Junos Space Fabric Deployment Overview
You can install and deploy Junos Space Hardware Appliances JA2500), Junos Space Virtual Appliances, or both to form a fabric. Each appliance in the fabric is called a node. All nodes in the fabric work together as a cluster of Junos Space instances running in active-active configuration (that is, all nodes are active in the cluster).
Figure 1 displays how a Junos Space fabric employs a software load balancer to distribute HTTP sessions across the nodes to ensure that the load presented by the Junos Space Network Management Platform user interface and NBI clients is equally distributed within the fabric.
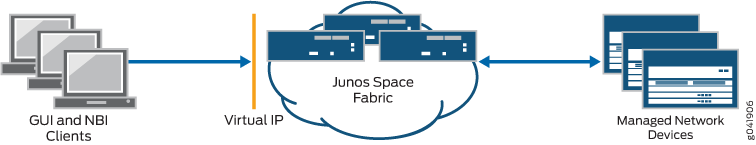
A Junos Space fabric of appliances provides scalability and ensures high availability of your management platform. The fabric provides an N+1 redundancy solution where the failure of a single node in the fabric does not affect the functioning of the fabric. When a node in the fabric fails, the sessions of the clients accessing Junos Space from the user interface automatically migrate away from the failed node. Similarly, managed devices that were connected to the failed node are automatically reconnected with another functioning node in the fabric.
Deploying a Junos Space Hardware Appliance
When you power on the Junos Space Hardware Appliance and log in to the CLI console, you can view a menu-driven command-line interface to specify the initial configuration of the appliance.
You need to specify the following parameters:
IP address and subnet mask for the “eth0” interface
Virtual IP address (when you configure the first node in the cluster) to access the Junos Space user interface from Web browsers. The IP address should be in the same subnet as the IP address assigned to the “eth0” interface.
IP address of the default gateway
IP address of the name server
IP address and subnet mask for the “eth3” interface if you choose to manage devices on a different Ethernet interface (see Figure 3).
Whether the appliance will be added to an existing cluster. Choose “n” to add the first node to a new cluster and choose “y” to add subsequent nodes to the cluster.
NTP server settings with which to synchronize the appliance’s time
Maintenance mode user ID and password
Note:Ensure that you remember the Maintenance mode user ID and password. These details are required when you upgrade software and restore databases.
Refer to the JA2500 Junos Space Appliance Quick Start Guide for detailed instructions on how to configure the hardware appliance during initial deployment.
Deploying a Junos Space Virtual Appliance
The Junos Space Virtual Appliance is stored in the open virtual appliance (OVA) format and is packaged as an *.ova file, which is a single folder that contains all the files of the Junos Space Virtual Appliance. OVA is not a bootable format and you must deploy each Junos Space Virtual Appliance to a hosted ESX or ESXi server before you can run the Junos Space Virtual Appliance.
You can deploy a Junos Space Virtual Appliance on a VMware ESX server version 4.0 or later or VMware ESXi server version 4.0 or later. After the Junos Space Virtual Appliance is deployed, you can use the VMware vSphere client that is connected to the VMware ESX (or VMware ESXi) server to configure the Junos Space Virtual Appliance. You can deploy Junos Space Virtual Appliance 14.1R2.0 and later on qemu-kvm Release 0.12.1.2-2/448.el6. You must deploy and configure the Junos Space Virtual Appliance on a KVM server by using the Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) client.
The CPU, RAM, and disk space provided by the VMware ESX server or KVM server must meet or exceed the documented CPU, RAM, and disk space requirements for deploying a Junos Space Virtual Appliance. In addition, we recommend that, for a multinode fabric, you deploy the first and second virtual appliances on separate servers to ensure failover support.
The distributed Junos Space Virtual Appliance files are created with 135 GB of disk space. If you create a multinode cluster, ensure that the first and second nodes that you deploy should contain the same amount of disk space. When the disk resources are used beyond 80% capacity, add sufficient disk space (more than 10 GB) to the disk partitions.
When you log in to the console of the VMware vSphere client or VMM client, you need to specify the same parameters used to deploy a hardware appliance. Refer to the Junos Space Virtual Appliance Deployment and Configuration Guide for detailed instructions on how to configure the virtual appliance during initial deployment.
Basic Requirements for a Fabric Deployment
When you deploy multiple appliances to create a Junos Space fabric, each appliance in the fabric uses the eth0 interface for all internode communication within the fabric. On each appliance, you can choose to use a separate interface (eth3) for all communication between the appliance and managed devices, as shown in Figure 3.
The following are required when you deploy a Junos Space fabric:
You must be able to ping the default gateway IP address, or else the fabric will not form correctly.
The IP addresses assigned to the eth0 interface on the first two appliances in the fabric must be in the same subnet.
The virtual IP address configured on the first appliance in the fabric must be in the same subnet as the eth0 interface on the first two appliances.
Multicast packets must be routable among all nodes because JBoss cluster-member discovery uses multicast routing.
If you are deploying a fabric of virtual appliances, we recommend that the first and second appliances added to the fabric be hosted on a separate VMware ESX or ESXI server to ensure failover support.
All appliances in the fabric must use the same external NTP source to ensure consistent time setting across all appliances in the fabric You must specify the NTP source on each appliance before adding the appliance to the fabric.
All nodes in the fabric are running the same version of the software.
Configuring Network Connectivity for a Junos Space Fabric
A Junos Space appliance (hardware or virtual) has four RJ45 10/100/1000 Ethernet interfaces that are named eth0, eth1, eth2, and eth3. When deploying the appliance, you need to ensure that it has IP connectivity with the following:
Devices in your managed network
Desktops, laptops, and workstations from which Junos Space users access the Junos Space user interface as well as external systems hosting NBI clients
Other appliances that form a Junos Space fabric along with this appliance
Junos Space allows you to use two of the four Ethernet interfaces: eth0 and eth3. The other two Ethernet interfaces are reserved for future use. You can choose one of the following two options for configuring interfaces for IP connectivity:
Use the eth0 interface for all network connectivity of the appliance, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Using a Single Ethernet Interface for All IP Connectivity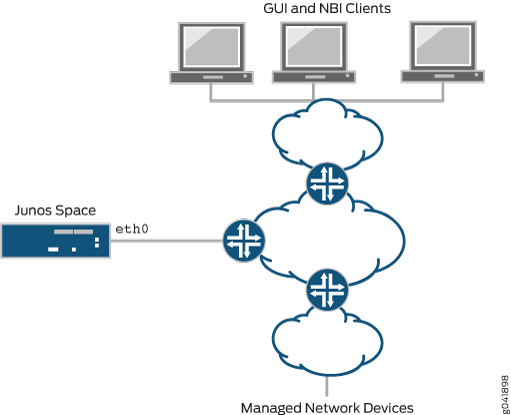
Use the eth0 interface for network connectivity with Junos Space user interface clients and other appliances in the same fabric, and use the eth3 interface for network connectivity with managed devices, as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Using Two Interfaces for IP Connectivity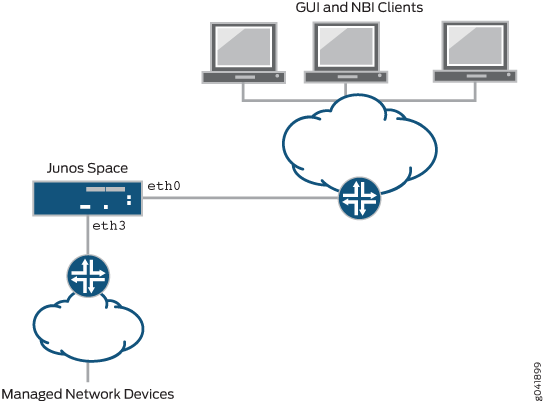
Adding Nodes to a Junos Space Fabric
You must be assigned the System Administrator user role to be able to add nodes to a Junos Space fabric. You add nodes to a Junos Space fabric from the Add Fabric Node page (Network Management Platform > Administration > Fabric > Add Fabric Node). To add a node to a fabric, you specify the IP address assigned to the eth0 interface of the new node, a name for the new node, and (optionally) a scheduled date and time to add the node to the fabric. Junos Space software automatically handles all necessary configuration changes to add the node to the fabric. After the new node is added to the fabric, you can monitor the status of the node from the Fabric page (Network Management Platform > Administration > Fabric).
For complete information about adding nodes to a fabric, see the Adding a Node to an Existing Junos Space Fabric topic (in the Junos Space Network Management Platform Workspaces User Guide).
