ON THIS PAGE
Example: Configure Ethernet CFM on Physical Interfaces
This example shows the configuration of Ethernet connectivity fault management (CFM) on physical interfaces.
Requirements
This example uses the following hardware and software components:
-
Any supported Junos OS.
Overview
CFM can be used to monitor the physical link between two routers. This functionality is similar to that supported by the IEEE 802.3ah LFM protocol.
The configurations in this example are only partial examples of complete and functional router configurations. Do not copy these configurations and use them directly on an actual system.
Configuration
In the following example, two routers (Router 1 and Router 2) are connected by a point-to-point Gigabit Ethernet link. The link between these two routers is monitored using CFM. This is shown in Figure 1. The single boundary is a “down mep” in CFM terminology.
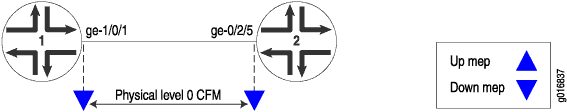
To configure Ethernet CFM on physical interfaces, perform these tasks:
CLI Quick Configuration
Router 1
Configure the interface and CFM:
[edit]
interfaces ge-1/0/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
protocols {
oam {
ethernet {
connectivity-fault-management {
maintenance-domain private {
level 0;
maintenance-association private-ma {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 100 {
interface ge-1/0/1;
direction down;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
The configuration on Router 2 mirrors that on Router 1, with the exception of the mep-id.
Router 2
Configure the interface and CFM:
[edit]
interfaces ge-0/2/5 {
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
protocols {
oam {
ethernet {
connectivity-fault-management {
maintenance-domain private {
level 0;
maintenance-association private-ma {
continuity-check {
interval 1s;
}
mep 200 {
interface ge-0/2/5;
direction down;
auto-discovery;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
To verify that the physical interface is configured correctly
for CFM, use the show interface command. To verify the
CFM configuration, use one or more of the show oam ethernet connectivity-fault-management commands listed in the CLI Explorer.
