Retrieve a Previous (Rollback) Configuration Using the Junos XML Protocol
A Junos XML protocol client application can retrieve a previously committed configuration by referencing its rollback index or its configuration revision identifier.
A Junos XML protocol client application can request a previously committed (rollback) configuration from a device running Junos OS or a device running Junos OS Evolved. The client can retrieve the configuration by referencing the configuration’s rollback index or its configuration revision identifier.
Understanding the Rollback Index and Configuration Revision Identifier
Junos OS and Junos OS Evolved store a copy of the most recently committed configuration and up to 49 previous configurations, depending on the platform. When you successfully commit a configuration, Junos OS assigns that configuration a unique configuration revision identifier. The configuration is also associated with a rollback index, where the most recently committed configuration has rollback index 0. Whereas the rollback index for a previously committed configuration increments with each commit, the configuration revision ID remains static for the same configuration. When you request a previously committed configuration, you can reference the configuration by its current rollback index or its static configuration revision ID.
A client application can view a device's commit history to see the configuration
revision identifier and the rollback index for committed configurations. To view the
commit history and include the configuration revision IDs, a client application
executes the <get-commit-information> RPC with the
<include-configuration-revision/> child element.
<rpc>
<get-commit-information>
<include-configuration-revision/>
</get-commit-information>
</rpc>
The server returns XML output equivalent to the show system commit
include-configuration-revision operational mode command.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="http://xml.juniper.net/junos/20.4R1/junos"> <commit-information> <commit-history> <sequence-number>0</sequence-number> <user>admin</user> <client>netconf</client> <date-time junos:seconds="1605236880">2020-11-12 19:08:00 PST</date-time> <configuration-revision>re0-1605236878-333</configuration-revision> </commit-history> <commit-history> <sequence-number>1</sequence-number> <user>user1</user> <client>netconf</client> <date-time junos:seconds="1605228068">2020-11-12 16:41:08 PST</date-time> <configuration-revision>re0-1605228066-332</configuration-revision> </commit-history> </commit-information> <commit-history> <sequence-number>2</sequence-number> <user>admin</user> <client>cli</client> <date-time junos:seconds="1605226205">2020-11-12 16:10:05 PST</date-time> <configuration-revision>re0-1605226203-331</configuration-revision> </commit-history> ... </rpc-reply>
If you already know the configuration revision ID for a particular configuration, you can determine the mapping between the ID and the current rollback index. Remember that the configuration revision ID for a given committed configuration is static whereas the rollback index increments with each commit.
To determine the rollback number corresponding to a specific configuration revision
ID, execute the <get-configuration-by-revision> RPC, specify
the revision identifier, and include the empty
<rollback-number/> tag.
<rpc>
<get-configuration-by-revision>
<revision-string>re0-1605226203-331</revision-string>
<rollback-number/>
</get-configuration-by-revision>
</rpc>The device returns the rollback index currently associated with that configuration revision identifier.
<rpc-reply> <configuration-revision-information> <rollback-number>2</rollback-number> </configuration-revision-information> </rpc-reply>
Similarly, to determine the configuration revision identifier currently associated
with a specific rollback number, execute the
<get-rollback-information> RPC, specify the rollback
index, and include the empty <configuration-revision/>
tag.
<rpc>
<get-rollback-information>
<rollback>2</rollback>
<configuration-revision/>
</get-rollback-information>
</rpc>
The device returns the configuration revision identifier currently associated with that rollback index.
<rpc-reply> <rollback-information> <configuration-revision>re0-1605226203-331</configuration-revision> </rollback-information>
Retrieve a Configuration Using the Rollback Number
A Junos XML protocol client application can retrieve a previously committed
(rollback) configuration using the rollback index. The client application
executes the <get-rollback-information> RPC with the
<rollback> element. The
<rollback> element specifies the rollback index of
the previous configuration to retrieve. The value can be from 0 (zero, for the
most recently committed configuration) through one less than the number of
stored previous configurations (maximum is 49). This operation is equivalent to
the show system rollback operational mode command.
To
request Junos XML-tagged output, which is the default, the application either
includes the <format>xml</format> element or omits
the <format> element.
<rpc>
<get-rollback-information>
<rollback>index-number</rollback>
</get-rollback-information>
</rpc>
The Junos XML protocol server encloses its response in
<rpc-reply>,
<rollback-information>, and
<configuration> elements. The
<load-success/> tag is a side effect of the
implementation and does not affect the
results.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<rollback-information>
<load-success/>
<configuration attributes>
<!-- tag elements for the complete previous configuration -->
</configuration>
</rollback-information>
</rpc-reply>To request formatted ASCII output, the
application includes the <format>text</format>
element.
<rpc>
<get-rollback-information>
<rollback>index-number</rollback>
<format>text</format>
</get-rollback-information>
</rpc>
The Junos XML protocol server encloses its response in
<rpc-reply>,
<rollback-information>,
<configuration-information>, and
<configuration-output> elements.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<rollback-information>
<load-success/>
<configuration-information>
<configuration-output>
<!-- formatted ASCII text for the complete previous configuration -->
</configuration-output>
</configuration-information>
</rollback-information>
</rpc-reply>To request JSON
format, the application includes the
<format>json</format> element.
<rpc>
<get-rollback-information>
<rollback>index-number</rollback>
<format>json</format>
</get-rollback-information>
</rpc>
The
Junos XML protocol server encloses its response in
<rpc-reply>,
<rollback-information>,
<configuration-information>, and
<json-output>
elements.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="URL">
<rollback-information>
<load-success/>
<configuration-information>
<json-output>
<!-- JSON data for the complete previous configuration -->
</json-output>
</configuration-information>
</rollback-information>
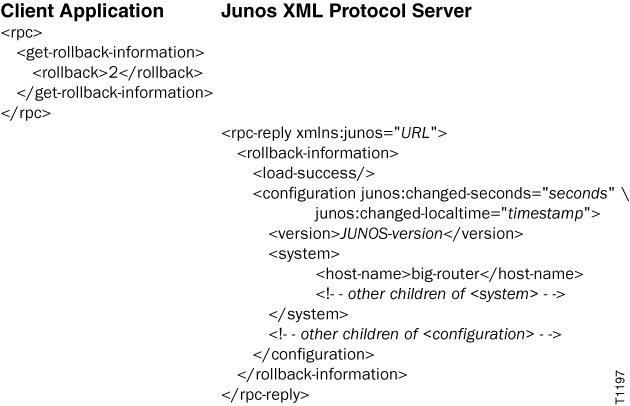
</rpc-reply>The following example requests Junos XML-tagged output for the rollback configuration that has an index of 2. In actual output, the JUNOS-version variable has a value such as 24.4R1, which is the initial version of Junos OS Release 24.4.
Retrieve a Configuration Using the Configuration Revision Identifier
When you successfully commit a configuration, Junos OS assigns that configuration
a unique configuration revision identifier. Starting in Junos OS Release 20.4R1,
a Junos XML protocol client application can use the
<get-configuration-by-revision> RPC to retrieve the
configuration by its configuration revision identifier. The
<revision-string> value specifies the configuration
revision ID. For example:
<rpc>
<get-configuration-by-revision>
<revision-string>re0-1605226203-331</revision-string>
</get-configuration-by-revision>
</rpc>The server returns the requested configuration enclosed in the
<configuration-revision-information> element.
<rpc-reply xmlns:junos="http://xml.juniper.net/junos/20.4R1/junos"> <configuration-revision-information> <load-success/> <configuration junos:changed-seconds="1605226201" junos:changed-localtime="2020-11-12 16:10:01 PST"> ... </configuration> </configuration-revision-information> </rpc-reply>
By default, the <get-configuration-by-revision> RPC
returns the configuration in XML format. To return the configuration as text or
JSON format, include the <format> element and specify
text or json.
<rpc>
<get-configuration-by-revision>
<revision-string>re0-1605226203-331</revision-string>
<format>text</format>
</get-configuration-by-revision>
</rpc><rpc>
<get-configuration-by-revision>
<revision-string>re0-1605226203-331</revision-string>
<format>json</format>
</get-configuration-by-revision>
</rpc>