Understanding How Firewall Filters Control Packet Flows
A switch supports firewall filters that allow you to control flows of data packets and local packets. Data packets transit a switch as they are forwarded from a source to a destination. Local packets are destined for or sent by a Routing Engine (they do not transit a switch). Local packets usually contain routing protocol data, data for IP services such as Telnet or SSH, or data for administrative protocols such as the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP).
Firewall filters affect packet flows entering into or exiting from a switch as follows:
-
Ingress firewall filters affect the flow of data packets that are received on switch interfaces. When a switch receives a data packet, the Packet Forwarding Engine in the system that contains the ingress interface determines where to forward the packet by looking in its Layer 2 or Layer 3 forwarding table for the best route to the destination. Data packets are forwarded to an egress interface. Locally destined packets are forwarded to the Routing Engine.
-
Egress firewall filters affect data packets that are transiting a switch but do not affect packets sent by the Routing Engine. These filters are applied by the Packet Forwarding Engine in the system that contains the egress interface.
On some QFX platforms which use PTX codebase, such as QFX10002-60C for example, there is support for firewall filter inspection of RE-based outgoing traffic.
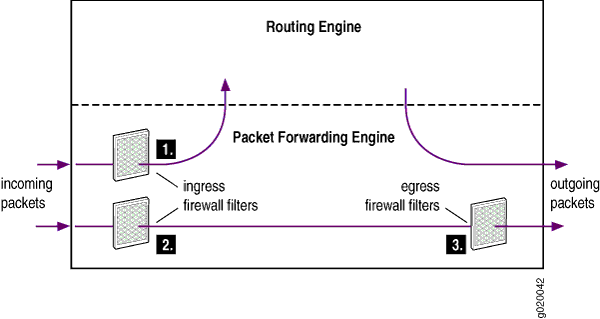
Figure 1 illustrates the application of ingress and egress firewall filters to control the flow of packets through a switch:
-
Ingress firewall filter applied to locally destined packets that are received on switch interfaces and are destined for the Routing Engine.
-
Ingress firewall filter applied to data packets that are received on switch interfaces and will transit the switch.
-
Egress firewall filter applied to data packets that are transiting the switch.