Example: Configuring Flow Collection
Figure 1 shows the path traveled by monitored traffic as it passes through the router. Packets arrive at input interfaces so-0/1/0, so-3/0/0, and so-3/1/0. The raw packets are directed into a filter-based forwarding routing instance and processed into cflowd records by the monitoring services interfaces mo-7/1/0, mo-7/2/0, and mo-7/3/0. The cflowd records are compressed into files at the flow collector interfaces cp-6/0/0 and cp-7/0/0 and sent to the FTP server for analysis. Finally, a mandatory class-of-service (CoS) configuration is applied to export channels 0 and 1 on the flow collector interfaces to manage the outgoing processed files.
Figure 1: Flow Collector Interface Topology
Diagram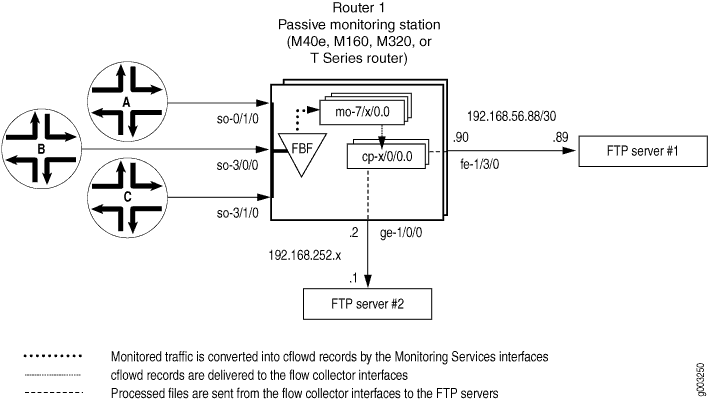

[edit]
chassis {
fpc 6 {
pic 0 {
monitoring-services {
application flow-collector; # This converts a Monitoring Services II or
# Multiservices 400 PIC into a flow collector interface.
}
}
}
fpc 7 {
pic 0 {
monitoring-services {
application flow-collector; # This converts a Monitoring Services II or
# Multiservices 400 PIC into a flow collector interface.
}
}
}
}
interfaces {
cp-6/0/0 {
unit 0 { # Logical interface .0 on a flow collector interface is export
family inet { # channel 0 and sends records to the FTP server.
filter {
output cp-ftp; # Apply the CoS filter here.
}
address 10.0.0.1/32 {
destination 10.0.0.2;
}
}
}
unit 1 { # Logical interface .1 on a flow collector interface is export
family inet {# channel 1 and sends records to the FTP server.
filter {
output cp-ftp; # Apply the CoS filter here.
}
address 10.1.1.1/32 {
destination 10.1.1.2;
}
}
}
unit 2 { # Logical interface .2 on a flow collector interface is the flow
family inet { # receive channel that communicates with the Routing Engine.
address 10.2.2.1/32 { # Do not apply a CoS filter on logical interface .2.
destination 10.2.2.2;
}
}
}
}
cp-7/0/0 {
unit 0 {# Logical interface .0 on a flow collector interface is export
family inet {# channel 0 and sends records to the FTP server.
filter {
output cp-ftp;# Apply the CoS filter here.
}
address 10.3.3.1/32 {
destination 10.3.3.2;
}
}
}
unit 1 {# Logical interface .1 on a flow collector interface is export
family inet {# channel 1 and sends records to the FTP server.
filter {
output cp-ftp;# Apply the CoS filter here.
}
address 10.4.4.1/32 {
destination 10.4.4.2;
}
}
}
unit 2 {# Logical interface .2 on a flow collector interface is the flow
family inet {# receive channel that communicates with the Routing Engine.
address 10.5.5.1/32 {# Do not apply a CoS filter on logical interface .2.
destination 10.5.5.2;
}
}
}
}
fe-1/3/0 { # This is the exit interface leading to the first FTP server.
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.56.90/30;
}
}
}
ge-1/0/0 { # This is the exit interface leading to the second FTP server.
unit 0 {
family inet {
address 192.168.252.2/24;
}
}
}
mo-7/1/0 { # This is the first interface that creates cflowd records.
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
mo-7/2/0 { # This is the second interface that creates cflowd records.
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
mo-7/3/0 { # This is the third interface that creates cflowd records.
unit 0 {
family inet;
}
}
so-0/1/0 { # This is the first input interface that receives traffic to be monitored.
encapsulation ppp;
unit 0 {
passive-monitor-mode; # This allows the interface to be passively monitored.
family inet {
filter {
input catch; # The filter-based forwarding filter is applied here.
}
}
}
}
so-3/0/0 { # This is the second interface that receives traffic to be monitored.
encapsulation ppp;
unit 0 {
passive-monitor-mode; # This allows the interface to be passively monitored.
family inet {
filter {
input catch; # The filter-based forwarding filter is applied here.
}
}
}
}
so-3/1/0 { # This is the third interface that receives traffic to be monitored.
encapsulation ppp;
unit 0 {
passive-monitor-mode; # This allows the interface to be passively monitored.
family inet {
filter {
input catch; # The filter-based forwarding filter is applied here.
}
}
}
}
forwarding-options {
monitoring group1 {# Always define your monitoring group here.
family inet {
output {
export-format cflowd-version-5;
flow-active-timeout 60;
flow-inactive-timeout 15;
flow-export-destination collector-pic; # Sends records to the flow collector.
interface mo-7/1/0.0 {
source-address 192.168.252.2;
}
interface mo-7/2/0.0 {
source-address 192.168.252.2;
}
interface mo-7/3/0.0 {
source-address 192.168.252.2;
}
}
}
}
firewall {
family inet {
filter cp-ftp { # This filter provides CoS for flow collector interface traffic.
term t1 {
then forwarding-class expedited-forwarding;
}
}
}
filter catch { # This firewall filter sends incoming traffic into the
interface-specific;# filter-based forwarding routing instance.
term def {
then {
count counter;
routing-instance fbf_instance;
}
}
}
}
routing-options {
interface-routes {
rib-group inet common;
}
rib-groups {
common {
import-rib [inet.0 fbf_instance.inet.0];
}
}
forwarding-table {
export pplb;
}
}
policy-options {
policy-statement pplb {
then {
load-balance per-packet;
}
}
}
routing-instances {
fbf_instance { # This instance sends traffic to the monitoring services interface.
instance-type forwarding;
routing-options {
static {
route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop mo-7/1/0.0;
}
}
}
}
class-of-service { # A class-of-service configuration for the flow collector interface
interfaces { # is required for flow collector services.
cp-6/0/0 {
scheduler-map cp-map;
}
cp-7/0/0 {
scheduler-map cp-map;
}
}
}
scheduler-maps {
cp-map {
forwarding-class best-effort scheduler Q0;
forwarding-class expedited-forwarding scheduler Q1;
forwarding-class network-control scheduler Q3;
}
}
schedulers {
Q0 {
transmit-rate remainder;
buffer-size percent 90;
}
Q1 {
transmit-rate percent 5;
buffer-size percent 5;
priority strict-high;
}
Q3 {
transmit-rate percent 5;
buffer-size percent 5;
}
}
services {
flow-collector { # Define properties for flow collector interfaces here.
analyzer-address 10.10.10.1; # This is the IP address of the analyzer.
analyzer-id server1; # This helps to identify the analyzer.
retry 3; # Maximum number of attempts by the PIC to send a file transfer log.
retry-delay 30; # The time interval between attempts to send a file transfer log.
destinations { # This defines the FTP servers that receive flow collector output.
"ftp://user@192.168.56.89//tmp/collect1/" { # The primary FTP server.
password "$ABC123"; # SECRET-DATA
}
"ftp://user@192.168.252.1//tmp/collect2/" { # The secondary FTP server.
password "$ABC123"; # SECRET-DATA
}
}
file-specification { # Define sets of flow collector characteristics here.
def-spec {
name-format "default-allInt-0-%D_%T-%I_%N.bcp.bi.gz";
data-format flow-compressed; # The default compressed output format.
} # When no overrides are specified, a collector uses default transfer values.
f1 {
name-format "cFlowd-py69Ni69-0-%D_%T-%I_%N.bcp.bi.gz";
data-format flow-compressed; # The default compressed output format.
transfer timeout 1800 record-level 1000000; # Here are configured values.
}
}
interface-map { # Allows you to map interfaces to flow collector interfaces.
file-specification def-spec; # Flows generated for default traffic are sent to the
collector cp-7/0/0; # default flow collector interface "cp-7/0/0".
so-0/1/0.0 { # Flows generated for the so-0/1/0 interface are sent
collector cp-6/0/0; # to cp-6/0/0, and the file-specification used is
} # "default."
so-3/0/0.0 { # Flows generated for the so-3/0/0 interface are sent
file-specification f1; # to cp-6/0/0, and the file-specification used is "f1."
collector cp-6/0/0;
}
so-3/1/0.0; # Because no settings are defined, flows generated for this
} # interface use interface cp-7/0/0 and the default file specification.
transfer-log-archive { # Sends flow collector interface log files to an FTP server.
filename-prefix so_3_0_0_log;
maximum-age 15;
archive-sites {
"ftp://user@192.168.56.89//tmp/transfers/" {
password "$ABC123";
}
}
]
}
}
