Understanding Dial-Out Telemetry
Dial-out telemetry is a method used in network monitoring where the device (for example, a router) initiates the connection to send data to a collector. In dial-out telemetry, the device "dials out" to the collector, which means it sends the initial SYN packet to establish the connection. This approach simplifies network management because it avoids the need to open ports for inbound management traffic.
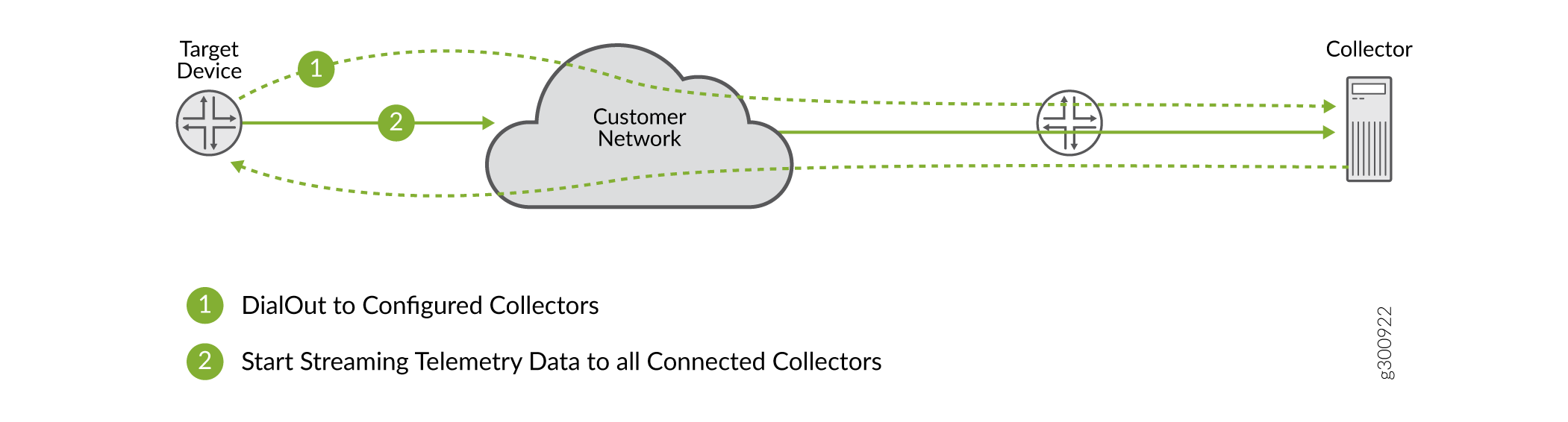
Starting with Junos OS Release 22.4R1, Junos Telemetry supports remote gRPC dial-out functionality on ACX Series routers, MX Series routers, PTX Series routers, and QFX Series switches. With gRPC dial-out, the target device (server) initiates a gRPC session with the collector (client). The target device (server) initiates a gRPC session with the collector (client) by using gRPC dial-out. When the session is established, the target streams the telemetry data specified by the sensor-group subscription to the collector. In contrast, the gRPC network management interface (gNMI) dial-in method that requires the collector to initiate a connection to the target device.
The gRPC dial-out method simplifies the streaming of telemetry statistics. Configuring the target device to stream statistics and export them to a collector IP address removes the burden of access being placed on the collector (client).
Junos Telemetry supports dial-out connections over UDP in Protobuf Compact Format (Juniper
Proprietary) and Protobuf Structured Format. It also supports dial-out connections over TCP in
Protobuf Structured Format. Starting with Junos OS Release 25.4R1, you can configure the
dial-out type using the CLI option export-profile (Junos Telemetry Interface) at the [edit
services analytics export-profile name] hierarchy.
Benefits of Using Dial-Out Telemetry
-
Reduces target device exposure to threats outside the topology.
-
Simplifies access to a target device. The dial-in method requires a collector to complete a series of complex firewall configurations to access the target device. Where as, the dial-out mechanism does not have such requirements.
-
Collectors can be stateless. They do not need to initiate a session, and they simply listen, subscribe, and store collected data.
-
Supports mutual encryption for heightened security.
