Subscriber Secure Policy Traffic Mirroring Architecture Using DTCP
Figure 1 shows the architecture of the DTCP-initiated subscriber secure policy mirroring environment.
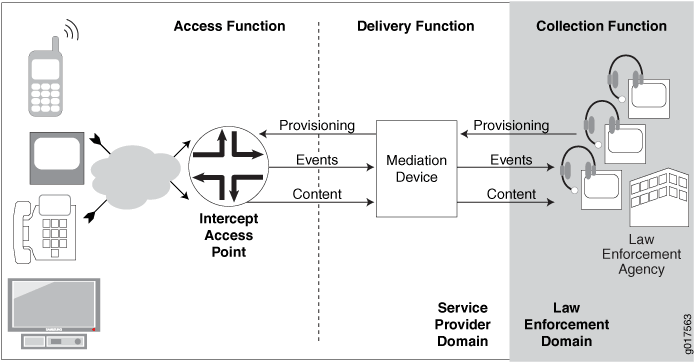
Table 1 describes the functions and components of a DTCP-initiated subscriber secure policy traffic mirroring environment.
|
Function or Component |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Collection function |
The collection function is responsible for collecting intercepted content and identifying information from the delivery function. The collection function is the responsibility of the law-enforcement agency (LEA). |
|
Delivery function |
The delivery function delivers information that it receives from the access function to the collection function. The delivery function is performed by the mediation device. |
|
Access function |
The access function has access to the intercept target’s traffic content and intercept-related events. It is responsible for collecting this information and sending it to the delivery function. The access function is performed by intercept access points (IAPs). |
|
Events |
Intercept-related events, such as login or logout events or mirroring session activation or deactivation. The router sends the events to the mediation device in SNMP traps. |
|
LEA |
Law enforcement agency. The LEA provides intercept targets to the service provider who provisions the mediation device. |
|
Mediation device |
The mediation device receives provisioning information from the LEA, and it uses the information to send provisioning information to the IAP (the router). The mediation device also receives intercept-related events and intercepted content from the router, and delivers the events and content to the LEA. |
|
IAP |
Intercept access point. In a subscriber access network the Juniper Networks router is the IAP. Using subscriber secure policies, the IAP intercepts traffic to and from the subscriber whose traffic is being mirrored. It encapsulates the intercepted content in a packet header and delivers it to the mediation device, while also sending the traffic to the intended destination. The IAP also sends intercept-related events to the mediation device using SNMP traps. |
