IS-IS Fast Reroute Convergence
Subsecond service restoration is a key requirement for MPLS and native IP-based network service providers. There are many ways to achieve fast reroute with a sub-optimal next-hop to reach the destination, such as loop-free alternate and remote loop-free alternate. In these cases, IGP downloads the primary and backup next-hop beforehand in the forwarding information base (FIB). A packet forwarding engine (PFE) performs a local repair when the primary next-hop loses its reachability to a given destination. Since the PFE already has an alternative path to reach its destination, subsecond restoration is possible. If the destination is reachable through equal-cost multi-path (ECMP), only the primary path is downloaded to the FIB. If a few ECMP links go down below the required bandwidth for a destination, fast reroute convergence is not possible.
To resolve this, the best ECMP links are grouped as a unilist of primary next-hops to reach the destination, and the sub-optimal ECMP links are grouped as a unilist of backup next-hops to reach the destination. If the bandwidth of the primary next-hops falls below the desired bandwidth, the PFE does a local repair and switches traffic to backup unilist next-hops. This is yet another backup, where the backup path is computed and installed in FIB for ECMP paths. Here, a set of best ECMP links is grouped as primary next-hops to reach the destination, and a set of sub-optimal ECMP links is grouped as backup next-hops to reach the destination. If the bandwidth of the primary next-hops falls below the desired bandwidth due to link failure on the primary group, the PFE should perform a local repair and switch the traffic to backup next-hops.
In the following topology, R1 has three ECMP links to D1 via R2. R1 also has three sub-optimal ECMP links to D1 via R3 and R2. All ECMP links L1, L2, and L3 can be placed under one group; a primary group, and also group sub-optimal ECMP links L3, L4, and L5 under another group, a backup group.
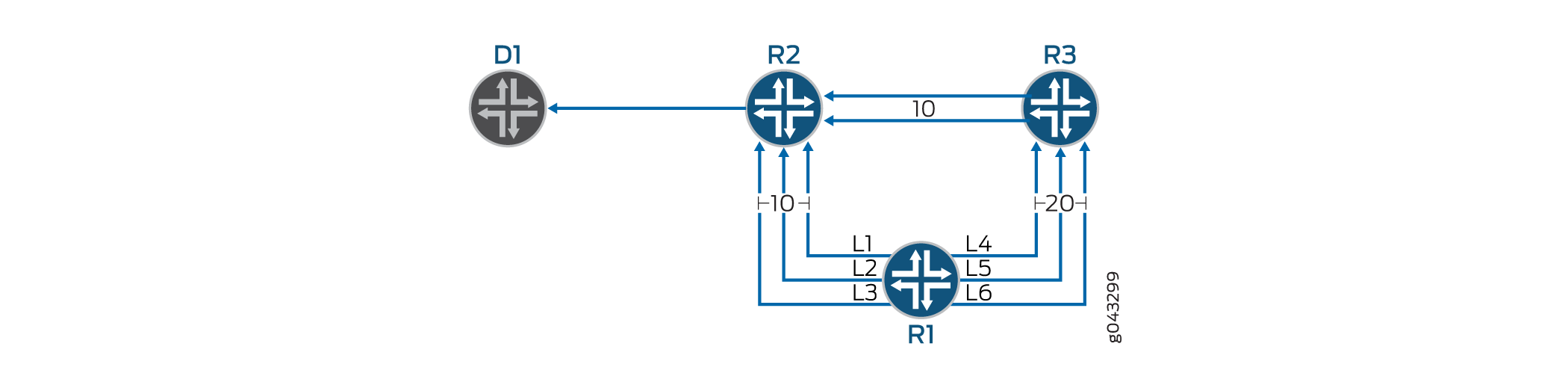
IS-IS calculates the shortest path using the shortest-path-first (SPF) algorithm and downloads primary next-hops with appropriate weight in FIB. IS-IS also calculates backup next-hops and downloads them to FIB with appropriate weight.
Backup next-hop weight will always be greater than the primary next-hop weight. If a link from the primary group goes down, the PFE performs a local repair and modifies the weight of the next-hops. The PFE forwards traffic to the destination with the least weight next-hops to achieve sub-millisecond convergence. IS-IS runs SPF and comes up with a set of primary and backup next-hops. IS-IS then updates the FIB with the updated next hops. PFE resumes traffic forwarding on new next-hops without any traffic loss.
