Dual-Stack Access Models in a PPPoE Network
IPv4 and IPv6 Dual Stack in a PPPoE Access Network
In a dual-stack architecture with a PPPoE access network that connects the CPE to the BNG, IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity are provided over a single PPP logical link. The PPP IPv4 control protocol (IPCP) and the IPv6 control protocol (IPv6CP) provide independent IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity over the logical link.
The BNG and the CPE handle both IPCP and IPv6CP identically and simultaneously over a single PPP connection. The BNG or the CPE can open and close any Network Control Protocol (NCP) session without affecting the other sessions. This capability allows for a dynamic setup where IPv4 (family inet) and IPv6 (family inet6) sessions can be brought up and down individually. As long as one family is active, the subscriber remains active.
Figure 1 shows a dual-stack interface stack in a PPPoE access network. The IPv4 family (inet) and the IPv6 family (inet6) can reside on the same PPPoE logical interfaces. The family inet and family inet6 parts of dynamic profiles are applied, and services are activated when each individual family is negotiated.
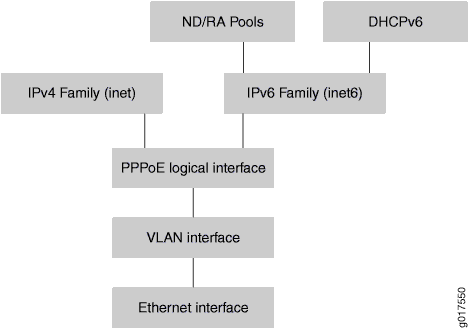
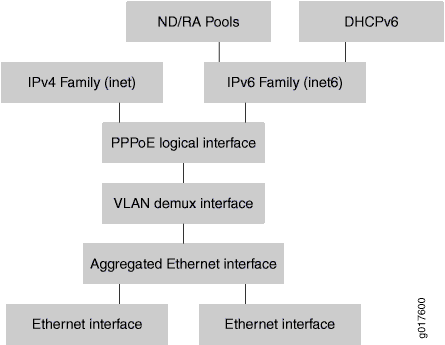
Figure 2 shows a dual-stack interface stack over aggregated Ethernet in a PPPoE access network.
- Support for Demultiplexing Interfaces
- Determining the Status of CPE in a PPPoE Access Network
- IPV6 Address Provisioning in the PPPoE Access Network
- Authentication in a PPPoE Access Network
- Negotiation of Network Control Protocols When Authorized Addresses Are Unavailable
Support for Demultiplexing Interfaces
IPv4 and IPv6 dual stack is supported on VLAN demultiplexing (demux) interfaces. Dual stack is not supported on IP demux interfaces.
Determining the Status of CPE in a PPPoE Access Network
In a PPPoE access network, you can enable keepalives to determine the status of the CPE.
IPV6 Address Provisioning in the PPPoE Access Network
IPv6CP negotiates the interface identifier, which can be used to provision link-local addresses that are used for direct connectivity between the BNG and the CPE. Because PPPoE negotiates only interface IDs and does not negotiate IPv6 addresses, PPPoE relies on other protocols for addressing. The protocols you can use are DHCPv6 and NDRA.
Authentication in a PPPoE Access Network
In a PPPoE network, you can use PAP and CHAP to identify and authenticate the CPE and subscriber sessions.
You can also use AAA for authentication and authorization through external RADIUS servers.
Negotiation of Network Control Protocols When Authorized Addresses Are Unavailable
NCP negotiation is initiated for subscriber sessions by default, even when authorized addresses are not available. An example of this situation is when the DHCPv6 local server is configured with an override so that the jpppd process never receives an IPv6 address or prefix from AAA, although the DHCPv6 local server receives a prefix from a delegated pool. In this situation, the client attempts to negotiate IPv6CP with the jpppd process.
By default, when IPCP negotiation is attempted for an IPv4-only
PPPoE subscriber session on a dynamic interface, the jpppd process
issues a Protocol-Reject message if AAA does not provide an IPv4 address.
However, negotiation is allowed to proceed when the on-demand-ip-address statement is included at the [edit protocols ppp-service] or [edit dynamic-profiles profile-name interfaces pp0 unit $junos-interface-unit ppp-options] hierarchy
level.
IPCP negotiation is enabled by default for an IP destination address defined on a static interface.
In contrast, IPv6CP negotiation is enabled to proceed by default
for an IPv6-only session when AAA has not provided an appropriate
IPv6 address or prefix. To prevent endless client negotiation of IPv6CP,
you can alter the behavior by including the reject-unauthorized-ipv6cp statement at the [edit protocols ppp-service] hierarchy
level. This statement enables the jpppd process to reject the negotiation
attempt.
When IPv6CP rejection is enabled, jpppd also issues a Protocol-Reject message when router advertisement is not enabled in the dynamic profile that instantiates the interface but only a Framed-IPv6-Prefix attribute is received.
AAA Service Framework in a Dual Stack over a PPPoE Access Network
You can use the AAA Service Framework for all authentication, authorization, accounting, address assignment, and dynamic request services that the BNG uses for network access. The framework supports authentication and authorization through external RADIUS servers. It also supports accounting and dynamic-request change of authorization (CoA) and disconnect operations through external servers, and address assignment through a combination of local address-assignment pools and RADIUS servers.
The BNG interacts with external servers to determine how individual subscribers access the broadband network. The BNG can also obtain information from external servers for the following:
-
How subscribers are authenticated.
-
How accounting statistics are collected and used.
-
How dynamic requests, such as CoA, are handled.
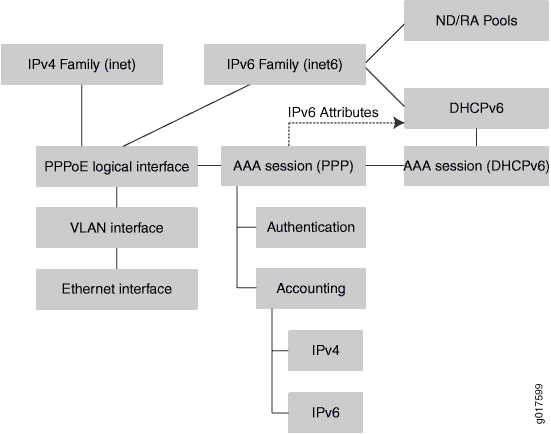
As shown in Figure 3, implementing a dual stack over a PPPoE access network that uses AAA can have the following characteristics:
-
DHCPv6—If used, it runs over the IPv6 family session, and it inherits attributes from the underlying PPPoE session.
-
NDRA—If used, it runs over the IPv6 family session.
-
IPv4 and IPv6 accounting—One accounting session handles both IPv4 and IPv6 accounting information.
Collection of Accounting Statistics in a PPPoE Access Network
AAA provides support for both IPv4 and IPv6 statistics in one accounting session. On MX Series 5G Universal Routing Platforms, AAA also provides support for separate IPv4 and IPv6 accounting statistics.
The following RADIUS attributes are included by default (when available) in Acct-Start, Interim, and Acct-Stop messages:
-
Framed-IPv6-Prefix
-
Framed-IPv6-Pool
-
Delegated-Ipv6-Prefix
-
Framed-IPv4-Route
-
Framed-IPv6-Route
You can configure the BNG to exclude these attributes in Acct-Start and Acct-Stop messages.
Change of Authorization (CoA)
RADIUS servers can initiate dynamic requests to the BNG. Dynamic requests include CoA requests, which specify vendor-specific attribute (VSA) modifications and service changes.
In your access profile configuration, you specify the IP addresses of RADIUS authentication servers that can initiate dynamic requests to the router. The list of authentication servers also provides RADIUS-based dynamic service activation and deactivation during subscriber login.
RADIUS Accounting Messages for Dual-Stack PPPoE Subscribers
Acct-Start messages sent to the RADIUS server contain all the learned and allocated addresses. Subsequent negotiation or allocation of addresses results in optionally sending immediate Acct-Interim-Update messages that contain all the negotiated and allocated addresses. For the dual-stack PPPoE subscriber, the following types of addresses are provided:
IP address–negotiated during the IPCP (NCP) phase of PPP
Interface identifier–negotiated during the IPv6CP (NCP) phase of PPP
NDRA prefix–sent during router advertisement after IPv6CP
DHCPv6 IA_NA address–negotiated by the DHCPv6 Solict, Advertise, Request, Reply (SARR) phase after IPv6CP
DHCPv6 IA_PD prefix–negotiated by the DHCPv6 SARR phase after IPv6CP
The BNG identifies addresses by the following methods:
Addresses or prefixes returned from an external authority, such as RADIUS
Addresses allocated locally using the pool names specified by external authority
Addresses allocated from a local pool not specified for PPP authorization
Addresses allocated by an external server outside of the BNG or RADIUS, such as a DHCPv6 external server (DHCPv6 relay or relay proxy)
IPCP and IPv6CP negotiation occur at the PPP NCP phase and can occur in any order. However, DHCPv6 PD or DHCPv6 IA_NA allocation and negotiation occur only after IPv6CP.
The following table lists the RADIUS attributes and their mapping:
Number |
RADIUS Attribute |
Address Type |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IP-Address |
IP Address |
2 |
Framed-Pool |
IP Address Pool |
3 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix |
NDRA_Prefix (prefix < 128) IA_NA (prefix = 128) |
4 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool |
NDRA Prefix pool IA_NA pool |
5 |
Framed-Interface-Id |
IPv6 Interface Identifier |
6 |
Delegated-IPv6-Prefix |
IA_PD Prefix |
7 |
Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (VSA 26-161) |
IA_PD Pool |
8 |
Jnpr-IPv6-Ndra-Pool-Name (VSA 26-157) NOTE. Not supported: Use Framed-IPv6-Pool to specify the NDRA pool. Alternatively, configure it locally by using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement. |
NDRA Pool |
Accounting Messages for PPPoE Using NDRA Prefixes
In the following tables, you can compare PPPoE dual-stack address allocation using Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) NDRA.
The following table lists SLAAC (NDRA) prefixes from RADIUS:
Number |
RADIUS Attributes |
IPv6 Address Negotiation Type |
RADIUS Accounting Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for NDRA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Because the required attributes are learned prior to the Acct-Start messages, these attributes are sent in Acct-Start messages and no immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. |
2 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for NDRA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Because the required attributes are learned prior to the Acct-Start messages, these attributes are sent in Acct-Start messages and no immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent after DHCPv6. |
3 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for NDRA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains only iFramed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update message (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. |
4 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for NDRA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD ) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update message (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. |
The following table lists prefixes from RADIUS selected pools:
Number |
RADIUS Attributes |
IPv6 Address Negotiation Type |
RADIUS Accounting Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for NDRA Prefix) NOTE: If RADIUS does not return Framed-IPv6-Pool, you can configure this locally using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement, which is used for allocating an NDRA prefix from the local pool. Framed-Interface-Id Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, Delegated-IPv6-Prefix, and Framed-Interface-Id. Framed-IPv6-Prefix is based on the configuration present in the dynamic profile IPv6 prefix that was allocated and sent in Acct-Start message. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-Interface-Id is sent in Acct-Start message because it is learned from RADIUS. No Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. |
2 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for NDRA Prefix) NOTE: If RADIUS does not return Framed-IPv6-Pool, you can configure this locally using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement, which is used for allocating an NDRA prefix from the local pool. Framed-Interface-Id Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, Delegated-IPv6-Prefix, and Framed-Interface-Id. Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Prefix are based on the configuration present in dynamic profile IPv6 prefix and is allocated prior and sent in Acct-Start message. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-Interface-Id is sent in Acct-Start message because it is learned from RADIUS. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. |
3 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for NDRA Prefix) NOTE: If RADIUS does not return Framed-IPv6-Pool, you can configure this locally using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement, which is used for allocating an NDRA prefix from the local pool. Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) |
4 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for NDRA Prefix) NOTE: If RADIUS does not return Framed-IPv6-Pool, you can configure this locally using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement, which is used for allocating an NDRA prefix from the local pool. Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) |
The following table lists prefixes from a local pool or an external server:
Number |
RADIUS Attributes |
IPv6 Address Negotiation Type |
RADIUS Accounting Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for NDRA Prefix) NOTE: If RADIUS does not return Framed-IPv6-Pool, you can configure this locally using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement, which is used for allocating an NDRA prefix from the local pool. Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool not sent |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Pool. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Pool. |
2 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for NDRA Prefix) NOTE: If RADIUS does not return Framed-IPv6-Pool, you can configure this locally using the neighbor-discovery-router-advertisement pool statement, which is used for allocating an NDRA prefix from the local pool. Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool not sent [IA_PD prefix is learned from DHCPv6 External Server (DHCPv6 Relay / Relay Proxy model) or reservation from a local pool by DHCPv6] |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Pool. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. Upon DHCPv6, immediate Acct-Interim-Update is sent which contains Framed-IPv6-Pool, Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-Interface-Id, and DHCPv6 IA_PD Prefix. Framed-Interface-Id value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer. DHCPv6 IA_PD is learned by DHCPv6 either by DHCPv6 external server or reservation from a local pool during DHCPv6 SARR phase. Any periodic Acct-Interim-Update before DHCPv6 completion contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to the attributes of the Acct-Start message. (This can occur if DHCPv6 occurs after periodic interval.) |
Accounting Messages for PPPoE Subscribers That Use DHCPv6 IA_NA Prefixes
In the following tables, you can compare PPPoE dual-stack address allocation using DHCPv6 IA_NA prefixes.
The following table lists DHCPv6 IA_NA prefixes from RADIUS:
Number |
RADIUS Attributes |
IPv6 Address Negotiation Type |
RADIUS Accounting Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for IA_NA prefix) Framed-Interface-Id Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Because the required attributes are learned prior to Acct-Start message, these attributes are sent in Acct-Start message and no immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. |
2 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Because the required attributes are learned prior to Acct-Start message, these attributes are sent in Acct-Start message and no immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. There is no immediate Acct-Interim-Update message sent after DHCPv6. |
3 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD ) |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. |
4 |
Framed-IPv6-Prefix (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Delegated-IPv6-Prefix (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message message contains iFramed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. |
The following table lists prefixes from RADIUS selected pools:
Number |
RADIUS Attributes |
IPv6 Address Negotiation Type |
RADIUS Accounting Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, Delegated-IPv6-Prefix, and Framed-Interface-Id . Framed-IPv6 Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated . Framed-Interface-Id is sent in Acct-Start message because it is learned from RADIUS. No Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. |
2 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for IA_NAPrefix) Framed-Interface-Id Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, Delegated-IPv6-Prefix, and Framed-Interface-Id. Framed-IPv6 is pre-allocated. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-Interface-Id is sent in Acct-Start message because it is learned from RADIUS. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. |
3 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. Framed-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) |
4 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool (used for DHCPv6 IA_PD) |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. Framed-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. Delegated-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, and Delegated-IPv6-Prefix. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) |
The following table lists prefixes from a local pool or an external server:
Number |
RADIUS Attributes |
IPv6 Address Negotiation Type |
RADIUS Accounting Messages |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool not sent |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Pool. Framed-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Pool. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) |
2 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool (used for IA_NA Prefix) Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool not sent [IA_PD prefix is learned from DHCPv6 External Server (DHCPv6 Relay / Relay Proxy model) or reservation from a local pool by DHCPv6] |
IPv6NCP + DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix and Framed-IPv6-Pool. Framed-IPv6-Prefix is pre-allocated. Framed-IPv6-Pool is learned from RADIUS. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon DHCPv6. Upon DHCPv6, an immediate Acct-Interim-Update is sent that contains Framed-IPv6-Pool, Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-Interface-Id, and DHCPv6 IA_PD Prefix. Framed-Interface-Id value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer. DHCPv6 IA_PD is learned by DHCPv6 either by DHCPv6 External Server or reservation from a local pool during DHCPv6 SARR phase. Any periodic Acct-Interim-Update before DHCPv6 completion contains Framed-Interface-Id in addition to the attributes of Acct-Start message. (This can occur if DHCPv6 occurs after periodic interval.) |
3 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool not sent [IA_NA Prefix is learned from DHCPv6 External Server (DHCPv6 Relay / Relay Proxy model) or reservation from a local pool by DHCPv6] Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool not sent [IA_PD prefix is learned from DHCPv6 External Server (DHCPv6 Relay / Relay Proxy model) or reservation from a local pool by DHCPv6] |
IPv6NCP |
Acct-Start message does not contain any of the IPv6-related prefixes and addresses or pool names. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) |
4 |
Framed-IPv6-Pool not sent [IA_NA Prefix is learned from DHCPv6 External Server (DHCPv6 Relay / Relay Proxy model) or reservation from a local pool by DHCPv6 ] Framed-Interface-Id not sent Jnpr-Delegated-IPv6-Pool not sent [IA_PD prefix is learned from DHCPv6 External Server (DHCPv6 Relay / Relay Proxy model) or reservation from a local pool by DHCPv6] |
IPv6NCP+DHCPv6 |
Acct-Start message does not contain any of the IPv6-related prefixes and addresses or pool names. No immediate Acct-Interim-Update message is sent upon IPv6NCP. Next periodic Acct-Interim-Update (based on interval) contains Framed-Interface-Id. (This value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer.) Upon DHCPv6, immediate Acct-Interim-Update is sent which contains Framed-IPv6-Prefix, Framed-IPv6-Pool, Framed-Interface-Id, and DHCPv6 IA_PD. Framed-IPv6-Prefix is the IA_NA prefix learned by DHCPv6 (either by external server or reservation from a local pool). Framed-IPv6-Pool is sent only if there is a reservation of an IA_NA prefix from local pool by DHCPv6. Framed-Interface-Id value is learned during IPv6NCP negotiation with the peer. DHCPv6 IA_PD prefix is learned by DHCPv6 either by DHCPv6 external server or reservation from a local pool during DHCPv6 SARR phase. Any periodic Acct-Interim-Update before DHCPv6 completion contains Framed-Interface-Id only. (This can occur if DHCPv6 occurs after periodic interval.) |
Suppressing Accounting Information That Comes from AAA
The following standard and vendor-specific IPv6 RADIUS attributes are included by default (when available) in Acct-Start and Acct-Stop messages:
Framed-IPv6-Prefix
Framed-IPv6-Pool
Delegated-Ipv6-Prefix
Framed-IPv4-Route
Framed-IPv6-Route
You can configure the software to exclude these attributes from Acct-Start or Acct-Stop messages. To do so, configure the access profile:
Avoiding Negotiation of IPv6CP in the Absence of an Authorized Address
You can control the behavior of the router in a situation where IPv6CP negotiation is initiated for subscriber sessions when no authorized addresses are available.
By default, IPv6CP negotiation is enabled to proceed for an
IPv6-only session when AAA has not provided an appropriate IPv6 address
or prefix. In the absence of the address, the negotiation cannot successfully
complete. To prevent endless client negotiation of IPv6CP, include
the reject-unauthorized-ipv6cp statement at the [edit
protocols ppp-service] hierarchy level, which enables the jpppd
process to reject the negotiation attempt.
To configure the router to reject IPv6CP negotiation messages when no IPv6 address is available for a dynamic interface:
Enable rejection of unauthorized IPv6CP negotiation messages.
[edit protocols ppp-service] user@host# set reject-unauthorized-ipv6cp
The reject-unauthorized-ipv6cp statement does
not prevent IPv6CP negotiation for static interfaces, because the
jpppd process cannot determine whether router advertisement of DHCPv6
is configured to run above the PPP interface.
