Configure GLB on 3-Clos IP Fabric with Multilinks
In a Clos network, congestion on the first two next hops impacts the load balancing decisions of the local node and the previous hop nodes and triggers global load balancing (GLB). We support GLB on 3-Stage Clos topologies with multilink between spine and top-of-rack switches.
Dynamic load balancing (DLB) helps to avoid congested links to mitigate local congestion. However, DLB cannot address some congestion experienced by remote devices in the network. In these cases, global load balancing (GLB) extends DLB by modulating the local path selection using path quality perceived at downstream switches to mitigate congestion. GLB allows an upstream switch to avoid downstream congestion hotspots and select a better end-to-end path. In a Clos network, congestion on the first two next hops impacts the load balancing decisions of the local node and the previous hop nodes and triggers GLB. If the route has only one next-next-hop, a simple path quality profile is created. If the route has more than one next next-hop node, then a simple path quality profile is created for each next next-hop node.
Profile Sharing in Clos Network
In extensive Clos network configurations with many GPUs, the profile-sharing mechanism optimizes limited profile resources. In Clos networks with five or more stages, some nodes, like super spines exceed 64 next-next-hop nodes. We can reuse the profiles under specific conditions to support more than 64 next-next-hop nodes. When managing large-scale network fabrics, particularly in hyperscale AI/ML environments, efficiently utilizing the profile capacity is critical. The profile-sharing feature allows two next-next-hop nodes to use a single profile if their paths do not overlap. Ensuring non-overlapping paths maintains efficient routing without exceeding constraints, maximizing resource utilization.
Profile sharing involves stringent criteria to prevent configuration conflicts and performance degradation. Nodes must operate on distinct next-hop link ranges to ensure appropriate use of shared profiles, maintaining network robustness. Understanding these criteria is essential, as misconfiguration could lead to suboptimal routing or instability.
Even with profile sharing, the total number of simple profiles must not be more than 1024. Maximum number of nexthops (paths) a HW profile can have is 352.
Transition from one profile space allocation to another profile space allocation might lead to over 64 hardware profiles in PFE during the transition. We strongly recommend to deactivate bgp global-load-balancing and wait until all profiles are cleared from PFE before changing the profile space allocation.
Benefits of GLB in 3-Clos Networks with Multilinks
-
Mitigates congestion when AI-ML traffic that has elephant flows and lacks entropy causes congestion in the fabric.
-
Efficient traffic distribution to ensure optimum link utilization. In a DC fabric, hashing is unable to ensure even load distribution over all ECMP links, which might result in underutilization of some links.
-
Reduces packet loss in case of remote link failures.
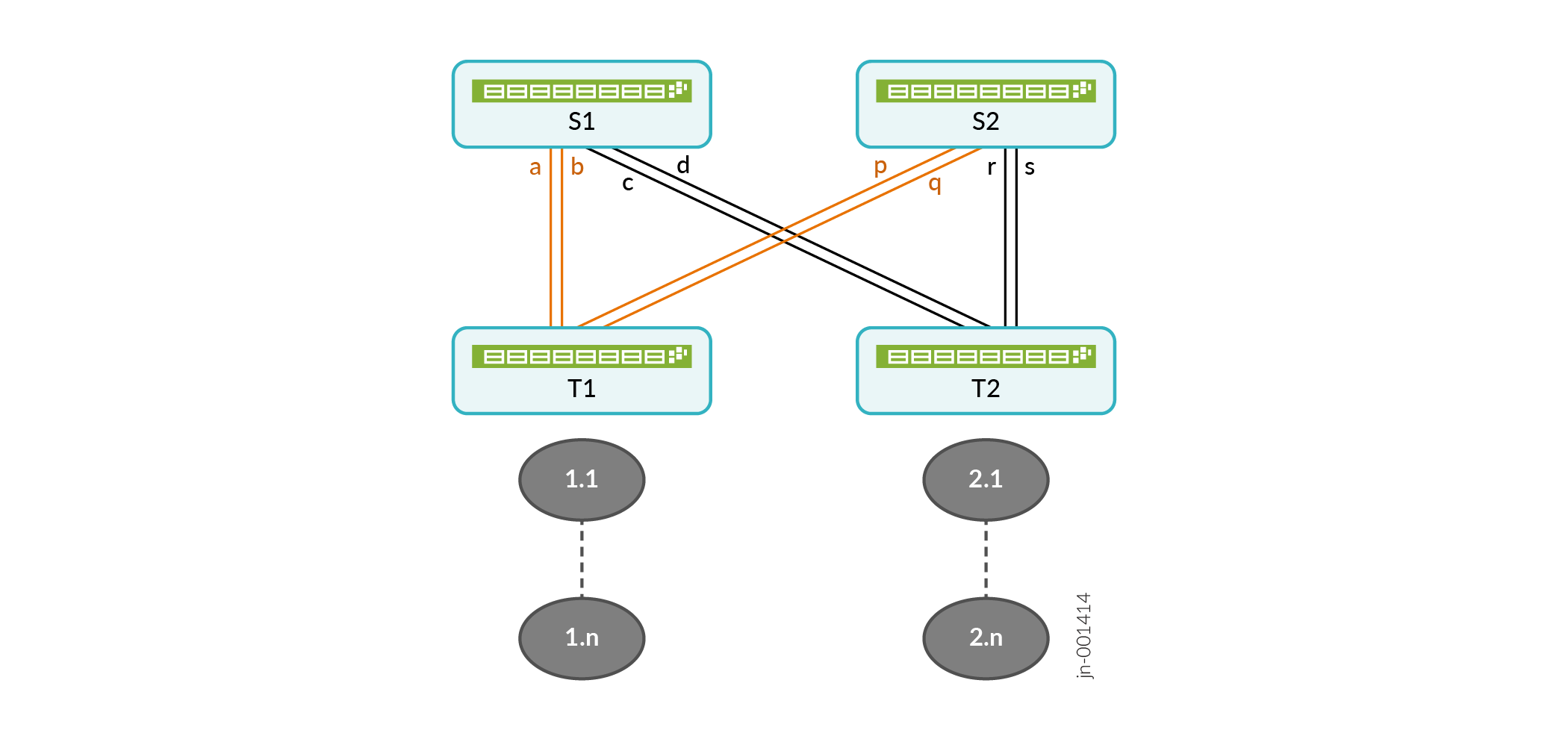
In Figure 1, S1 and S2 are spine nodes connecting to T1 and T2 top of rack (ToR) devices with multiple links a, b, c, d and p, q, r, s. S1 and S2 aggregate the quality of all available paths to a remote device and advertises the overall path quality to ToR devices. 1.1 to 1.n and 2.1 to 2.n are the hosts or routes behind the ToR devices T1 and T2 respectively. If one or more links go down, the spine continues to apply same aggregation logic to the remaining active links. The remote link state is only advertised as ‘down’ when all links in the multilink group are down.