Understanding the Ansible for Junos OS Collections and Modules
Juniper Networks provides Ansible modules that you can use to manage Junos devices.
Understanding Ansible Collections and Modules for Managing Junos Devices
Ansible is an IT automation framework that is used for infrastructure configuration management. You use Ansible modules, which are discrete units of code, to perform specific functions on a managed node. You can execute individual modules on remote hosts to perform ad-hoc tasks, or you can execute modules through playbooks.
Ansible and Juniper Networks provide Ansible modules that you can use to manage Junos devices. The Juniper Networks Ansible modules are grouped and distributed through Ansible collections, which are hosted in the Ansible Galaxy repository. Table 1 outlines the different content sets available for managing Junos devices.
|
Content Set |
Description |
Ansible Releases |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Collection for managing Junos devices, which Juniper Networks provides and manages as an open-source project. |
Ansible 2.10 and later |
|
|
Collection for managing Junos devices, which Ansible provides, maintains, and supports. |
Ansible 2.10 and later |
|
Ansible core modules |
Ansible modules included in the Ansible base installation. In Ansible 2.10, the core modules moved from the base
installation into Ansible’s
|
Ansible 2.1 through Ansible 2.9 |
|
|
Role for managing Junos devices, which Juniper Networks provides, maintains, and supports. This role is superseded by the |
Ansible 2.1 and later |
An Ansible role is a set of tasks and supporting variables, files, templates, and modules for configuring a host. Starting in Ansible 2.10, Ansible supports Ansible Content Collections, a format for distributing Ansible content that is not included as part of the Ansible base installation. Ansible collections can include a wider range of content, including modules, playbooks, plugins, and roles. Ansible collections also have their own repositories and can be developed and released independently from the Ansible base installation.
In Ansible 2.9 and earlier, you can manage Junos devices by using the modules
provided in the Juniper Networks Juniper.junos role or by using the
core modules provided as part of the Ansible base installation. Starting in Ansible
2.10, the Juniper.junos role and the Ansible core modules are
superseded by the corresponding collection. With the introduction of Juniper
Networks’ juniper.device collection, the modules in the
Juniper.junos role were duplicated under new names in the
collection and thus retain the same functionality and parameters as the original
modules, with the exception of the provider parameter. We recommend
that you use the juniper.device collection, because new features
are only being added to the collection going forward.
How to Execute Modules on Junos Devices
To use the collections that are hosted in the Ansible Galaxy repository, you must
first install Ansible on the control node and then install the collection. For more
information about installing the juniper.device collection, see
Ansible for Junos OS Server Requirements.
Ansible modules can perform operations on a managed node. Typically, the Ansible control node sends a module to a managed node, where it is executed and then removed. In this scenario, the managed node must have the ability to execute the module. Because most Ansible modules are written in Python, Ansible typically requires Python on the managed node.
The Juniper Networks modules in the juniper.device collection,
however, do not require Python on the managed nodes. In contrast to the typical
operation, you execute the modules locally on the Ansible control node, and the
modules use Junos PyEZ and the Junos XML API over NETCONF to interface with the
managed node. This method of execution enables you to use Ansible to manage any
supported Junos device. Figure 1 illustrates the communication between the Ansible control node and a managed
Junos device.
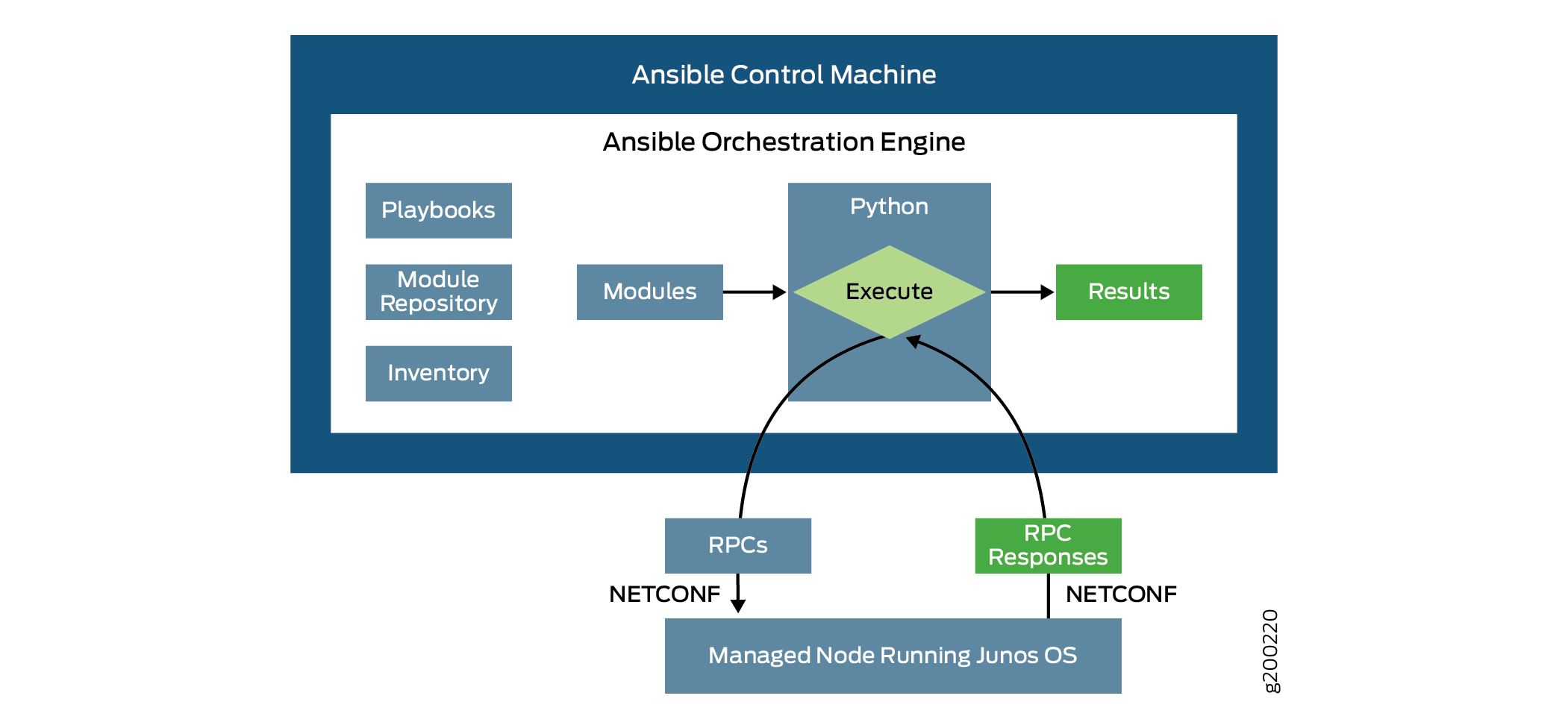
To use the juniper.device collection modules, the playbook or
command must:
-
Specify the collection or FQCN—To specify the collection, include the
collectionskey in the play. Alternatively, you can omit thecollectionskey and instead reference collection content by its fully qualified collection name (FQCN), which is the recommended method. -
Execute the modules locally on the control node—To run Ansible modules locally, you define the
connectionparameter aslocal, for example, by includingconnection: localin your playbook or including--connection localon the command line.Note:When you use
connection: local, Ansible establishes a separate connection to the device for each task in the play that requires a connection. Thejuniper.devicecollection modules also support usingconnection: juniper.device.pyez, which still executes the modules locally but instead establishes a single, persistent connection to a device for all tasks in a play. -
Provide appropriate connection and authentication information to connect to the managed device—For more information, see:
You can execute Ansible modules using any user account that has access to the managed Junos device. When you execute Ansible modules, Junos OS user account access privileges are enforced, and the class configured for the Junos OS user account determines the permissions. Thus, if a user executes a module that loads configuration changes onto a device, the user must have permissions to change the relevant portions of the configuration.
The following playbook executes the juniper.device collection’s
facts module to retrieve the device facts and save them to a
file. The example uses existing SSH keys in the default location to authenticate
with the device and thus does not explicitly provide credentials in the
playbook.
---
- name: Get Device Facts
hosts: dc1
connection: local
gather_facts: no
tasks:
- name: Retrieve facts from a Junos device
juniper.device.facts:
savedir: "{{ playbook_dir }}"
- name: Print version
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: junos.versionYou can also perform ad-hoc operations on the command line. The following command
executes the juniper.device collection’s facts
module and retrieves device facts from hosts in inventory group dc1.
user@ansible-cn:~$ ansible --connection local -i production dc1 -m juniper.device.facts
Juniper Networks juniper.device Collection
Juniper Networks provides the juniper.device Ansible
Content Collection, which is hosted on the Ansible Galaxy
website. The collection includes Ansible modules that enable you to manage Junos
devices.
Table 2 outlines the modules in the juniper.device collection. In the
collection’s initial release, the collection modules retain the same functionality
and parameters as the corresponding module in the Juniper.junos
role, with the exception of the provider parameter, which is not
supported for the collection modules.
For the most current list, documentation, and usage examples for the modules, see https://ansible-juniper-collection.readthedocs.io/.
|
juniper.device Module Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Execute CLI commands on the Junos device and save the output locally. |
|
|
Manage the configuration of Junos devices. |
|
|
Retrieve device-specific information from the remote host, including the Junos OS version, serial number, and hardware model number. |
|
|
Transfer a file between the local Ansible control node and the Junos device. |
|
|
Execute Junos Snapshot Administrator in Python (JSNAPy) tests through Ansible. |
|
|
Execute the |
|
|
Perform path MTU discovery on Junos devices. |
|
|
Execute Junos OS RPCs. |
|
|
Install a Junos OS software package and reboot a Junos device. |
|
|
Create an SRX Series chassis cluster for cluster-capable SRX Series Firewalls. |
|
|
Perform system operations on Junos devices, including resetting, rebooting, or shutting down the device. |
|
|
Use Junos PyEZ operational Tables and Views to retrieve operational information from Junos devices. |
