Paragon Automation System Requirements
Before you install the Paragon Automation software, ensure that your system meets the requirements that we describe in these sections.
To determine the resources required to implement Paragon Automation, you must understand the fundamentals of the Paragon Automation underlying infrastructure.
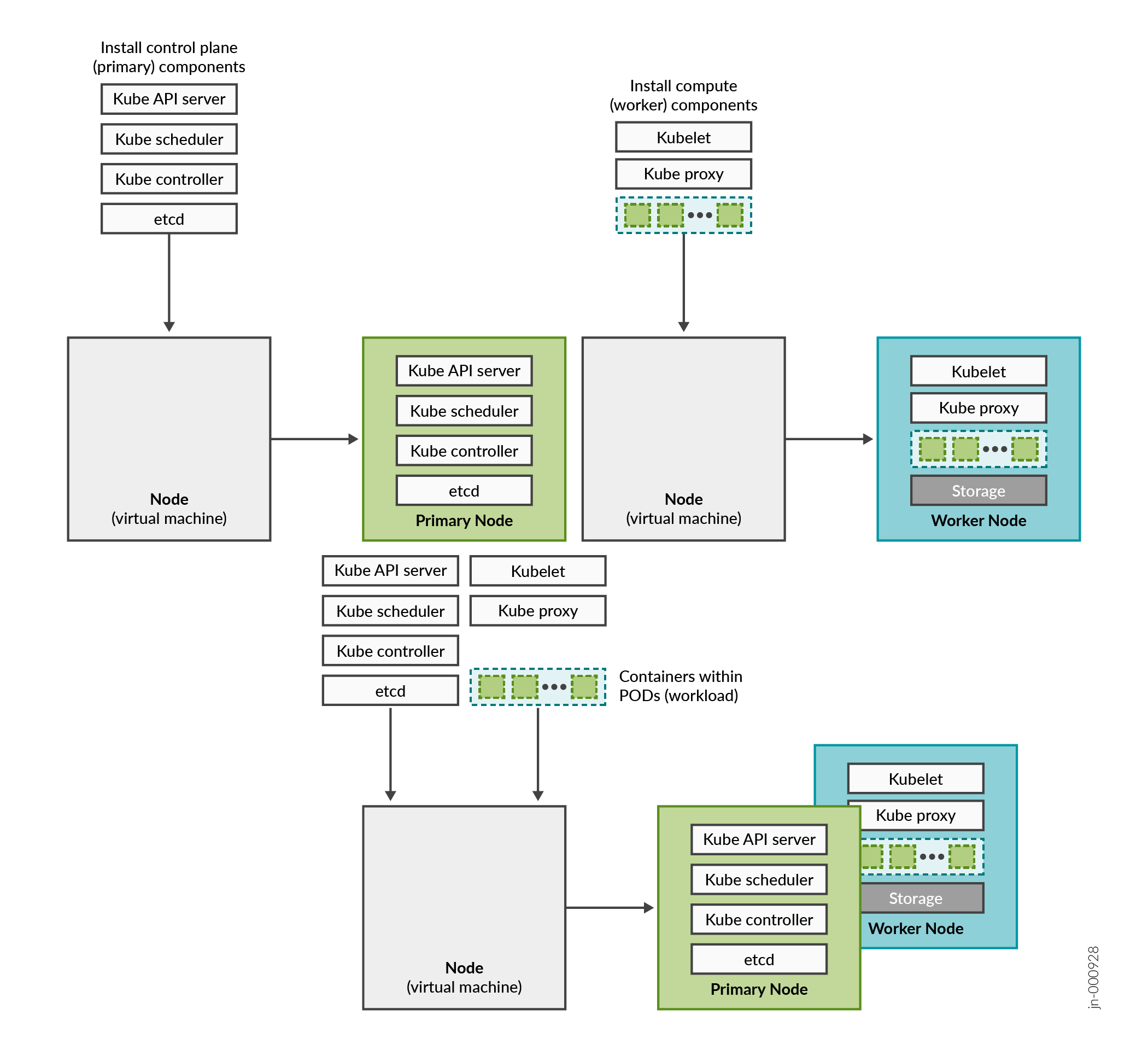
Paragon Automation is a collection of microservices that interact with one another through APIs and run within containers in a Kubernetes cluster. A Kubernetes cluster is a set of nodes or virtual machines (VMs) running containerized applications.
A Kubernetes cluster comprises one or more primary and worker nodes.
-
Control plane (primary) node—The primary node performs the Kubernetes control-plane functions.
-
Compute (worker) node—The worker node provides resources to run the pods. Worker nodes do not have control-plane function.
The two types of nodes can be deployed separately or co-located in the same VM. A single node can function as both primary and worker if the components required for both roles are installed in the same node.
In Paragon Automation, by default, the primary nodes also serve as worker nodes.
You need to consider the intended system's capacity (number of devices to be managed, use cases, and so on), the level of availability required, and the expected system's performance, to determine the following cluster parameters:
- Total number of nodes in the cluster
- Amount of resources on each node (CPU, memory, and disk space)
- Number of nodes acting as primary and worker nodes
The amount of resources on each node are described later in this topic.
Paragon Automation Implementation
Paragon Automation is implemented on top of a Kubernetes cluster, which consists of one or more primary nodes and one or more worker nodes. Paragon Automation is implemented as a multinode cluster. At minimum, three nodes that function as both primary and worker nodes and one node that functions as a worker-only node is required for a functional cluster. The four-node cluster is the recommended and supported implementation.
This implementation not only improves performance but allows for high availability within the cluster:
-
Control plane high availability—The three nodes that function as both primary and worker nodes provide the required control plane redundancy. The cluster remains functional when a single node fails. We do not recommend more than three primary nodes.
-
Workload high availability—For workload high availability and workload performance, you must have more than one worker. In Paragon Automation, the three nodes that function as both primary and worker nodes and the one node that serves as a worker-only node provide workload high availability.
-
Storage high availability—For storage high availability, all the nodes provide Ceph storage.
Hardware Requirements
This section describes the minimum hardware resources that are required on each node VM in the Paragon Automation cluster, for evaluation purposes or for small deployments.
The compute, memory, and disk requirements of the cluster nodes can vary based on the intended capacity of the system. The intended capacity depends on the number of devices to be onboarded and monitored, types of sensors, and frequency of telemetry messages. If you increase the number of devices, you'll need higher CPU and memory capacities.
To get a scale and size estimate of a production deployment and to discuss detailed dimensioning requirements, contact your Juniper Partner or Juniper Sales Representative. Paragon Automation Release 2.1.0 supports a scale of a maximum of 500 devices.
Each of the four nodes in the cluster must have:
-
16-core vCPU
-
32-GB RAM
-
300-GB SSD
The VMs do not need to be on the same server, but they need to be able to communicate over the same Layer 2 network. You need one or more servers with enough CPU, memory, and disk space to accommodate the hardware resources listed in this section.
Software Requirements
Use VMware ESXi 8.0 to deploy Paragon Automation.
Network Requirements
The four nodes must be able to communicate with each other through SSH. The nodes must be able to sync to an NTP server. SSH is enabled automatically during the VM creation, and you will be asked to enter the NTP server address during the cluster creation. Ensure that there is no firewall blocking NTP or blocking SSH traffic between the nodes in case they are on different servers.
You need to have the following addresses available for the installation, all in the same subnet.
-
Four interface IP addresses, one for each of the four nodes
-
Internet gateway IP address
-
Two virtual IP (VIP) addresses for:
-
Generic ingress IP address shared between GNMI, OC-TERM (SSH connections from devices), and the Web UI—This is a general-purpose VIP address that is shared between multiple services and used to access Paragon Automation from outside the cluster.
-
Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent gateway (TAGW)—This VIP address serves HTTP-based traffic to the Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent endpoint.
The VIP addresses are added to the outbound SSH configuration that is required for a device to establish a connection with Paragon Automation. The outbound SSH commands for OC-TERM and GNMI both use VIP addresses.
-
-
One VIP address for the PCE server—This VIP address is used to establish Path Computational Element Protocol (PCEP) sessions between Paragon Automation and the devices.
The PCE server VIP configuration is necessary to view live topology updates in your network.
-
Hostnames mapped to the VIP addresses—Along with VIP addresses, you can also enable devices to connect to Paragon Automation using hostnames. However, you must ensure that the hostnames and the VIP addresses are correctly mapped in the DNS and your device is able to connect to the DNS. If you configure Paragon Automation to use hostnames, the hostnames are added to the outbound SSH configuration instead of the VIP addresses.
Figure 2 illustrates the IP and VIP addresses required to install a Paragon Automation cluster. The illustration displays two ways of deploying the cluster, that is, on a single server or two servers.
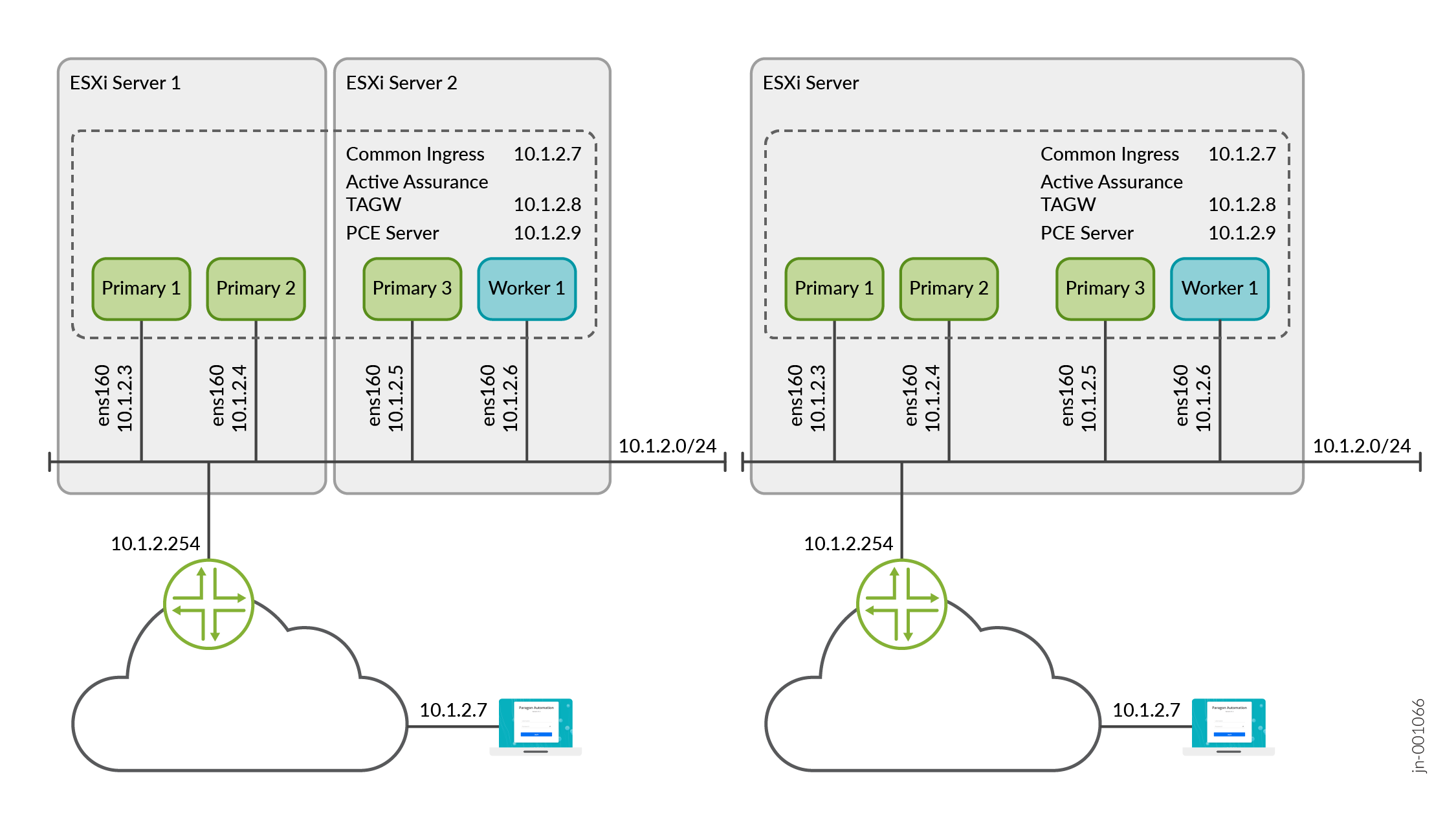
Communication within and from outside of the cluster
You must allow intracluster communication between the nodes. In particular, you must keep the ports listed in Table 1 open for communication.
|
Port |
Usage |
From |
To |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Ports | ||||
|
22 |
SSH for management |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Require a password or SSH-key |
|
2222 TCP |
Paragon Shell configuration sync |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Require password or SSH-key |
|
443 TCP |
HTTPS for registry |
All cluster nodes |
Primary nodes |
Anonymous read access Write access is authenticated |
|
2379 TCP |
etcd client port |
Primary nodes |
Primary nodes |
Certificate-based authentication |
|
2380 TCP |
etcd peer port |
Primary nodes |
Primary nodes |
Certificate-based authentication |
|
5473
|
Calico CNI with Typha |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
— |
|
6443 |
Kubernetes API |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Certificate-based authentication |
|
7472 TCP |
MetalLB metric port |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Anonymous read only, no write access |
|
7946 UDP |
MetalLB member election port |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
— |
| 8443 |
HTTPS for registry data sync |
Primary nodes |
Primary nodes |
Anonymous read access Write access is authenticated |
|
9345 |
rke2-server |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Token based authentication |
|
10250 |
kubelet metrics |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Standard Kubernetes authentication |
|
10260 |
RKE2 cloud controller |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Standard Kubernetes authentication |
|
32766 TCP |
Kubernetes node check for PCE service local traffic policy |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
Read access only |
|
Calico CNI Ports |
||||
|
4789 UDP |
Calico CNI with VXLAN |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
— |
|
5473 TCP |
Calico CNI with Typha |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
— |
|
51820 UDP |
Calico CNI with Wireguard |
All cluster nodes |
All cluster nodes |
— |
The following ports must be open for communication from outside the cluster.
|
Port |
Usage |
From |
To |
|---|---|---|---|
|
443 |
Web GUI + API |
External user computer/desktop |
Web GUI Ingress VIP address(es) |
|
443 |
Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent |
External network devices |
Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent VIP address |
|
2200 |
OC-TERM |
External network devices |
Web GUI Ingress VIP address(es) |
|
4189 |
PCE Server |
External network devices |
PCE Server VIP address |
|
6800 |
Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent |
External network devices |
Paragon Active Assurance Test Agent VIP address |
|
32767 |
gNMI |
External network devices |
Web GUI Ingress VIP address(es) |
Web Browser Requirements
The latest versions of Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari.
We recommend that you use Google Chrome.
