9 vlan-tagging user@R0# set ge-1/1/9 encapsulation vlan-ccc user@R0# set ge-1/1/9 unit 0 encapsulation vlan-ccc user@R0# set ge-1/1/9 unit 0 vlan-id 512 user@R0# set ge-2/0/0 unit 0 family inet address 192.0.2.1/24 user@R0# set ge-2/0/0 unit 0 family mpls user@R0# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 198.51.100.0/24
Configure the nonstop routing option, the static route, and the router ID routing options.
[edit routing-options] user@R0# set nonstop-routing user@R0# set static route 203.0.113.0/24 next-hop 192.0.2.2 user@R0# set router-id 198.51.100.0
Configure the RSVP protocol.
[edit protocols rsvp] user@R0# set interface ge-2/0/0.0
Configure the MPLS protocol.
[edit protocols mpls] user@R0# set label-switched-path lsp1 to 203.0.113.0 user@R0# set interface ge-2/0/0.0
Configure the OSPF protocol.
[edit protocols ospf] user@R0# set traffic-engineering user@R0# set area 0.0.0.0 interface ge-2/0/0.0
Configure the LDP protocol.
[edit protocols ldp] user@R0# set interface all
Configure the virtual circuit ID for the neighbor of Layer 2 circuit protocols.
[edit protocols l2circuit] user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 virtual-circuit-id 1
Configure the oam attributes of the Layer 2 circuit protocol.
[edit protocols l2circuit] user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection minimum-interval 300 user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection minimum-receive-interval 10 user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection multiplier 3 user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval minimum-interval 5 user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection transmit-interval threshold 30 user@R0# set neighbor 203.0.113.0 interface ge-1/1/9.0 oam bfd-liveness-detection detection-time threshold 40
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show chassis, show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands.
If the output does not display the intended configuration, repeat
the instructions in this example to correct the configuration.
user@R0# show chassis
redundancy {
graceful-switchover;
}
user@R0# show interfaces
ge-1/1/9 {
vlan-tagging;
encapsulation vlan-ccc;
unit 0 {
encapsulation vlan-ccc;
vlan-id 512;
}
}
ge-2/0/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.0.2.1/24;
}
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 198.51.100.0/24;
}
}
}
user@R0# show protocols
rsvp {
interface ge-2/0/0.0;
}
mpls {
label-switched-path lsp1 {
to 203.0.113.0;
}
interface ge-2/0/0.0;
}
ospf {
traffic-engineering;
area 0.0.0.0 {
interface ge-2/0/0.0;
}
}
ldp {
interface all;
}
l2circuit {
neighbor 203.0.113.0 {
interface ge-1/1/9.0 {
virtual-circuit-id 1;
oam {
bfd-liveness-detection {
minimum-interval 300;
minimum-receive-interval 10;
multiplier 3;
transmit-interval {
minimum-interval 5;
threshold 30;
}
detection-time {
threshold 40;
}
}
}
}
}
}
user@R0# show routing-options
nonstop-routing;
static {
route 203.0.113.0/24 next-hop 192.0.2.2;
}
router-id 198.51.100.0;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Verify that the configuration is working properly.
- Verifying the Layer 2 Circuit Connections
- Verifying the BFD Session
- Verifying Detailed BFD Session Information
Verifying the Layer 2 Circuit Connections
Purpose
Verify the connections in a Layer 2 Circuit.
Action
From operational mode, run the show l2circuit
connections command for Device R0.
user@R0> show l2circuit connections
Layer-2 Circuit Connections:
Legend for connection status (St)
EI -- encapsulation invalid NP -- interface h/w not present
MM -- mtu mismatch Dn -- down
EM -- encapsulation mismatch VC-Dn -- Virtual circuit Down
CM -- control-word mismatch Up -- operational
VM -- vlan id mismatch CF -- Call admission control failure
OL -- no outgoing label IB -- TDM incompatible bitrate
NC -- intf encaps not CCC/TCC TM -- TDM misconfiguration
BK -- Backup Connection ST -- Standby Connection
CB -- rcvd cell-bundle size bad SP -- Static Pseudowire
LD -- local site signaled down RS -- remote site standby
RD -- remote site signaled down HS -- Hot-standby Connection
XX -- unknown
Legend for interface status
Up -- operational
Dn -- down
Neighbor: 203.0.113.0
Interface Type St Time last up # Up trans
ge-1/1/9.0(vc 1) rmt Up Jun 2 03:19:44 2014 1
Remote PE: 203.0.113.0, Negotiated control-word: Yes (Null)
Incoming label: 299792, Outgoing label: 299792
Negotiated PW status TLV: No
Local interface: ge-1/1/9.0, Status: Up, Encapsulation: VLAN
Flow Label Transmit: No, Flow Label Receive: No
Flow Label Transmit: No, Flow Label Receive: No
Meaning
The output shows the Layer 2 virtual circuit information from Device R0 to its neighbor.
Verifying the BFD Session
Purpose
Verify the BFD session.
Action
From operational mode, run the show bfd session command for Device R0.
user@R0> show bfd session
Detect Transmit
Address State Interface Time Interval Multiplier
203.0.113.7 Up ge-2/0/0.0 0.030 0.010 3
1 sessions, 1 clients
Cumulative transmit rate 100.0 pps, cumulative receive rate 100.0 pps
Meaning
The output shows the address, and the interface on which the BFD session is active. The state Up indicates that the BFD session is up. The BFD session has a time interval of 30 milliseconds to detect BFD control packets , the transmitting system has a time interval of 10 milliseconds to send BFD control packets, and the transmitting system determines the detection time by multiplying 3 with the time interval. Total number of active BFD sessions and total number of clients that are hosting active BFD sessions. Cumulative transmit rate indicates the total number of BFD control packets transmitted, per second, on all active sessions and cumulative receive rate indicates the total number of BFD control packets received, per second, on all active sessions.
Verifying Detailed BFD Session Information
Purpose
Verify detailed BFD session information.
Action
From operational mode, run the show bfd session
extensive command for Device R0.
user@R0> show bfd session extensive
Detect Transmit
Address State Interface Time Interval Multiplier
203.0.113.7 Up ge-2/0/0.0 0.030 0.010 3
Client L2CKT-OAM, TX interval 0.005, RX interval 0.010
Session up time 03:47:14
Local diagnostic None, remote diagnostic None
Remote state Up, version 1
Replicated
Session type: VCCV BFD
Min async interval 0.005, min slow interval 1.000
Adaptive async TX interval 0.005, RX interval 0.010
Local min TX interval 0.005, minimum RX interval 0.010, multiplier 3
Remote min TX interval 0.005, min RX interval 0.010, multiplier 3
Threshold transmission interval 0.030, Threshold for detection time 0.040
Local discriminator 20, remote discriminator 13004
Echo mode disabled/inactive
Remote is control-plane independent
Neighbor address 203.0.113.0, Virtual circuit id 1
Session ID: 0x0
1 sessions, 1 clients
Cumulative transmit rate 100.0 pps, cumulative receive rate 100.0 pps
Meaning
The output shows detailed information for the BFD session.
