MPLS Configuration on IRB Interfaces
MPLS Support on IRB Interfaces
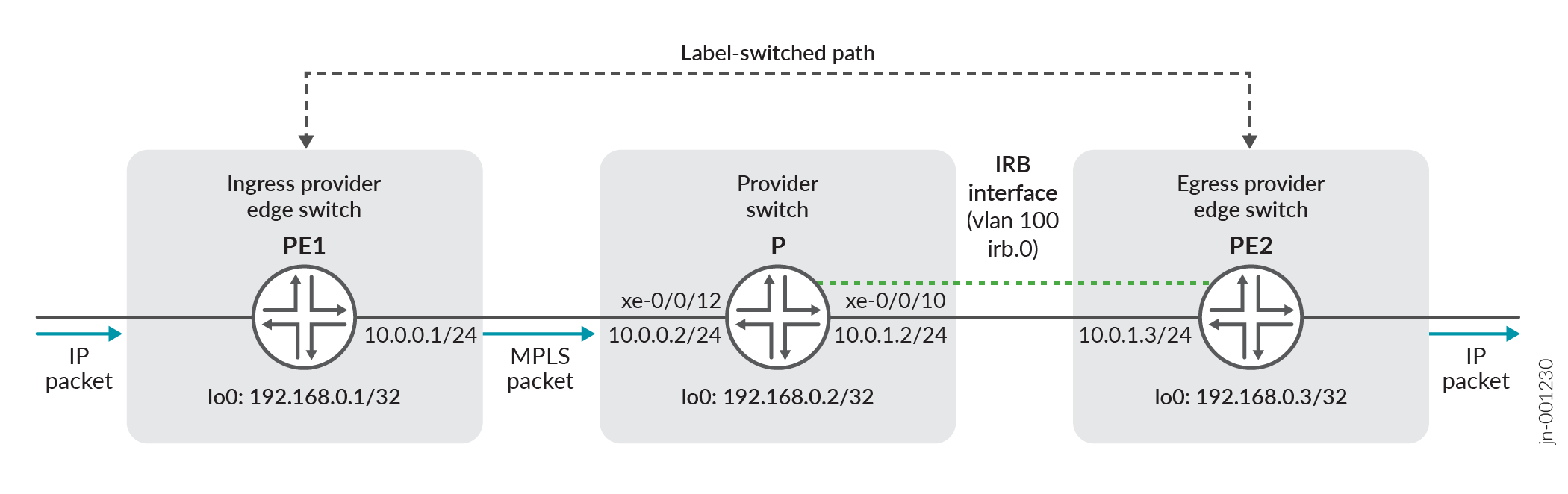
With the introduction of MPLS support for IRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging) interfaces on the MX240, MX304, MX480, MX960, MX10004, and MX10008 platforms, you can seamlessly integrate routing and switching over an MPLS core. This feature allows for efficient traffic forwarding, supporting VLAN-based routing (IRB) while maintaining MPLS label switching. By leveraging this enhancement, your network can optimize the path selection process, reduce forwarding delays, and ensure compatibility with complex MPLS topologies.
This feature addresses prior limitations where MPLS encapsulation was not supported on IRB interfaces. With this update, IRB interfaces can encapsulate MPLS labels, ensuring interoperability and full MPLS functionality.
MPLS over IRB Interfaces Overview
With MPLS support on IRB interfaces, you can seamlessly integrate Layer 2 and Layer 3 forwarding over an MPLS-enabled network. This enhancement allows IRB interfaces to encapsulate MPLS labels, enabling efficient label switching alongside VLAN-based routing. You can now bridge and route VLAN traffic while taking full advantage of MPLS features such as Label Switched Paths (LSPs) and end-to-end traffic engineering.
This feature is particularly valuable in scenarios such as Data Center Interconnect (DCI), where VLANs need to be transported over an MPLS backbone, or when you require a unified approach to bridging and routing. By enabling MPLS on IRB interfaces, you reduce operational complexity, enhance scalability, and ensure compatibility with modern MPLS-based architectures.
Using Junos OS, you can configure IRB interfaces to support MPLS for both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic. This involves defining IRB units for routing VLANs, applying MPLS family settings, and integrating these interfaces with your MPLS configuration. Once configured, the IRB interfaces perform MPLS encapsulation, allowing seamless forwarding across MPLS-enabled devices.
The MPLS over IRB feature enables you to use IRB interfaces for routing between VLANs while simultaneously leveraging MPLS for efficient label switching. This integration is crucial in scenarios requiring VLAN segmentation over MPLS networks, such as Data Center Interconnect (DCI) stitching.
CE1 --- PE1 (IRB) --- P --- PE2 (IRB) --- CE2
-
PE1: Ingress provider edge with IRB.638 for VLAN 638.
-
P: Core switch performing MPLS label swaps.
-
PE2: Egress provider edge.
Benefits of Configuring MPLS over IRB Interfaces
-
Simplified Interconnectivity: Integrates routing and bridging with MPLS for streamlined operations.
-
Enhanced Flexibility: Supports both unicast and multicast traffic.
-
Reduced Overhead: Utilizes MPLS label switching to minimize routing table lookups.
-
Data Center Interconnect (DCI): Simplifies interconnecting geographically dispersed data centers over MPLS while maintaining VLAN segregation.
-
Multicast and Unicast Traffic Support: Seamlessly handle both traffic types using MPLS-enabled IRB interfaces.
By implementing this feature, you enhance your network's ability to efficiently route and switch traffic across MPLS cores while preserving the flexibility of VLAN routing.
Configure MPLS on IRB Interfaces
Verification Commands
Verify MPLS Configuration:
show mpls interface show mpls interface detail
Check IRB Interface:
show interfaces irb.638
