Subscriber LAN Addressing with DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
Using DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation Overview
You can use DHCPv6 prefix delegation to automate the delegation of IPv6 prefixes to the CPE. With prefix delegation, a delegating router (the BNG) delegates IPv6 prefixes to a requesting router (the CPE). The requesting router then uses the prefixes to assign global IP addresses to the devices on the subscriber LAN. The requesting router can also assign subnet addresses to subnets on the LAN.
DHCPv6 prefix delegation is useful when the delegating router does not have information about the topology of the networks in which the requesting router is located. In such cases, the delegating router requires only the identity of the requesting router to choose a prefix for delegation.
DHCPv6 prefix delegation replaces the need for NAT in an IPv6 network.
Figure 1 shows how DHCPv6 prefix delegation is used in a dual-stack network.
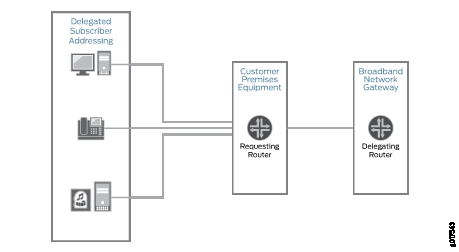
DHCPv6 prefix delegation operates as follows:
A delegating router is provided with IPv6 prefixes to be delegated to requesting routers. These prefixes can come from a local address-assignment pool or an external AAA server.
Each prefix has an associated valid and preferred lifetime, which can be extended.
A requesting router requests one or more prefixes from the delegating router.
The delegating router chooses prefixes for delegation, and responds with prefixes to the requesting router.
The requesting router is then responsible for the delegated prefixes.
The address allocation mechanism in the subscriber network can be performed with ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery in router advertisements, DHCPv6, or a combination of these two methods.
See Also
Using a Delegated Prefix on the CPE Loopback Interface
For networks in which the service provider directly controls the CPE, a delegated prefix can be used to create an IPv6 address on the loopback interface between the CPE and the BNG. This address can be used to manage the CPE, and the CPE uses it as a source address when it communicates with the BNG.
See Also
DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation over PPPoE
The process of DHCPv6 prefix delegation when DHCPv6 is running over a PPPoE access network is as follows:
The CPE obtains a link-local address by appending the interface ID that it receives through IPv6CP negotiation to the IPv6 link-local prefix (FE80::/10). The link-local address provides an initial path for protocol communication between the BNG and CPE
The CPE sends a DHCPv6 Solicit message that includes an IA_PD option.
The BNG chooses a prefix for the CPE with information from an external AAA server or from a local prefix pool.
The BNG sends an Advertise message to the CPE. The message includes the delegated prefix, an IA_PD option, and an IA_PD prefix option. The prefix length in the IA_PD prefix option is 48. The message can also contain other configuration information, such as a maximum lease time.
The CPE sends a Request message to the BNG. The message requests the prefix that was advertised.
The BNG returns the delegated prefix to the CPE in a Reply message. This message also contains the delegated prefix, an IA_PD option, and an IA_PD prefix option. The prefix length in the IA_PD prefix option is 48. The message can also contain other configuration information, such as a maximum lease time.
The CPE uses the delegated prefix to allocate global IPv6 addresses to host devices on the subscriber network. It can use router advertisements, DHCPv6, or a combination of these two methods to allocate addresses on the subscriber LAN.
See Also
Methods for Obtaining IPv6 Prefixes for DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
You can set up the BNG to select IPv6 prefixes to be delegated to the requesting router in one the following ways:
An external source such as a AAA RADIUS server or a DHCP server using the DHCPv6 relay agent.
Dynamic assignment from a local pool of prefixes that is configured on the BNG
You can specify the name of a delegated pool to use for prefix delegation, which means that you do not need to use AAA to obtain the pool name. In this configuration, if you have also specified a pool match order, the specified delegated pool takes precedence.
Using a AAA RADIUS Server to Obtain IPv6 Prefixes for Prefix Delegation
When the BNG needs to obtain a prefix for DHCPv6 prefix delegation, it uses the values in one of the following RADIUS attributes:
Delegated-IPv6-Prefix—The attribute (123) contains an IPv6 prefix that the BNG can send to the CPE.
Jnpr-IPv6-Delegated-Pool-Name—The attribute (VSA 26-161) contains the name of an address-assignment pool configured on the BNG from which the BNG can select a prefix to send to the CPE.
Both attributes are sent from the RADIUS server to the BNG in RADIUS Access-Accept messages.
See Also
Subscriber Delegated Prefix Preservation
Subscriber delegated prefix preservation supports preserving and restoring IPv6 prefixes assigned using DHCPv6 prefix delegation.
Configure address preservation under [edit access] hierarchy:
user@host# set access address-preservation address-types delegated-prefix user@host# set access address-preservation aging-time address-aging-time
The subscriber's delegated prefix is preserved even when subscriber logs out. After logout the output of "show network-access address-assignment preserved" command is updated and the subscriber gets allocated the same delegated prefix after login.
user@host> show network-access address-assignment preserved
Subscriber delegated prefix preservation supports preserving and restoring a subscriber’s
delegated prefix through multiple logins. Receiving the same delegated prefix from the JUNOS
device prevents an IA-PD change, that triggers renegotiation for all hosts on the LAN behind
the CPE. To utilise this functionality, a configuration command is executed. This
functionality is disabled by default. To enable address preservation for DHCPv6 prefix
delegation, use the access address-preservation configuration command.
Each participating subscriber is identified by the Agent-Circuit-Id. The Agent-Circuit-Id is available in standard upstream control traffic. (For example: Option-82 sub-option 1 for DHCP, Option 18 for DHCPv6). If the access address-preservation prefix is configured and a subscriber has an Agent-Circuit-Id, the subscribers prefix is preserved through multiple logins. The Agent-Circuit-Id is the key that is used to store the subscriber’s prefix when the subscriber logs out. When the subscriber with the same Agent-Circuit-Id, logs in again the prefix is retrieved and associated to the subscriber.
The show network-access address-assignment preserved command supports an
optional routing-instance <routing-instance-name> output.
user@host> show network-access address-assignment preserved routing-instance SUBSCRIBERS Key Delegated Prefix Reservation End interfaceId_Port //1/1 2001:0db8:aaaa:1::/64 May 22 12:06:19
See Also
DHCPv6 Prefix Exclusion
You can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol v6 (DHCPv6) prefix delegation to automate the delegation of IPv6 prefixes to the customer premises equipment (CPE) devices. With prefix delegation, a delegating router - the broadband network gateway (BNG) router, delegates IPv6 prefixes to a requesting router such as a CPE device. The requesting router then uses the prefixes to assign global IP addresses to the devices on the subscriber LAN. The requesting router can also assign subnet addresses to subnets on the LAN. DHCPv6 prefix delegation is useful when the delegating router does not have information about the topology of the networks in which the requesting router is located. In such cases, the delegating router requires only the identity of the requesting router to choose a prefix for delegation. DHCPv6 prefix delegation replaces the need for NAT in an IPv6 network.
Figure 2 shows how DHCPv6 prefix delegation is used in a dual-stack network.

DHCPv6 prefix delegation operates as follows:
A delegating router is provided with IPv6 prefixes to be delegated to requesting routers. These prefixes can come from a local address-assignment pool or an external AAA server.
Each prefix has an associated valid and preferred lifetime, which can be extended.
A requesting router requests one or more prefixes from the delegating router.
The delegating router chooses prefixes for delegation, and responds with prefixes to the requesting router.
The requesting router is then responsible for the delegated prefixes.
The address allocation mechanism in the subscriber network can be performed with ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) in router advertisements, DHCPv6, or a combination of these two methods.
The requesting router cannot use a sub-prefix of the delegated prefix assigned to it by the delegating router to the link between the delegating router and the requesting router. Because of this limitation, there are usually two routes to the CPE device. One is the delegated prefix, for the customer site behind the CPE device and the other for the link between the requesting router and the delegating router. To overcome this, Junos OS allows the exclusion of one specific prefix from a delegated prefix set while using DHCPv6 based prefix delegation as described in RFC 6603. This excluded prefix is used as the link between the delegating router and the requesting router. This prefix link is intended for use in networks where each requesting router is in its own Layer 2 domain.
To support prefix exclude delegation, the requesting router includes the Option Request option (ORO) with the PD_Exclude option in the solicit, request, renew, or rebind message to inform the delegating router about the support for the prefix delegation. When the Juniper Networks router acting as the DHCP server receives these message and finds the exclude prefix option (option 67) in ORO, it decides the prefix to be excluded. (The length of the prefix to be excluded is bigger than the delegated prefix length.) The excluded prefix is then added in the IA_Prefix options. The DHCP server acting as relay forwards the requested option to the server and relays the excluded prefix, assigned by the server, back to the client.
To exclude a prefix length in a DHCP server, configure the exclude-prefix-len statement at the [edit access address-assignment pool pool-name family dhcpv6 dhcp-attributes] hierarchy
level. The length of the prefix can range from 1 through 128.
If the DHCP server supporting the exclude prefix wants the client
to request for a prefix exclude after reconfiguration, then you can
configure thesupport-option-pd-exclude statement either
at the [edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6] hierarchy
level or at the [edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6
group group-name] hierarchy level.
Configuring DHCPv6 Prefix Exclude Option
To configure DHCPv6 prefix exclude:
Configure the prefix length to be excluded from a delegated prefix set pool. This prefix is used as the link between the delegating router and the requesting router. The exclude prefix length is bigger than the given prefix length.
[edit access address-assignement pool pool-name family inet6 dhcp-attributes] user@host# set exclude-prefix-len prefix-length
For example, for prefix delegated in 2001:db8::/32 , configure the exclude prefix as 2001:db8:ffff:fffc::/72 for delegated pool prefix_delegate_pool.
[edit access address-assignment pool prefix_delegate_pool family inet6 dhcp-attributes] user@host# set exclude-prefix-len 72
Configure PD_Exclude option support in the reconfigure message. In case the server wants the client to request for the prefix to be excluded after reconfiguration then the exclude prefix options are added in the Option Request option (ORO) in the reconfigure message.
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 reconfigure] user@host# set support-option-pd-exclude
Configure PD_Exclude option support in the reconfigure message for a given group.
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 group group-name reconfigure] user@host# set support-option-pd-exclude
Configuring an Address-Assignment Pool for Use by DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
This procedure shows how to configure IPv6 local address pools to allocate IPv6 prefixes for use by DHCPv6 prefix delegation.
You must configure separate pools for DHCPv6 prefix delegation, DHCPv6 IA_NA, and NDRA.
To configure the pool to be used for prefix delegation:
Specifying the Delegated Address-Assignment Pool to Be Used for DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation
You can explicitly specify which address pool the BNG uses to assign IPv6 prefixes for use by DHCPv6 prefix delegation. This feature enables you to identify the address pool without using RADIUS or a network match.
If the Juniper Networks IPv6-Delegated-Pool-Name VSA (26–161)
provides assigns a delegated address pool, the VSA-specified value
takes precedence over the delegated-address statement.
You can specify the local delegated address pool at the following levels:
Globally for the server at the
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 overrides]hierarchy level.For a named group of interfaces at the
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 group group-name overrides]hierarchy level.For a specific interface within a named group of interface at the
[edit system services dhcp-local-server dhcpv6 group group-name interface interface-name overrides]hierarchy level.
The following steps show only how to specify a local pool used globally by the local server.
To specify the pool to be used for prefix delegation:
