Add an EVPN Service Instance
A superuser or network administrator can use Routing Director to provision an Ethernet VPN (EVPN) service in their network.
An EVPN service provides multipoint Layer 2 connectivity and enables you to connect dispersed customer sites or devices.
Figure 1 illustrates the high-level workflow for provisioning an EVPN service.
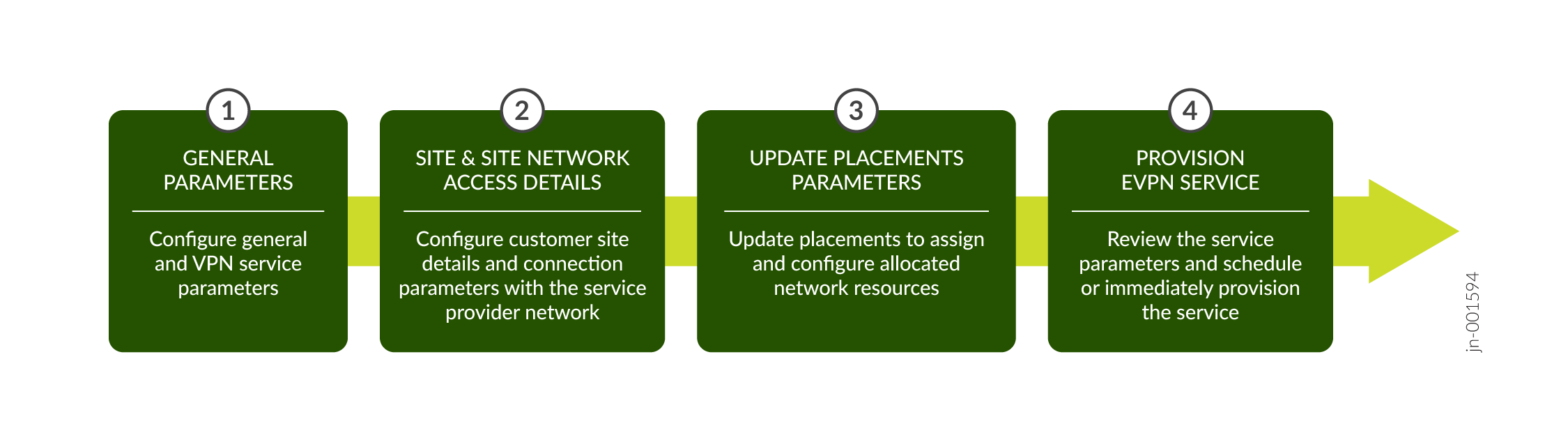
When you create and save an EVPN service instance, Routing Director generates a create service order. After you provision the service instance, Routing Director activates the automated workflow for fulfilling the service order and provisions the service in the network.
You can create an EVPN service instance by uploading preconfigured JSON files or by entering the details in the fields on the Add E-LAN EVPN CSM page.
To create an EVPN service instance:
-
Click Orchestration > Instances.
The Service Instances page appears.
-
Click Add > E-LAN EVPN CSM.
The Add E-LAN EVPN CSM service page appears.
-
On the General page of the Add E-LAN EVPN CSM wizard, enter the values by referring to
the following table:
Note: Fields marked with an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
Table 1: Fields on the General Page (EVPN) Field
Description
Upload JSON File
Click Browse to upload a preconfigured JSON file.
You see a message that the file is successfully imported. The values specified in the file are automatically populated in the corresponding UI fields.
Note:If you are uploading a preconfigured JSON file to create an EVPN service instance, you must clear the placement section in the file before you provision the service order.
Customer*
Enter the name of the customer for whom you are provisioning the service:
-
If you already added the customer name by using the Customer Inventory page (Orchestration > Service > Customers), click the Customer field to see a drop-down with the customer names that you added. Select the customer name from the drop-down list.
-
Alternatively, click the Add Customer link to create a new customer. See Add a Customer.
The customer name must be unique within an organization. For example, network-operator.
Instance Name*
Enter a name for the service instance. For example, irb-evpn-1.
The instance name can be a set of alphanumeric characters and the special character hyphen (-). The maximum number of characters allowed is 64.
VPN Service
VPN Id*
Enter the ID you want to assign to the VPN. For example, vpn10.
The VPN ID must not exceed 64 characters.
VPN Service Topology
The topology for the VPN service.
Only the any-to-any topology is supported in this release. In this service topology, all VPN sites can exchange network traffic with each other without any restrictions.
VPN Service Type
The service type for EVPN service provisioned by the service provider.
Routing Director supports only the EVPN-MPLS service type.
Route Distinguisher Type
Select the route distinguisher (RD) type. The default RD type is Type 0.
If Type 0 is selected, after the service instance is configured and the placements are updated, the Type 0 values are populated from the VPN resource pool in the Route Distinguishers table at the bottom of the page. If Type 1 is selected, the Type 1 values are populated from the NIP or topo resource pool in the Route Distinguishers table at the bottom of the page.
EVPN Service Type
Select the type of EVPN service:
-
vlan-aware—VLAN-aware supports multiple broadcast domains to map to a single bridge domain. Multiple VLANs are mapped to a single EVPN instance and share the same bridge table in the MAC-VRF table.
Note:-
The VLAN-aware EVPN service type is not supported for untagged interfaces and Q-in-Q tagged interfaces.
-
-
vlan-based—VLAN-based supports a one-to-one mapping of a single broadcast domain to a single bridge domain. Each VLAN is mapped to a single EVPN instance, resulting in a separate bridge table for each VLAN.
The default EVPN service type is vlan-based.
Multiplatform
Switch the Multiplatform toggle to True to enable the VPN service to span multiple device platforms.
The default setting is False.
Note: When Routing Director is upgraded from release 2.5.0 to release 2.6.0, the toggle button is automatically set to true.Pinned Reservation
Configure the service to use reserved resources (pinned resources).
Brownfield
Enable this flag if this is a brownfield service. When enabled, this service would be provisioned by using resources reserved for migrating brownfield services to Routing Director.
Customer
Enable this flag to allow the service to be provisioned by using resources that are exclusively reserved for the customer associated with this service.
Instance
Enable this flag to allow the service to be provisioned by using resources exclusively reserved for this service.
Service Settings
Enter common settings applicable for the service.
Use instance name instead of UUID in device configuration.
Toggle to True to use the service instance name, instead of UUID, in the device configurations. The specified name is used in configuration such as routing instance name, filter name, policer name, community name, policy statement name, and so on. The instance name must be unique across customers and can be a maximum of 32 characters long.
Disable it to set it to False, so that the service instance name is auto-converted to a UUID and used in the device configuration. The UUID is a system generated alphanumeric value.
This option is disabled, by default.
-
- Click Next to proceed to the Customer Site Settings page of the Add E-LAN EVPN CSM wizard. See Add EVPN Site and Site Network Access Details.
- Configure post update placement parameters for the E-LAN EVPN CSM service. See Add EVPN Service Post Update Placements Parameters.
- View summary of the E-LAN EVPN CSM service and then save and provision the service. See View Summary and Provision an EVPN Service.
