gNOI Diagnostic (Diag) Service
Use the gNOI diagnostic (Diag) service to test the reliability of a link
between two devices.
Overview
Use the Diag service RPCs to perform a bit error rate test (BERT) on a pair of
connected ports. The Diag service proto definition file is located
at https://github.com/openconfig/gnoi/blob/master/diag/diag.proto.
A BERT, also known as a pseudo-random binary sequence (PRBS) test, tests the reliability of a link. The StartBERT() gNOI RPC initiates a bidirectional BERT on a pair of connected physical interfaces. The devices exchange a set pattern of 1s and 0s across the link. The devices compare the received message to the sent message and count the number of errors. The lower the number of errors, the higher the quality of the link.
You must run a gNOI BERT on both sides of the link so the devices can compare results. The link you are testing goes down during the BERT and comes back up after the BERT ends. However, if one of the devices where you are running the BERT reboots, the link remains down unless you stop the BERT on the other device.
You can choose the test pattern from several predetermined types. BERT or PRBS test patterns are titled in the form PRBSx, where x is a number. Junos devices support the following test patterns for gNOI BERTs:
- PRBS7
- PRBS9
- PRBS15
- PRBS23
- PRBS31
You must give each gNOI BERT a unique operation ID. The RPCs to start the BERT, stop the BERT, and get the BERT results are linked by the BERT operation ID. When you run a new BERT, you must change the operation ID to a new string. Because the RPCs identify each BERT by its operation ID, you can run multiple BERTs on different interfaces with the same ID.
The device keeps the results of the last 5 BERT operations. However, the saved BERT results are not persistent. They are lost if the system reboots.
To view the result of a specific saved BERT operation, send the GetBERTResultRequest message for the desired BERT operation ID and set the result_from_all_ports field to False. To view all request results for different IDs, set the result_from_all_ports field in the GetBERTResultRequest message to True.
When you run the GetBERTResult() RPC on a device, the RPC displays the number of mismatched bits that particular device detected during the BERT. Since the RPC does not have pass or fail criteria configured, it is up to the user to evaluate the results. You might see a high number of errors for several reasons, including:
- The quality of the link is poor.
- One of the devices went offline during the BERT.
- The BERT only ran on one device.
- The BERT did not start and stop on both devices simultaneously.
To avoid the last error, we recommend sending the StartBERT() RPC to both devices simultaneously. If you start a BERT on one device before the other, the first device doesn't receive a response until the BERT starts on the other device. The first device records the lack of response as mismatched bits. The first device continues to report errors until BERT starts on the second device. If it is not possible to start the BERT simultaneously, we recommend running the GetBERTResult() RPC on the device that started the BERT last. Since the BERT was already running on the first device, the second device should not report any false missing bits.
Supported RPCs
| RPC | Description | Introduced in Release |
|---|---|---|
StartBERT()
|
Start a BERT on a set of ports. Junos devices support the following PRBS patterns for gNOI BERTs:
|
Junos OS Evolved 22.2R1 |
StopBert()
|
Stop an already in-progress BERT on a set of ports. |
Junos OS Evolved 22.2R1 |
GetBERTResult()
|
Get BERT results during the BERT or after it completes. |
Junos OS Evolved 22.2R1 |
Network Device Configuration
Before you begin:
- Configure gRPC services on the network device as described in Configure gRPC Services.
- Configure the network management system to support gNOI operations as described in Configure gNOI Services.
- For the link you want to run the BERT on, configure the server and peer interfaces speeds to match. BERT only runs if the interface speeds match.
Example: Run a BERT
While a BERT is in progress on an interface, the physical link on that interface goes down.
After you have configured the gNOI client and server, you are ready to write and execute your application to run the BERT. In this example, the client executes the gnoi_bert_client.py Python application to test a link between the server and a peer device. The gnoi_bert_client.py application can start the BERT, stop the BERT, or get the BERT results depending on the arguments.
First, the client uses gnoi_bert_client.py to send the StartBERT() RPC to start the BERT on the server and the peer. While the BERT is running, the server and peer exchange BERT test packets across the link between the et-1/0/2 and et-1/0/3 interfaces.
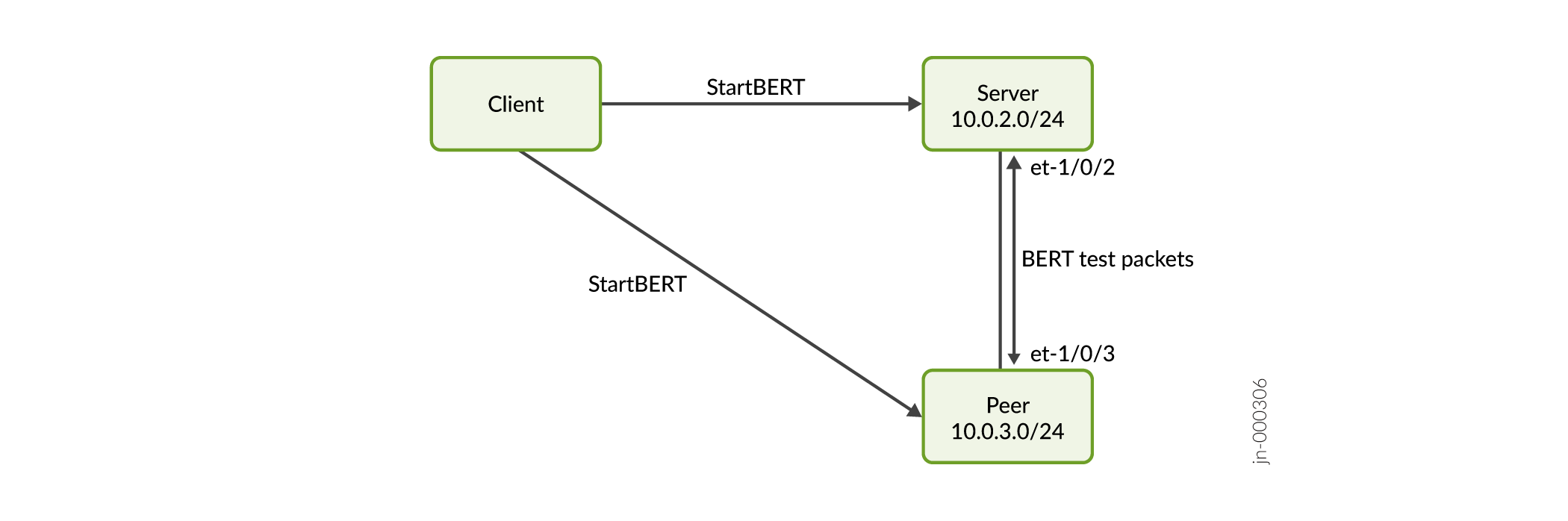
The BERT ends after the set time expires. Then the client executes the application a second time with the GetBERTResult() RPC to get the BERT results from the server.
The parameters for the StartBERTRequest message are stored in the input_bert_start.json JSON file. This file specifies that the BERT should run for 60 seconds using PRBS pattern 31. The parameters for the GetBERTResultRequest message are stored in the input_bert_get.json JSON file. The result_from_all_ports field is set to False, so the GetBERTResult() RPC only retrieves the result for this particular BERT from this port. The BERT operation ID is BERT-operation id 1 in both JSON files.
The application imports the grpc_channel module to establish the channel. The grpc_channel module is described in Configure gNOI Services. The application file and JSON files are presented here.
gnoi_bert_client.py
"""gRPC gNOI BERT utility.""" from __future__ import print_function import argparse import json import sys import logging from getpass import getpass import diag_pb2 import diag_pb2_grpc from grpc_channel import grpc_authenticate_channel_mutual from google.protobuf.json_format import MessageToJson from google.protobuf.json_format import ParseDict def get_args(parser): # Main arguments parser.add_argument('--server', dest='server', type=str, default='localhost', help='Server IP or name. Default is localhost') parser.add_argument('--port', dest='port', nargs='?', type=int, default=32767, help='The server port. Default is 32767') parser.add_argument('--client_key', dest='client_key', type=str, default='', help='Full path of the client private key. Default ""') parser.add_argument('--client_cert', dest='client_cert', type=str, default='', help='Full path of the client certificate. Default ""') parser.add_argument('--root_ca_cert', dest='root_ca_cert', required=True, type=str, help='Full path of the Root CA certificate.') parser.add_argument('--user_id', dest='user_id', required=True, type=str, help='User ID for RPC call credentials.') # BERT arguments parser.add_argument('--input_file', dest='input_file', type=str, default=None, help='Input JSON file to convert to a Message Object. Default NULL string') parser.add_argument('--output_file', dest='output_file', type=str, default=None, help='Output file. Default NULL string') parser.add_argument('--message', dest='message', type=str, default=None, help='The type of Message Object. Must correspond to input file JSON. Default NULL string') args = parser.parse_args() return args def check_inputs(args): # Check each of the default=None arguments if args.server is None: print('\nFAIL: --server is not passed in\n') return False if args.port is None: print('\nFAIL: server port (--port) is not passed in\n') return False if args.input_file is None: print('\nFAIL: --input_file is not passed in\n') return False if args.output_file is None: print('\nFAIL: --output_file is not passed in\n') return False if args.message is None: print('\nFAIL: --message is not passed in\n') return False return True # Create a dictionary where top-level keys match what is passed in via args.message # The values are pointers to the relevant classes and method names needed to build/send message objects MESSAGE_RELATED_OBJECTS = { 'StartBERTRequest': { 'msg_type': diag_pb2.StartBERTRequest, 'grpc': diag_pb2_grpc.DiagStub, 'method': 'StartBERT' }, 'StopBERTRequest': { 'msg_type': diag_pb2.StopBERTRequest, 'grpc': diag_pb2_grpc.DiagStub, 'method': 'StopBERT' }, 'GetBERTResultRequest': { 'msg_type': diag_pb2.GetBERTResultRequest, 'grpc': diag_pb2_grpc.DiagStub, 'method': 'GetBERTResult' } } def send_rpc(channel, metadata, args): if not check_inputs(args): print('\nFAIL: One of the inputs was not as expected.\n') return False print('\nMessage Type is {}'.format(args.message)) # Message objects to send msg_object_list = [] with open(args.input_file) as json_file: user_input = json.load(json_file) # Choose the Request Message Object type based on the --message type passed request_message = MESSAGE_RELATED_OBJECTS[args.message]['msg_type']() # Convert the dictionary to the type of message object specified by request_message try: msg_object_list.append(ParseDict(user_input, request_message)) except Exception as error: print('\n\nError:\n{}'.format(error), file=sys.stderr) raise # Assemble callable object to use for sending, e.g. diag_pb2_grpc.DiagStub(channel).StartBERT method = MESSAGE_RELATED_OBJECTS[args.message]['method'] send_message = getattr( MESSAGE_RELATED_OBJECTS[args.message]['grpc'](channel), method) # send the Request Object(s) for msg_object in msg_object_list: resp = send_message(msg_object, metadata=metadata) print('\n\nResponse:\n{}'.format(resp)) print('=================================') resp_json = MessageToJson(resp) print('\n\nResponse JSON:\n{}'.format(resp_json)) with open(args.output_file, 'w') as data: data.write(str(resp_json)) return True def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() args = get_args(parser) grpc_server_password = getpass("gRPC server password for executing RPCs: ") metadata = [('username', args.user_id), ('password', grpc_server_password)] try: # Establish grpc channel to network device channel = grpc_authenticate_channel_mutual( args.server, args.port, args.root_ca_cert, args.client_key, args.client_cert) response = send_rpc(channel, metadata, args) except Exception as e: logging.error('Received error: %s', e) print(e) if __name__ == '__main__': logging.basicConfig(filename='gnoi-testing.log', format='%(asctime)s %(levelname)-8s %(message)s', level=logging.INFO, datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') main()
input_bert_start.json
{
"bert_operation_id": "BERT-operation id 1",
"per_port_requests": [
{
"interface": {
"origin": "origin",
"elem": [
{"name": "interfaces"},
{"name": "interface", "key": {"name": "et-1/0/2"}}
]
},
"prbs_polynomial": "PRBS_POLYNOMIAL_PRBS31",
"test_duration_in_secs": "60"
}
]
}input_bert_get.json
{
"bert_operation_id": "BERT-operation id 1",
"result_from_all_ports": false,
"per_port_requests": [
{
"interface": {
"origin": "origin",
"elem": [
{"name": "interfaces"},
{"name": "interface", "key": {"name": "et-1/0/2"}}
]
}
}
]
}Execute the Application
-
From the client, run the
gnoi_bert_client.pyapplication to start the BERT on the peer (not shown). Then run thegnoi_bert_client.pyapplication to start the BERT on the server (shown below). To start the BERT, setmessagetoStartBERTRequestand setinput_fileto the input_bert_start.json file path. For each device, the input file should specify the interface tested on that device. TheBERT_STATUS_OKstatus indicates that the BERT started successfully.lab@gnoi-client:~/src/gnoi/proto$ python3 gnoi_bert_client.py --server 10.0.2.1 --port 32767 --root_ca_cert /etc/pki/certs/serverRootCA.crt --client_key /home/lab/certs/client.key --client_cert /home/lab/certs/client.crt --user_id gnoi-user --message StartBERTRequest --input_file diag/input_bert_start.json --output_file diag/output/bert-start-resp1.json gRPC server password for executing RPCs: Message Type is StartBERTRequest Response: bert_operation_id: "BERT-operation id 1" per_port_responses { interface { origin: "origin" elem { name: "interfaces" } elem { name: "interface" key { key: "name" value: "et-1/0/2" } } } status: BERT_STATUS_OK } ================================= Response JSON: { "bertOperationId": "BERT-operation id 1", "perPortResponses": [ { "interface": { "origin": "origin", "elem": [ { "name": "interfaces" }, { "name": "interface", "key": { "name": "et-1/0/2" } } ] }, "status": "BERT_STATUS_OK" } ] } -
(Optional) While you are running the BERT, use the
show interfacescommand on the server or peer device to view the ongoing BERT results. When a BERT is running, the PRBS Mode isEnabled. The output in this example has been truncated for clarity.user@server> show interfaces et-1/0/2 Physical interface: et-1/0/2, Enabled, Physical link is Down Interface index: 1018, SNMP ifIndex: 534 [...] PRBS Mode : Enabled PRBS Pattern : 31 PRBS Statistics Lane 0 : Error Bits : 0 Total Bits : 200000000000 Monitored Seconds : 8 Lane 1 : Error Bits : 0 Total Bits : 200000000000 Monitored Seconds : 8 Lane 2 : Error Bits : 0 Total Bits : 200000000000 Monitored Seconds : 8 Lane 3 : Error Bits : 0 Total Bits : 200000000000 Monitored Seconds : 8 Interface transmit statistics: Disabled Link Degrade : Link Monitoring : Disable [...] -
After the BERT is finished, run the
gnoi_bert_client.pyapplication again withmessageset toGetBERTResultRequestandinput_fileset to the input_bert_get.json file path to get the results of the test. In this example, the BERT found zero errors during a one-minute test.lab@gnoi-client:~/src/gnoi/proto$ python3 gnoi_bert_client.py --server 10.0.2.1 --port 32767 --root_ca_cert /etc/pki/certs/serverRootCA.crt --client_key /home/lab/certs/client.key --client_cert /home/lab/certs/client.crt --user_id gnoi-user --message GetBERTResultRequest --input_file diag/input_bert_get.json --output_file diag/output/bert-get-resp1.json gRPC server password for executing RPCs: Message Type is GetBERTResultRequest Response: per_port_responses { interface { origin: "origin" elem { name: "interfaces" } elem { name: "interface" key { key: "name" value: "et-1/0/2" } } } status: BERT_STATUS_OK bert_operation_id: "BERT-operation id 1" prbs_polynomial: PRBS_POLYNOMIAL_PRBS31 last_bert_start_timestamp: 1652379568178 last_bert_get_result_timestamp: 1652379688037 peer_lock_established: true error_count_per_minute: 0 total_errors: 0 } ================================= Response JSON: { "perPortResponses": [ { "interface": { "origin": "origin", "elem": [ { "name": "interfaces" }, { "name": "interface", "key": { "name": "et-1/0/2" } } ] }, "status": "BERT_STATUS_OK", "bertOperationId": "BERT-operation id 1", "prbsPolynomial": "PRBS_POLYNOMIAL_PRBS31", "lastBertStartTimestamp": "1652379568178", "lastBertGetResultTimestamp": "1652379688037", "peerLockEstablished": true, "errorCountPerMinute": [ 0 ], "totalErrors": "0" } ] }The BERT completed successfully and shows the quality of the link is good.
