Example: Dynamic Endpoint Tunneling Configuration
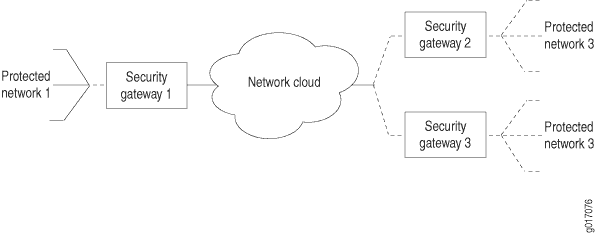
Figure 1 shows a local network N-1 located behind security gateway SG-1. SG-1 is a Juniper Networks router terminating dynamic peer endpoints. The tunnel termination address on SG-1 is 10.7.7.2 and the local network address is 172.16.1.0/24.
A remote peer router obtains addresses from an ISP pool and runs RFC-compliant IKE. Remote network N-2 has address 172.16.2.0/24 and is located behind security gateway SG-2 with tunnel termination address 10.7.7.1.
On Router SG-1, configure an IKE access profile to accept proposals from SG-2. Apply the interface identifier from the access profile to the inside services interface and apply the IKE access profile itself to the IPSec next-hop style service set.
Router SG-1
[edit]
access {
profile ike_access {
client * { # Accepts proposals from specified peers that use the preshared key.
ike {
allowed-proxy-pair local 10.255.14.63/32 remote 10.255.14.64/32;
pre-shared-key ascii-text "$ABC123"; # SECRET-DATA
interface-id test_id; # Apply this ID to the inside services interfaces.
}
}
}
}
interfaces {
fe-0/0/0 {
description "Connection to the local network";
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 172.16.1.1/24;
}
}
}
so-1/0/0 {
description "Connection to SG-2";
no-keepalives;
encapsulation cisco-hdlc;
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.7.7.2/30;
}
}
}
sp-3/3/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
unit 3 {
dial-options {
ipsec-interface-id test_id; # Accepts dynamic endpoint tunnels.
shared;
}
service-domain inside;
}
unit 4 {
family inet;
service-domain outside;
}
}
}
services {
service-set dynamic_nh_ss { # Create a next-hop service set
next-hop-service { # for the dynamic endpoint tunnels.
inside-service-interface sp-3/3/0.3;
outside-service-interface sp-3/3/0.4;
}
ipsec-vpn-options {
local-gateway 10.7.7.2;
ike-access-profile ike_access; # Apply the IKE access profile here.
}
}
}
Verifying Your Work
To verify proper operation of a dynamic endpoint tunnel configured on the AS PIC, use the following command:
show services ipsec-vpn ipsec security-associations (detail)
The following section shows output from this command used with the configuration example. The dynamically created rule _junos_ appears in the output, as well as the establishment of the inbound and outbound dynamically created tunnels.
user@router> show services ipsec-vpn ipsec security-associations detail
Service set: dynamic_nh_ss
Rule: _junos_ , Term: tunnel4, Tunnel index: 4
Local gateway: 10.7.7.2, Remote gateway: 10.7.7.1
Local identity: ipv4(any:0,[0..3]=10.255.14.63)
Remote identity: ipv4(any:0,[0..3]=10.255.14.64)
Direction: inbound , SPI: 428111023, AUX-SPI: 0
Mode: tunnel, Type: dynamic, State: Installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha1-96, Encryption: 3des-cbc
Soft lifetime: Expires in 27660 seconds
Hard lifetime: Expires in 27750 seconds
Anti-replay service: Enabled, Replay window size: 64
Direction: outbound , SPI: 4035429231, AUX-SPI: 0
Mode: tunnel, Type: dynamic, State: Installed
Protocol: ESP, Authentication: hmac-sha1-96, Encryption: 3des-cbc
Soft lifetime: Expires in 27660 seconds
Hard lifetime: Expires in 27750 seconds
Anti-replay service: Enabled, Replay window size: 64
