ON THIS PAGE
Example: Advertising Label-Switched Paths into IS-IS
This example shows how to advertise label-switched paths (LSPs) into IS-IS as point-to-point links (sometimes referred to as forwarding adjacencies) so that the LSPs can be used in SPF calculations. The advertisement contains a local address (the from address of the LSP), a remote address (the to address of the LSP), and a metric.
Requirements
No special configuration beyond device initialization is required before configuring this example.
Overview
Figure 1 shows the topology used in this example.
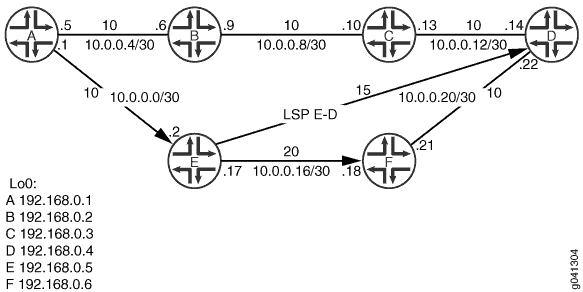
The example shows how to configure the LSP from Device E to Device D and then advertise this path through IS-IS. The configuration is verified by performing a traceroute operation from Device A to Device D and making sure that the LSP is used for forwarding.
CLI Quick Configuration shows the configuration for all of the devices in Figure 1. The section #configuration442__isis-lsp-advertise-step-by-step describes the steps on Device E.
Configuration
Procedure
CLI Quick Configuration
To quickly configure
this example, copy the following commands, paste them into a text
file, remove any line breaks, change any details necessary to match
your network configuration, and then copy and paste the commands into
the CLI at the [edit] hierarchy level.
Device A
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.1/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.5/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.1/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0001.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.4 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.5 level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.5 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.1 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Device B
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.6/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.9/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.2/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0002.00 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.2
Device C
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.10/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.13/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.3/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0003.00 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.3
Device D
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.14/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.22/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.4/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0004.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path E-D to 192.168.0.5 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.4 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.14 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set protocols isis label-switched-path E-D level 2 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.4 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Device E
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0005.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls label-switched-path E-D to 192.168.0.4 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.4 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 2 metric 20 set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set protocols isis label-switched-path E-D level 2 metric 15 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.5 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Device F
set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.18/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.21/30 set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso set interfaces fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.6/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0006.00 set protocols rsvp interface lo0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols rsvp interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/0.0 set protocols mpls interface fe-1/2/1.0 set protocols bgp group int type internal set protocols bgp group int local-address 192.168.0.6 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.1 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.5 set protocols bgp group int neighbor 192.168.0.4 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 2 metric 10 set protocols isis interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable set protocols isis interface lo0.0 set routing-options router-id 192.168.0.6 set routing-options autonomous-system 1
Step-by-Step Procedure
The following example requires you to navigate various levels in the configuration hierarchy. For information about navigating the CLI, see Using the CLI Editor in Configuration Mode in the CLI User Guide.
To advertise LSPs into IS-IS:
Configure the interfaces.
[edit interfaces] user@E# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.2/30 user@E# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family iso user@E# set fe-1/2/0 unit 0 family mpls user@E# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family inet address 10.0.0.17/30 user@E# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family iso user@E# set fe-1/2/1 unit 0 family mpls user@E# set lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.0.5/32 user@E# set lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0002.0192.0168.0005.00
Enable a signaling protocol on the interfaces.
[edit protocols rsvp] user@E# set interface lo0.0 user@E# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@E# set interface fe-1/2/1.0
Enable MPLS on the interfaces.
[edit protocols mpls] user@E# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 user@E# set interface fe-1/2/1.0
Configure the LSP.
Make sure that you configure the reverse LSP on the endpoint, in this case on Device D.
[edit protocols mpls] user@E# set label-switched-path E-D to 192.168.0.4
Configure internal BGP (IBGP) peering among the devices that must run MPLS.
[edit protocols bgp group int] user@E# set type internal user@E# set local-address 192.168.0.5 user@E# set neighbor 192.168.0.6 user@E# set neighbor 192.168.0.1 user@E# set neighbor 192.168.0.4
Enable IS-IS on the interfaces, and set the link metric.
IS-IS Level 1 and Level 2 are enabled when you include the interface at
[edit protocols isis]. By disabling Level 1, you are in effect creating a Level 2 IS-IS interface.[edit protocols isis] user@E# set interface fe-1/2/0.0 level 1 disable user@E# set interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 1 disable user@E# set interface fe-1/2/1.0 level 2 metric 20 user@E# set interface lo0.0
Advertise the LSP through IS-IS.
Make sure that you advertise the LSP on the endpoint, in this case on Device D.
[edit protocols isis] user@E# set label-switched-path E-D level 2 metric 15
Configure the router ID and the autonomous system (AS) number.
[edit routing-options] user@E# set router-id 192.168.0.5 user@E# set autonomous-system 1
Results
From configuration mode, confirm your configuration
by entering the show interfaces, show protocols, and show routing-options commands. If the output does
not display the intended configuration, repeat the instructions in
this example to correct the configuration.
user@E# show interfaces
fe-1/2/0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.2/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
fe-1/2/1 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 10.0.0.17/30;
}
family iso;
family mpls;
}
}
lo0 {
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.0.5/32;
}
family iso {
address 49.0002.0192.0168.0005.00;
}
}
}
user@E# show protocols
rsvp {
interface lo0.0;
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
}
mpls {
label-switched-path E-D {
to 192.168.0.4;
}
interface fe-1/2/0.0;
interface fe-1/2/1.0;
}
bgp {
group int {
type internal;
local-address 192.168.0.5;
neighbor 192.168.0.6;
neighbor 192.168.0.1;
neighbor 192.168.0.4;
}
}
isis {
interface fe-1/2/0.0 {
level 1 disable;
}
interface fe-1/2/1.0 {
level 1 disable;
level 2 metric 20;
}
interface lo0.0;
label-switched-path E-D {
level 2 metric 15;
}
}
user@E# show routing-options
router-id 192.168.0.5;
autonomous-system 1;
If you are done configuring the device, enter commit from configuration mode.
Verification
Confirm that the configuration is working properly.
Verifying the IS-IS Neighbor
Purpose
Verify that another neighbor is listed and is reachable over the LSP. The interface field indicates the name of the LSP.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show isis adjacency
detail command.
user@E> show isis adjacency detail D Interface: E-D, Level: 2, State: One-way, Expires in 0 secs Priority: 0, Up/Down transitions: 1, Last transition: 1d 00:34:58 ago Circuit type: 3, Speaks: IP Topologies: Unicast Restart capable: No, Adjacency advertisement: Advertise IP addresses: 192.168.0.4 F Interface: fe-1/2/1.0, Level: 2, State: Up, Expires in 7 secs Priority: 64, Up/Down transitions: 1, Last transition: 1d 01:16:22 ago Circuit type: 2, Speaks: IP, IPv6, MAC address: 0:5:85:8f:c8:bd Topologies: Unicast Restart capable: Yes, Adjacency advertisement: Advertise LAN id: F.02, IP addresses: 10.0.0.18 A Interface: fe-1/2/0.0, Level: 2, State: Up, Expires in 20 secs Priority: 64, Up/Down transitions: 1, Last transition: 1d 01:17:20 ago Circuit type: 2, Speaks: IP, IPv6, MAC address: 0:5:85:8f:c8:bc Topologies: Unicast Restart capable: Yes, Adjacency advertisement: Advertise LAN id: E.02, IP addresses: 10.0.0.1
Meaning
As expected, Interface: E-D is shown in the output, and the state is shown as One-way.
Checking the IS-IS SPF Calculations
Purpose
Verify that the LSP is being used in the SPF calculations.
Action
From operational mode, enter the show isis spf
brief command.
user@E> show isis spf brief IS-IS level 1 SPF results: Node Metric Interface NH Via SNPA E.00 0 1 nodes IS-IS level 2 SPF results: Node Metric Interface NH Via SNPA C.02 30 fe-1/2/0.0 IPV4 A 0:5:85:8f:c8:bc C.00 25 fe-1/2/1.0 LSP E-D D.03 25 fe-1/2/1.0 LSP E-D D.02 25 fe-1/2/1.0 LSP E-D F.00 20 fe-1/2/1.0 IPV4 F 0:5:85:8f:c8:bd B.00 20 fe-1/2/0.0 IPV4 A 0:5:85:8f:c8:bc B.02 20 fe-1/2/0.0 IPV4 A 0:5:85:8f:c8:bc D.00 15 fe-1/2/1.0 LSP E-D A.00 10 fe-1/2/0.0 IPV4 A 0:5:85:8f:c8:bc E.02 10 E.00 0 11 nodes
Meaning
As expected, the SPF results include the LSP, E-D.
Checking the Forwarding Path
Purpose
Verify that a traceroute operation from Device A to Device D uses the LSP.
Action
user@A> traceroute 192.168.0.4
traceroute to 192.168.0.4 (192.168.0.4), 30 hops max, 40 byte packets
1 10.0.0.2 (10.0.0.2) 1.092 ms 1.034 ms 1.174 ms
2 10.0.0.18 (10.0.0.18) 1.435 ms 2.062 ms 2.232 ms
MPLS Label=299792 CoS=0 TTL=1 S=1
3 bb04-cclab-lo0.spglab.juniper.net (192.168.0.4) 2.286 ms 1.432 ms 1.354 msMeaning
The output shows that the LSP is used.
