EVPN-VXLAN for AI-ML Data Centers
Overview of EVPN-VXLAN for AI-ML Data Centers
This document covers the steps necessary to configure Ethernet VPN-Virtual Extensible LAN (EVPN-VXLAN) in an artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) data center fabric.
Features and Benefits of an AI-ML Data Center
-
Improve scalability: You can enable multitenancy within the same data center using an IP fabric overlay.
-
Improve productivity: You can run different AI workloads (multiple large language models (LLMs) for different tenants) in the same data center.
-
Improve security: You can isolate L2 at the local top-of-rack (ToR) level with multiple MAC-VRF instances, or L3 at the ToR level with multiple EVPN Type 5 routing instances (IP-VRF-to-IP-VRF model). See the configuration section for examples of these use cases.
-
Reduce configuration efforts: You can extend the tenants' logical context between different ToR switches in different points of delivery (PODs) without changing the configuration of the intermediate spine or superspine devices.
Use Feature Explorer to confirm platform and release support for specific features.
Configuration
- Configuration Overview
- Topology
- How to Configure Two MAC-VRFs
- Verification
- How to Configure Two Type 5 IP-VRFs
- Verification
Configuration Overview
We'll look at two use cases relevant to this topic. The first use case is running two MAC-VRF instances on the same device in a data center. The second use case is running two EVPN Type 5 VRF instances on the same device in a data center.
Use Case #1: Two MAC-VRF instances on the same device:
-
Separate MAC-VRF instances help to isolate the AI data center tenants at the L2 level, and extend this isolation using the EVPN-VXLAN overlay.
-
The intermediate AI data center spine and superspine devices don't require provisioning each new AI data center tenant.
-
The L2 connectivity is closer to the actual service connection.
-
AI data center tenants can be in the same MAC-VRF L2 EVPN instance (EVI) when you configure the tenants with the
vlan-awareEVPN service type.
Use Case #2: Two EVPN Type 5 IP-VRF instances on the same device:
-
Multiple EVPN Type 5 routing instances can isolate the AI data center tenants at the L3 routing level. Pure Type 5 routing can also extend the context within a POD or between PODs.
-
EVPN signaling exchanges between the ToR switches of the AI data center automatically establish VXLAN tunnels for Type 5 routes.
Topology
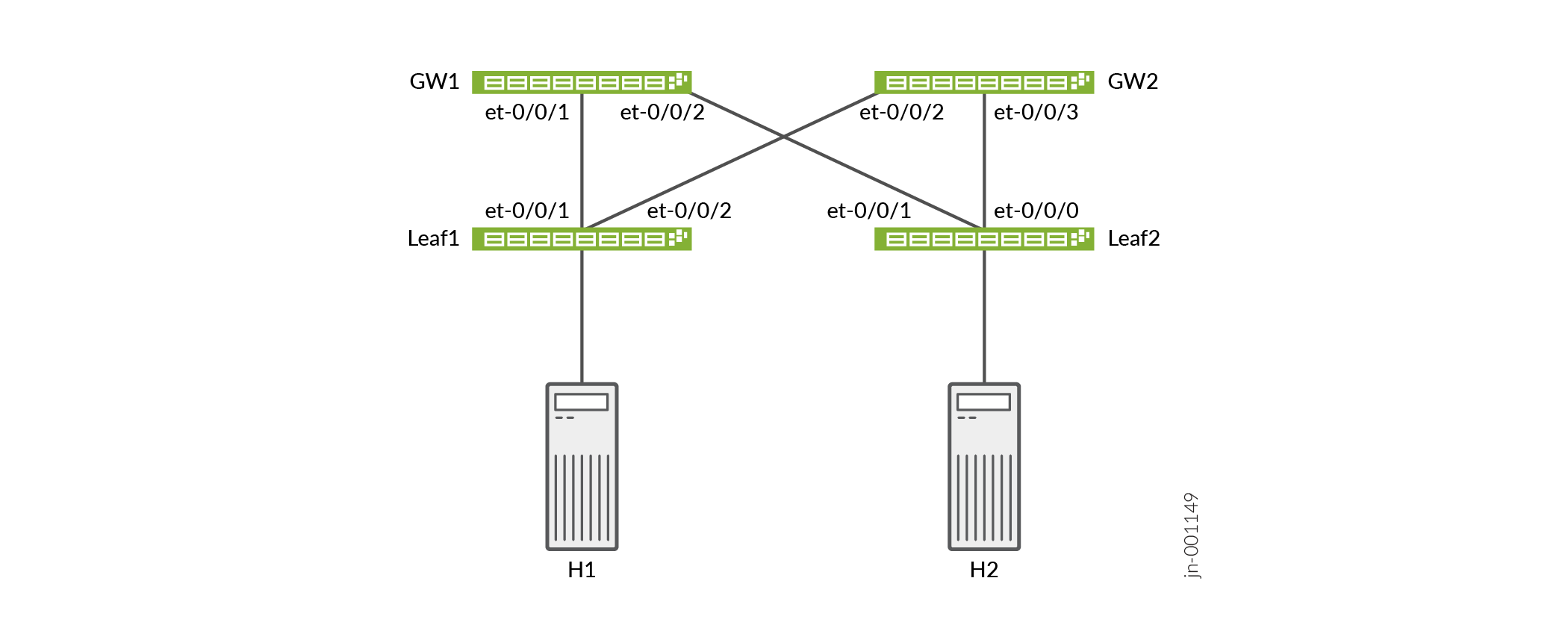
The topology for these examples uses QFX5240-64QD switches for both the spine and leaf layers. The network is an edge-routed bridging (ERB) architecture.
How to Configure Two MAC-VRFs
Verification
user@device> show route table myMACVRF101.evpn.0 active-path
myMACVRF101.evpn.0: 10 destinations, 15 routes (10 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
2:10.203.113.10:101::5101::00:10:94:00:00:05/304 MAC/IP
*[EVPN/170] 04:43:28
Indirect
2:10.203.113.10:101::5101::6c:62:fe:b9:3b:3d/304 MAC/IP
*[EVPN/170] 05:23:00
Indirect
2:10.203.113.11:101::5101::00:10:94:00:00:06/304 MAC/IP
*[BGP/170] 04:36:14, localpref 100, from 10.203.113.14
AS path: 65101 64513 I, validation-state: unverified
to 192.0.2.11 via et-0/0/1.0, Push 5101
to 192.0.2.9 via et-0/0/0.0, Push 5101
> to 192.0.2.13 via et-0/0/2.0, Push 5101
2:10.203.113.11:101::5101::6c:62:fe:b9:22:3d/304 MAC/IP
*[BGP/170] 04:36:26, localpref 100, from 10.203.113.13
AS path: 65101 64513 I, validation-state: unverified
to 192.0.2.11 via et-0/0/1.0, Push 5101
to 192.0.2.9 via et-0/0/0.0, Push 5101
> to 192.0.2.13 via et-0/0/2.0, Push 5101user@device> show mac-vrf forwarding vlans
Routing instance VLAN name Tag Interfaces
default-switch default 1
myMACVRF101 vlan101 101
et-0/0/4.0*
vtep-53.32773*
myMACVRF102 vlan102 102
et-0/0/5.0
vtep-54.32773*user@device> show ethernet-switching table vlan-id 101
MAC flags (S - static MAC, D - dynamic MAC, L - locally learned, P - Persistent static, C - Control MAC
SE - statistics enabled, NM - non configured MAC, R - remote PE MAC, O - ovsdb MAC,
B - Blocked MAC)
Ethernet switching table : 3 entries, 3 learned
Routing instance : myMACVRF101
Vlan MAC MAC GBP Logical SVLBNH/ Active
name address flags tag interface VENH Index source
vlan101 00:10:94:00:00:05 D et-0/0/4.0
vlan101 00:10:94:00:00:06 DR vtep-53.32773 10.203.113.11
vlan101 6c:62:fe:b9:22:3d DRP vtep-53.32773 10.203.113.11How to Configure Two Type 5 IP-VRFs
Use the following steps as a guide to configuring two Type 5 IP-VRFs on the same leaf node. We use actual values for example purposes. You should customize these steps with relevant values for your implementation.
Verification
user@device> show bgp summary
Threading mode: BGP I/O
Default eBGP mode: advertise - accept, receive - accept
Groups: 3 Peers: 6 Down peers: 1
Table Tot Paths Act Paths Suppressed History Damp State Pending
inet.0
11 11 0 0 0 0
bgp.evpn.0
34 17 0 0 0 0
Peer AS InPkt OutPkt OutQ Flaps Last Up/Dwn State|#Active/Received/Accepted/Damped...
192.0.2.9 65534 713 699 0 0 5:17:25 Establ
inet.0: 4/4/4/0
192.0.2.11 65534 709 699 0 0 5:17:25 Establ
inet.0: 3/3/3/0
192.0.2.13 65534 713 699 0 0 5:17:25 Establ
inet.0: 4/4/4/0
198.51.100.5 65512 18 24 0 1 5:40:07 Idle
10.203.113.13 65101 724 705 0 0 5:13:39 Establ
bgp.evpn.0: 14/17/17/0
myMACVRF101.evpn.0: 3/5/5/0
myMACVRF102.evpn.0: 3/3/3/0
__default_evpn__.evpn.0: 0/0/0/0
RT5-IPVRF1.evpn.0: 4/5/5/0
RT5-IPVRF2.evpn.0: 4/4/4/0
10.203.113.14 65101 687 679 0 0 5:04:10 Establ
bgp.evpn.0: 3/17/17/0
myMACVRF101.evpn.0: 2/5/5/0
myMACVRF102.evpn.0: 0/3/3/0
__default_evpn__.evpn.0: 0/0/0/0
RT5-IPVRF1.evpn.0: 1/5/5/0
RT5-IPVRF2.evpn.0: 0/4/4/0user@device> show route table RT5-IPVRF1.evpn.0
RT5-IPVRF1.evpn.0: 10 destinations, 15 routes (10 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden)
+ = Active Route, - = Last Active, * = Both
5:10.203.113.10:200::0::10.10.101.0::24/248
*[EVPN/170] 05:28:52
Fictitious
5:10.203.113.10:200::0::10.10.101.1::32/248
*[EVPN/170] 05:28:52
Fictitious
5:10.203.113.10:200::0::10.10.101.10::32/248
*[EVPN/170] 04:49:20
Fictitious
5:10.203.113.10:200::0::192.168.10.10::32/248
*[EVPN/170] 05:32:20
Fictitious
5:10.203.113.10:200::0::192.168.101.1::32/248
*[EVPN/170] 05:32:20
Fictitious
5:10.203.113.11:200::0::10.10.101.0::24/248
*[BGP/170] 04:42:18, localpref 100, from 10.203.113.13
AS path: 65101 64513 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 192.0.2.11 via et-0/0/1.0, Push 1100
to 192.0.2.9 via et-0/0/0.0, Push 1100
to 192.0.2.13 via et-0/0/2.0, Push 1100
[BGP/170] 04:42:06, localpref 100, from 10.203.113.14
AS path: 65101 64513 I, validation-state: unverified
> to 192.0.2.11 via et-0/0/1.0, Push 1100
to 192.0.2.9 via et-0/0/0.0, Push 1100
to 192.0.2.13 via et-0/0/2.0, Push 1100