Unified Access Control (UAC)
Learn about the use of firewall as an Infranet Enforcer in a Unified Access Control (UAC) network.
A Unified Access Control (UAC) uses the following components to secure a network and ensure that only qualified end users can access protected resources:
-
IC Series UAC Appliances—An IC Series appliance is a policy decision point in the network. It uses authentication information and policy rules to determine whether or not to provide access to individual resources on the network. You can deploy one or more IC Series appliances in your network.
-
Infranet Enforcers—An Infranet Enforcer is a policy enforcement point in the network. It receives policies from the IC Series appliance and uses the rules defined in those policies to determine whether or not to allow an endpoint access to a resource. You deploy the Infranet Enforcers in front of the servers and resources that you want to protect.
-
Infranet agents—An Infranet agent is a client-side component that runs directly on network endpoints (such as users’ computers). The agent checks that the endpoint complies to the security criteria specified in Host Checker policies and relays that compliance information to the Infranet Enforcer. The Infranet Enforcer then allows or denies the endpoint access based on the compliance results.
Unified Access Control in Junos OS
A firewall can act as an Infranet Enforcer in a UAC network. Specifically, it acts as a Layer 3 enforcement point, controlling access by using IP-based policies pushed down from the IC Series appliance. When deployed in a UAC network, an firewall is called a Junos OS Enforcer.
Benefits
-
Granularly and dynamically controls end user access based on user identity, device security state, and location information.
-
Leverages your existing network infrastructure from user authentication to access points and switches, Juniper firewalls and IDP Series appliances through an open, standards-based architecture.
How does UAC work in Junos OS Environment?
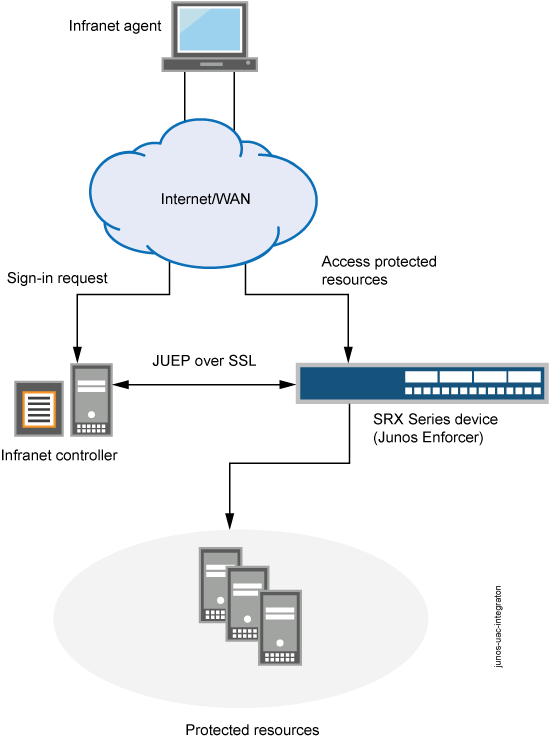
-
Set up the interfaces through which UAC traffic should enter the firewall.
-
Group interfaces with identical security requirements into zones. See Example: Creating Security Zones.
-
Create security policies to control the traffic that passes through the security zones. See Example: Configuring a Security Policy to Permit or Deny All Traffic.
Junos OS security policies enforce rules for transit traffic, defining what traffic can pass through the Juniper Networks device. The policies control traffic that enters from one zone (from-zone) and exits another (to-zone). To enable an firewall as a Junos OS Enforcer in a UAC deployment, you must:
-
Identify the source and destination zones through which UAC traffic will travel. It also needs the list of interfaces, including which zones they are in. The IC Series UAC Appliance uses the destination zone to match its own IPsec routing policies configured on IC Series appliance.
-
Identify Junos OS security policies that encompass those zones, and enable UAC for those policies.
The UAC with Junos OS security policies only supports a traditional security policy but not dynamic-application configuration. To configure UAC through a Junos OS security policy, enter the following configuration statement:
user@host# set security policies from-zone zone-name to-zone zone-name policy match then permit application-services uac-policy
Junos OS Enforcer with IC Series UAC Appliance
- What is Junos OS Enforcer with IC Series UAC appliance?
- How Junos OS Enforcer with IC Series UAC appliance works?
- What is Junos OS Enforcer with cluster of IC Series UAC appliances?
What is Junos OS Enforcer with IC Series UAC appliance?
In a Unified Access Control (UAC) network, a firewall is called as Junos OS Enforcer when it is deployed in the UAC environment. The firewall verifies the certificate which IC Series UAC appliance submits. The firewall and IC Series UAC appliance perform mutual authentication. After authentication, the IC Series UAC appliance sends user and resource access policy information to the firewall to act as the Junos OS Enforcer.
How Junos OS Enforcer with IC Series UAC appliance works?
When you configure an firewall to connect to an IC Series UAC Appliance, the firewall and the IC Series UAC appliance establish secure communications as follows:
-
If more than one IC Series device are configured as Infranet Controllers on the firewall, a round-robin algorithm determines which of the configured IC Series devices is the active Infranet Controller. The others are failover devices. If the active Infranet Controller becomes inoperative, the algorithm is reapplied to the remaining IC Series devices that are configured to establish the new active Infranet Controller.
-
The active IC Series appliance presents its server certificate to the firewall. If configured to do so, the firewall verifies the certificate. (Server certificate verification is not required; however, as an extra security measure you can verify the certificate to implement an additional layer of trust.)
-
The firewall and the IC Series appliance perform mutual authentication using the proprietary challenge-response authentication. For security reasons, the password is not included in the message sent to the IC Series appliance.
-
After successfully authenticating with the firewall, the IC Series appliance sends its user authentication and resource access policy information. The firewall uses this information to act as the Junos OS Enforcer in the UAC network.
-
Thereafter, the IC Series appliance and the Junos OS Enforcer can communicate freely with one another over the SSL connection. The communications are controlled by a proprietary protocol called Junos UAC Enforcer Protocol (JUEP).
What is Junos OS Enforcer with cluster of IC Series UAC appliances?
You can configure a Junos OS Enforcer to work with more than one IC Series UAC Appliance in a high availability configuration known as an IC Series appliance cluster. The Junos OS Enforcer communicates with only one IC Series appliance at a time; the other IC Series appliances are used for failover. If the Junos OS Enforcer cannot connect to the first IC Series appliance you added to a cluster, it tries to connect to the failed IC Series appliance again. Then it fails over to the other IC Series appliances in the cluster. It continues trying to connect to IC Series appliances in the cluster until a connection occurs.
When the Junos OS Enforcer cannot establish a connection to an Infranet Enforcer, it preserves all its existing authentication table entries and Unified Access Control (UAC) policies and takes the timeout action that you specify. Timeout actions include:
-
close—Close existing sessions and block any further traffic. This is the default option. -
no-change—Preserve existing sessions and require authentication for new sessions. -
open—Preserve existing sessions and allow new sessions access.
Once the Junos OS Enforcer can reestablish a connection to an IC Series appliance, the IC Series appliance compares the authentication table entries and UAC policies stored on the Junos OS Enforcer with the authentication table entries and policies stored on the IC Series appliance and reconciles the two as required.
The IC Series appliances configured on a Junos OS Enforcer should all be members of the same IC Series appliance cluster.
Junos OS Enforcer with IPsec
To configure an firewall to act as a Junos OS Enforcer using IPsec, you must:
-
Include the identity configured under the security IKE gateway. The identity is a string such as “gateway1.mycompany.com”, where gateway1.mycompany.com distinguishes between IKE gateways. (The identities specify which tunnel traffic is intended.)
-
Include the preshared seed. This generates the preshared key from the full identity of the remote user for Phase 1 credentials.
-
Include the RADIUS shared secret. This allows the IC Series UAC Appliance to accept RADIUS packets for extended authentication (XAuth) from the Junos OS Infranet Enforcer.
When configuring IPsec between the IC Series appliance, the Odyssey Access Client, and the firewall, you should note that the following are IKE (or Phase 1) proposal methods or protocol configurations that are supported from the IC Series appliance to the Odyssey Access Client:
-
IKE proposal:
authentication-method pre-shared-keys(you must specifypre-shared-keys) -
IKE policy:
-
mode aggressive(you must use aggressive mode) -
pre-shared-key ascii-text key(only ASCII text preshared-keys are supported)
-
-
IKE gateway: dynamic
-
hostname identity(you must specify a unique identity among gateways) -
ike-user-type group-ike-id(you must specifygroup-ike-id) -
xauth access-profile profile(you must specifyxauth)
-
The following are IPsec (or Phase 2) proposal methods or protocol configurations that are supported from the IC Series appliance to the Odyssey Access Client.
-
IPsec proposal:
protocol esp(you must specifyesp) -
IPsec VPN:
establish-tunnels immediately(you must specifyestablish-tunnels immediately)
Policy Enforcement and Endpoint Security with Junos OS Enforcer
In a Unified Access Control (UAC) environment, after an firewall becomes Junos OS Enforcer, the firewall allows or denies traffic based on Junos OS security policy. Infranet agent runs on the endpoints to secure traffic by checking UAC Host Checker policies. Based on the Host Checker compliance results, Junos OS Enforcer allows or denies the endpoint access.
Enforce Policy with Junos OS Enforcer
Once the firewall has successfully established itself as the Junos OS Enforcer, it secures traffic as follows:
-
First, the Junos OS Enforcer uses the appropriate Junos OS security policy to process the traffic. A security policy uses criteria such as the traffic’s source IP address or the time of day that the traffic was received to determine whether or not the traffic should be allowed to pass.
-
Once it determines that the traffic may pass based on the Junos OS security policy, the Junos OS Enforcer maps the traffic flow to an authentication table entry. The Junos OS Enforcer uses the source IP address of the first packet in the flow to create the mapping.
-
An authentication table entry contains the source IP address and user role(s) of a user who has already successfully established a UAC session. A user role identifies a group of users based on criteria such as type (for instance, “Engineering” or “Marketing”) or status (for instance, “Antivirus Running”). The Junos OS Enforcer determines whether to allow or deny the traffic to pass based on the authentication results stored in the appropriate authentication table entry.
-
The IC Series UAC Appliance pushes authentication table entries to the Junos OS Enforcer when the devices first connect to one another and, as necessary, throughout the session. For example, the IC Series appliance might push updated authentication table entries to the Junos OS Enforcer when the user’s computer becomes noncompliant with endpoint security policies, when you change the configuration of a user’s role, or when you disable all user accounts on the IC Series appliance in response to a security problem such as a virus on the network.
-
If the Junos OS Enforcer drops a packet because of a missing authentication table entry, the device sends a message to the IC Series appliance, which in turn may provision a new authentication table entry and send it to the Junos OS Enforcer. This process is called dynamic authentication table provisioning.
-
-
Once it determines that the traffic may pass based on the authentication table entries, the Junos OS Enforcer maps the flow to a resource. The Junos OS Enforcer uses the destination IP address specified in the flow to create the mapping. Then the device uses that resource as well as the user role specified in the authentication table entry to map the flow to a resource access policy.
-
A resource access policy specifies a particular resource to which you want to control access based on user role. For instance, you might create a resource access policy that allows only users who are members of the Engineering and Antivirus Running user roles access to the Engineering-Only server. Or you might create a resource access policy that allows members of the No Antivirus Running user role access to the Remediation server on which antivirus software is available for download.
-
The IC Series appliance pushes resource access policies to the Junos OS Enforcer when the devices first connect to one another and when you modify your resource access policy configurations on the IC Series appliance.
-
If the Junos OS Enforcer drops the packet because of a “deny” policy, the Junos OS Enforcer sends a message to the IC Series appliance, which in turn sends a message to the endpoint’s Odyssey Access Client (if available). (The IC Series appliance does not send “deny” messages to the agentless client.)
-
-
Once it determines that the traffic may pass based on the resource access policies, the Junos OS Enforcer processes the traffic using the remaining application services defined in the Junos OS policy. The Junos OS Enforcer runs the remaining services in the following order: Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDP), URL filtering, and Application Layer Gateways (ALGs).
Endpoint Security using Infranet Agent with Junos OS Enforcer
An Infranet agent helps you secure traffic on your network starting with the endpoints that initiate communications as follows:
-
The Infranet agent, which runs directly on the endpoint, checks that the endpoint is compliant with your Unified Access Control (UAC) Host Checker policies.
-
You can use a wide variety of criteria within a UAC Host Checker policy to determine compliance. For example, you can configure the Host Checker policy to confirm that the endpoint is running antivirus software or a firewall or that the endpoint is not running specific types of malware or processes.
-
The Infranet agent transmits the compliance information to the Junos OS Enforcer.
-
The Junos OS Enforcer allows or denies the endpoint access to the resources on your network based on the Host Checker compliance results.
Because the Infranet agent runs directly on the endpoint, you can use the Infranet agent to check the endpoint for security compliance at any time. For instance, when a user tries to sign into the IC Series UAC Appliance, you can require the Infranet agent to send compliance results immediately—the user will not even see the sign-in page until the Infranet agent returns positive compliance results to the IC Series appliance. You can also configure the Infranet agent to check for compliance after the user signs in or periodically during the user session.
If the endpoints running the Infranet agent have appropriate access, they will automatically send their compliance results to the IC Series appliance, and the IC Series appliance will update the authentication table entries accordingly and push them to the Junos OS Enforcer. The Junos OS Enforcer supports connections with the Odyssey Access Client and “agentless” Infranet agents.
Captive Portal with Junos OS Enforcer
In a Unified Access Control (UAC) deployment, users might not be aware that they must first sign in to the IC Series UAC Appliance for authentication and endpoint security checking before they are allowed to access a protected resource behind the Junos OS Enforcers.
To help users sign in to the IC Series appliance, you can configure the captive portal feature. For more information, see Example: Creating a Captive Portal Policy on Junos OS Enforcer. The captive portal feature allows you to configure a policy in the Junos OS Enforcer that automatically redirects HTTP traffic destined for protected resources to the IC Series appliance or to a URL configured in the Junos OS Enforcer.
You can configure a captive portal for deployments that use either source IP enforcement or IPsec enforcement, or a combination of both enforcement methods.
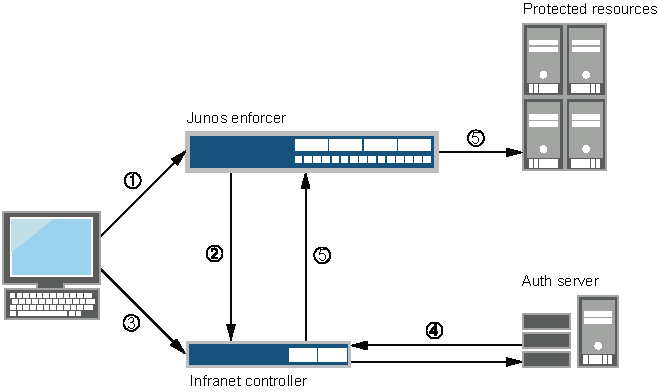
-
Users point to a protected resource using the browser.
-
The Junos OS Enforcer determines that the user is not authenticated and redirects the request to the IC Series appliance or another server.
-
Users enter their Infranet username and password to log in.
-
The IC Series appliance passes the user credentials to an authentication server.
-
After authentication, the IC Series appliance redirects the users to the protected resource they wanted to access.
By default, the Junos OS Enforcer encodes and forwards to the IC Series appliance the protected resource URL that the user entered. The IC Series appliance uses the protected resource URL to help users navigate to the protected resource. The manner in which the IC Series appliance uses the protected resource URL depends on whether or not the user’s endpoint is running the Odyssey Access Client or Pulse Secure.
If the user’s endpoint is not running the Odyssey Access Client or Pulse Secure (that is, it is in an agentless or Java agent configuration), the IC Series appliance automatically opens a new browser window and uses HTTP to access the protected resource after the user signs in.
If the endpoint is using the Odyssey Access Client, the IC Series appliance inserts a hypertext link in the webpage that automatically opens after the user signs in. The user must then click that hypertext link to access the protected resource by means of HTTP in the same browser window.
The Junos OS Enforcer supports the captive portal feature only for HTTP traffic. If you attempt to access a protected resource by using HTTPS or a non-browser application (such as an e-mail application), the Junos OS Enforcer does not redirect the traffic. When using HTTPS or a non-browser application, you must manually sign in to the IC Series appliance first before attempting to access protected resources.
