Understand Ethernet OAM Connectivity Fault Management for Switches
Use Feature Explorer to confirm platform and release support for specific features.
Review the Platform-Specific OAM CFM Behavior section for notes related to your platform.
The IEEE 802.1ag specification provides for Ethernet connectivity fault management (CFM). CFM monitors Ethernet networks that might comprise one or more service instances for network-compromising connectivity faults.
The major features of CFM are:
-
Fault monitoring using the continuity check protocol. This is a neighbor discovery and health check protocol that discovers and maintains adjacencies at the VLAN level.
-
Path discovery and fault verification using the linktrace protocol.
-
Fault isolation using the loopback protocol.
CFM partitions the service network into various administrative domains. For example, operators, providers, and customers might be part of different administrative domains. Each administrative domain is mapped into one maintenance domain providing enough information to perform its own management, thus avoiding security breaches and making end-to-end monitoring possible.
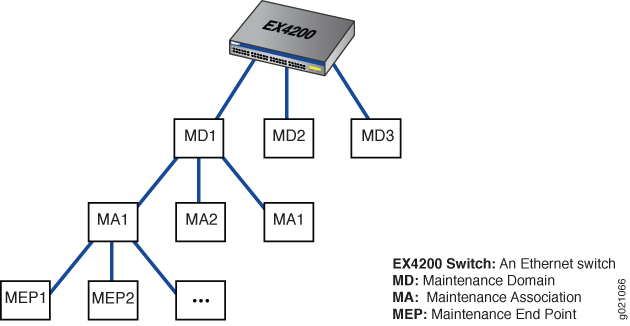
In a CFM maintenance domain, each service instance is called a maintenance association. A maintenance association can be thought of as a full mesh of maintenance association endpoints (MEPs) having similar characteristics. MEPs are active CFM entities generating and responding to CFM protocol messages. There is also a maintenance intermediate point (MIP), which is a CFM entity similar to the MEP, but more passive (MIPs only respond to CFM messages).
Each maintenance domain is associated with a maintenance domain level from 0 through 7. Level allocation is based on the network hierarchy, where outer domains are assigned a higher level than the inner domains. Configure customer end points to have the highest maintenance domain level. The maintenance domain level is a mandatory parameter that indicates the nesting relationships between various maintenance domains. The level is embedded in each CFM frame. CFM messages within a given level are processed by MEPs at that same level.
To enable CFM on an Ethernet interface, you must configure maintenance domains, maintenance associations, and maintenance association end points (MEPs). Figure 1 shows the relationships among maintenance domains, maintenance association end points (MEPs), and maintenance intermediate points (MIPs) configured on a switch.
Platform-Specific OAM CFM Behavior
Use Feature Explorer to confirm platform and release support for specific features.
Use the following table to review platform-specific behaviors for your platform.
| Platform | Difference |
|---|---|
|
EX Series |
|
|
QFX Series |
|
