Understanding Using Probes for Real-Time Performance Monitoring on ACX, MX, and PTX Series Routers and EX and QFX Switches
Real-time performance monitoring (RPM) enables you to configure active probes to track and monitor traffic. Probes collect packets per destination and per application, including PING Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets, User Datagram Protocol and Transmission Control Protocol (UDP/TCP) packets with user-configured ports, user-configured Differentiated Services code point (DSCP) type-of-service (ToS) packets, and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) packets. RPM provides Management Information Base (MIB) support with extensions for RFC 2925, Definitions of Managed Objects for Remote Ping, Traceroute, and Lookup Operations. For more information about SNMP MIBs that Juniper supports, see SNMP MIB Explorer.
Overview
When RPM is configured on a device, the device calculates network performance based on packet response time, jitter, and packet loss. The device gathers RPM statistics by sending out probes to a specified probe target, identified by an IP address. When the target receives a probe, it generates responses that are received by the device. A test can contain multiple probes. The probe type specifies the packet and protocol contents of the probe. You can use the history of the most recent 50 probes to analyze trends in your network and predict future needs.
Use Feature Explorer: Real-time Performance Monitoring and Feature Explorer: RPM and TWAMP to confirm platform and release support.
With probes, you can monitor:
-
Average round-trip time
-
Jitter of the round-trip time—The difference between the minimum and maximum round-trip time
-
Maximum round-trip time
-
Minimum round-trip time
-
Standard deviation of the round-trip time (Junos OS only)
One-way measurements for ICMP timestamp probes include:
-
Minimum, maximum, standard deviation, and jitter measurements for egress and ingress times
-
Number of probe responses received
-
Number of probes sent
-
Percentage of lost probes
You can set thresholds to trigger SNMP traps when the values are exceeded. You can configure the following RPM thresholds:
-
Ingress/egress delay
-
Jitter
-
Round-trip time
-
Standard deviation (Junos OS only)
-
Successive lost probes
-
Total lost probes (per test)
You can also configure CoS classifiers and prioritization of RPM packets over regular data
packets received on an input interface with the dscp-code-points
configuration statement.
Hardware Timestamps
To account for latency or jitter in the communication of probe messages, you can enable timestamping of the probe packets (hardware timestamps). If hardware timestamps are not configured, you are using software-based timestamps. Timestamps that are generated at the software level are less accurate than they would have been with hardware timestamps.
Use Feature Explorer: Hardware timestamping of RPM probe messages, Feature Explorer: RPM hardware timestamps with routed VLAN interfaces, and Feature Explorer: RPM and TWAMP hardware-timestamp and RTT measurement to confirm platform and release support for this feature.
RPM hardware timestamping is supported on Junos OS only, with some restrictions:
-
ACX Series routers: The ACX710 and ACX5448 Series routers are the only ACX routers running Junos OS that support the
hardware-timestampstatement configuration. This support started in Junos OS Release 22.3R1. -
EX Series switches: EX Series switches support hardware timestamps for UDP and ICMP probes. EX Series switches do not support hardware timestamps for HTTP or TCP probes.
On the EX4300 switch, RPM timestamping is performed in the software. The RPM probes at the requester and responder devices are timestamped in the Packet Forwarding Engine instead of the Junos OS process (rmopd) that runs on the Routing Engine. This timestamping method is referred to as pseudo-hardware timestamping.
-
QFX Series switches: QFX Series switches do not support hardware timestamps.
You can timestamp the following RPM probes to improve the measurement of latency or jitter.
-
ICMP ping
-
ICMP ping timestamp
-
UDP ping
-
UDP ping timestamp
icmp-ping is the default probe type on devices running Junos OS.
The probe packets are time-stamped with the times at which they are sent and received at both the source and destination endpoints.
You should configure the requester (the RPM client) with hardware timestamps (see Figure 1) to get more meaningful results than you would get without the timestamps. The responder (the RPM server) does not need to be configured to support hardware timestamps. If the responder supports hardware timestamps, it timestamps the RPM probes. If the responder does not support hardware timestamps, RPM can only report round-trip measurements that include the processing time on the responder.
On the EX4300 switch, you must configure the switch as both the requester (the RPM client) and the responder (the RPM server) to timestamp the RPM packet.
Figure 1 shows the timestamps:
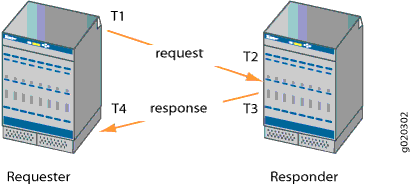
-
T1 is the time the packet leaves the requester port.
-
T2 is the time the responder receives the packet.
-
T3 is the time the responder sends the response.
-
T4 is the time the requester receives the response.
The round-trip time is T4 – T1 – (T3 – T2). If the responder does not support hardware timestamps, then the round-trip time is (T4 – T1), and thus includes the processing time of the responder.
You can use RPM probes to find the following time measurements:
-
Minimum round-trip time
-
Maximum round-trip time
-
Average round-trip time
-
Standard deviation of the round-trip time
-
Jitter of the round-trip time—Difference between the minimum and maximum round-trip time
The RPM feature provides a configuration option to set one-way hardware timestamps. Use one-way timestamps when you want information about one-way time, rather than round-trip times, for packets to traverse the network between the requester and the responder. As shown in Figure 1, one-way timestamps represent the time T2 – T1 and the time from T4 – T3. Use one-way timestamps when you want to gather information about delay in each direction and to find egress and ingress jitter values.
For correct one-way measurement, the clocks of the requester and responder must be synchronized. If the clocks are not synchronized, one-way jitter measurements and calculations can include significant variations, in some cases orders of magnitude greater than the round-trip times.
When you enable one-way timestamps in a probe, the following one-way measurements are reported:
-
Minimum, maximum, standard deviation, and jitter measurements for egress and ingress times
-
Number of probes sent
-
Number of probe responses received
-
Percentage of lost probes
Junos OS Support
- Probe configuration and results
- IPsec and GRE tunnel support
- RPM-tracked static routes
- RPM and related timestamp support on MPC, MS-MIC/MPC, and Routing Engine
Probe configuration and results
In Junos OS, probe configuration and probe results are supported by both the command-line
interface (CLI) and SNMP. You set the probe options in the test
test-name statement at the [edit services rpm
probe owner] hierarchy level. You use the show
services rpm probe-results command to view the results of the most recent RPM
probes.
Limitations for EX Series and QFX Series switches:
-
Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol (TWAMP) is not supported on QFX switches.
-
The switches do not support user-configured class-of-service (CoS) classifiers or prioritization of RPM packets over regular data packets received on an input interface.
-
Timestamps:
-
If the responder does not support hardware timestamps, RPM can only report the round-trip measurements and cannot calculate round-trip jitter. (QFX Series switches do not support hardware timestamps.)
-
EX Series switches do not support hardware timestamps or pseudo-hardware timestamps for HTTP and TCP probes.
-
Timestamps apply only to IPv4 traffic.
-
In-Service Software Upgrades (ISSU) and Nonstop Software Upgrades (NSSU) do not support pseudo-hardware timestamps.
-
To specify the packet and protocol contents of the probe, include the
probe-type statement at the [edit services rpm probe
owner test test-name] hierarchy level.
The following probe types are supported:
-
http-get—Sends a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) get request to a target URL. -
http-metadata-get—Sends an HTTP get request for metadata to a target URL. -
icmp-ping—Sends ICMP echo requests to a target address. -
icmp-ping-timestamp—Sends ICMP timestamp requests to a target address. -
tcp-ping—Sends TCP packets to a target. -
udp-ping—Sends UDP packets to a target. -
udp-ping-timestamp—Sends UDP timestamp requests to a target address.
IPsec and GRE tunnel support
You can apply RPM to IPsec tunnels and GRE tunnels for PIC-based and Routing Engine-based RPM clients and servers if you are using MS-MPCs or MS-MICs. Packet Forwarding Engine-based RPM is not supported for IPsec tunnels. Support of RPM on IPSec tunnels enables service level agreement (SLA) monitoring for traffic transported in IPSec tunnels.
RPM is not supported on logical systems.
Use Feature Explorer: RPM support for IPsec and GRE tunnels to confirm platform and release support for this feature.
RPM-tracked static routes
In Junos OS, you can also configure RPM services to determine automatically whether a
path exists between a host device and its configured BGP neighbors. You can view the
results of the discovery using an SNMP client. Results are stored in
pingResultsTable, jnxPingResultsTable,
jnxPingProbeHistoryTable, and
pingProbeHistoryTable.
Use Feature Explorer: Activating or deactivating static routes on the basis of RPM test results, Feature Explorer: Tracking static RPM routes across multiple next hops, and Feature Explorer: An extension to the RPM-tracked static routes to confirm platform and release support for this feature.
For those devices that support this feature, you can use RPM probes to detect link
status, and change the preferred-route state on the basis of the probe results.
RPM-tracked routes can be IPv4 or IPv6, and support a single IPv4 or IPv6 next hop. You
configure this feature with the rpm-tracking statement at the
[edit routing-options] or [edit routing-instances
routing-options] hierarchy level. For example, RPM probes can be sent to an IP
address to determine if the link is up, and if so, the software installs a static route in
the route table. RPM-tracked static routes are installed with preference 1 and thus are
preferred over any existing static routes for the same prefix. For those devices that
support multiple next hops, you can track up to 16 next hops for each IPv4 or IPv6
RPM-tracked static route and you can configure route preference and tag values for each
IPv4 or IPv6 destination prefix.
RPM and related timestamp support on MPC, MS-MIC/MPC, and Routing Engine
Table 1 provides information about RPM and related timestamp support on MPC, MS-MIC/MPC, and Routing Engine:
|
Feature |
Role |
IP Version |
Support (Y/N) |
Timestamp on Routing Engine |
Timestamp on MPC (hardware-timestamp) |
Timestamp on MPC (si-interface) |
Timestamp on MS-MIC/MPC (delegate-probes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RPM |
Client |
IPv4 |
Y |
Y (µsec) 2000 maximum probes |
Y (µsec) 2000 maximum probes |
N |
Y (msec) 1 million maximum probes |
|
IPv6 |
Y |
Y (µsec) 2000 maximum probes |
N |
N |
Y (msec) 1 million maximum probes |
||
|
Server |
IPv4 |
Y |
Y (µsec) 2000 maximum probes |
Y (µsec) 2000 maximum probes |
N |
Y (msec) 1 million maximum probes |
|
|
IPv6 |
Y |
Y (µsec) 2000 maximum probes |
N |
N |
Y (msec) 1 million maximum probes |
Junos OS Evolved Support
Probe configuration and results
Starting in Junos OS Evolved Release 20.1R1 for devices that support this feature, you
can configure RPM probes. For Junos OS Evolved, RPM is configured at the [edit
services monitoring rpm] hierarchy level. The scope of support is limited
to:
-
Probe generation and reception (client) as well as reflection (server) for the following RPM probe types:
-
http-get (added in Junos OS Evolved 23.4R1)
You must set the
offload-typestatement tononeto configure this probe type. -
http-metadata-get (added in Junos OS Evolved 23.4R1)
You must set the
offload-typestatement tononeto configure this probe type. -
icmp-ping
-
icmp-timestamp
-
tcp-ping (added in Junos OS Evolved 23.4R1)
You must set the
offload-typestatement tononeto configure this probe type. -
udp-ping
-
udp-timestamp
-
-
Probe history management
-
Reporting through syslog only
Starting in Junos OS Evolved Release 21.2R1, reporting through SNMP MIB objects is supported for RPM.
Use Feature Explorer: Inline RPM Services to confirm platform and release support for Junos OS Evolved.
RPM-tracked static routes
Starting in Junos OS Evolved Release 24.4R1 for devices that support this feature, we've
extended support for static route tracking to Junos OS Evolved and included Two-Way Active
Measurement Protocol (TWAMP) test support as well. You use RPM or TWAMP probes to detect
link status and to change the preferred-route state on the basis of the probe results.
Tracked static routes can be IPv4 or IPv6, and each IPv4 and IPv6 tracked static route
supports up to 16 next hops. You can also configure the metric, route preference, and tag
values for each IPv4 or IPv6 destination prefix. However, you configure this feature
differently on Junos OS Evolved devices; you configure the sla-tracking
statement at the [edit routing-options] hierarchy level. You also use a
different command, show route sla-tracking, to see information about
these routes. For Junos OS, you would configure the rpm-tracking
statement at the same hierarchy level and you would use the command show route
rpm-tracking to see information about these
routes.
Change History Table
Feature support is determined by the platform and release you are using. Use Feature Explorer to determine if a feature is supported on your platform.
sla-tracking statement at the [edit routing-options]
hierarchy level. For Junos OS, you would configure the rpm-tracking
statement at the same hierarchy level.tcp-ping, http-get, and
http-metadata-get probes for RPM.