Operating Companies Overview
Contrail Service Orchestration (CSO) supports operating companies in a service provider environment. An operating company (OpCo) is a region-specific service provider that can create and manage its own tenants and provide services to them—thus an OpCo is a subset of the global service provider and functions as a service provider for its own tenants.
A global service provider can create one or more operating companies and share resources (cloud hub devices, device templates, and so on) with the operating companies. The global service provider manages its own tenants as well as the operating companies.
For example, the Global SP administrator can create operating companies such as OpCo_Spain, OpCo_Italy, and OpCo_France under the global service provider V1_Global and share the resources with these operating companies.
Tenants managed by one OpCo are isolated from tenants of another OpCo—that is, resources from one OpCo cannot be shared with other operating companies.
When an SP administrator creates one or more operating companies under the service provider, the service provider is called a global service provider and the SP administrator is called the Global SP administrator.
This topic contains the following sections:
OpCo Hierarchy Management
The CSO multitenant hierarchy has the following levels:
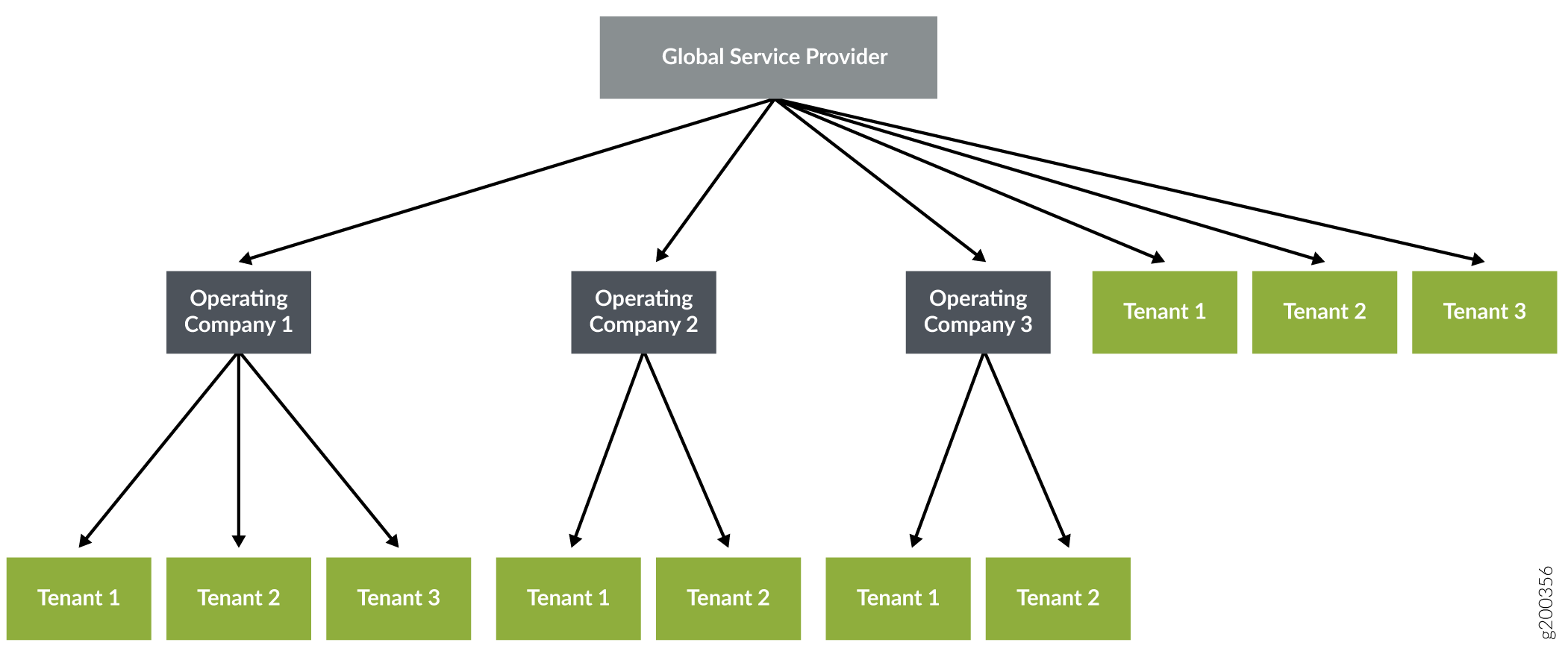
Global service provider—Contains one or more operating companies and its tenants, manages resources at the service provider level, and shares common resources with operating companies and tenants. The Global SP administrator has the required access privileges to view and access resources across operating companies.
Operating company—A region-specific service provider that can manage its tenants and provide services to them. Tenants managed by one OpCo are isolated from tenants of another OpCo. A global service provider share resources (cloud hub devices, device templates, and so on) with the operating companies and their tenants.
Tenant—A tenant uses the resources that the global service provider or the tenant's OpCo shares with it.
Figure 1 shows the relationship between the global service provider, operating companies, and tenants. A global service provider can have one or more operating companies and tenants, and each OpCo can be assigned one or more tenants.
OpCo Authentication and Authorization
A newly created OpCo can use either the same authentication method used by the global service provider or its own SSO server to authenticate its users. If the OpCo uses its own SSO server, the SSO server details need to be added in the Authentication (Administration > Authentication) page. For more information about configuring a SSO server, see Configuring a Single Sign-On Server.
The following authentication methods are available for OpCo users:
Local authentication
Authentication using an SSO server
Authentication and authorization using an SSO server
For more information about authentication methods, see Authentication Methods Overview.
Access Privileges for Global SP, OpCo, and Tenant Users
Global SP, OpCo, and tenant users can perform tasks based on the access privileges assigned to these roles.
An OpCo administrator, Global SP administrator, tenant administrator, or users with administrator role privileges can can perform an administrator's tasks.
Global SP users cannot access operating companies and tenants automatically. An OpCo administrator, a tenant administrator, or users with administrator role privileges need to provide the required access privileges to the Global SP users. Therefore, global users can view and access operating companies and tenants.
An OpCo administrator, tenant administrator, or users with the administrator role privileges can add global SP users to the OpCo or to the tenant. Therefore, global SP users can perform tasks specific to an OpCo or a tenant by switching the scope to a specific OpCo or tenant.
For more information about roles, see Role-Based Access Control Overview.
Table 1 shows the access privileges of Global SP, OpCo, and Tenant Users.
Main Menu |
Submenu |
Access Privileges |
|---|---|---|
Dashboard—Display widgets for both global SP and an OpCo users when they log in to CSO. However, for OpCo users, the following information is filtered based on OpCo tenants. |
||
Tenant Sites – Total Alerts |
Global SP users can view alerts across all tenants. OpCo users can view alerts across their tenants. |
|
POPs – Capacity Used |
Global SP users can create and manage all POPs and share the POPs with operating companies. Global SP and OpCo users can view POPs usage (CPU, Memory, and Storage). |
|
Cloud Services: POP Resources Used |
Global SP and OpCo users can view POPs usage (CPU, Memory, and Storage). |
|
Top 5 POPs with Alerts |
Global SP and OpCo users can view POPs alerts. However, OpCo users can only view POP alerts across their tenants. |
|
Top 5 Tenants with Alerts |
Global SP users can view alerts across all tenants. OpCo users can only view alerts across their tenants. |
|
Top 5 Sites with Alerts |
Global SP users can view alerts across their tenant sites. OpCo users can only view alerts across their tenant sites. |
|
Monitor—Displays a geographical map of all POPs and alerts associated with each POP. Global SP users can create and manage all POPs and share the POPs with operating companies. Both Global SP and OpCo users can view POPs and their associated alerts. However, tenants can view only the alerts of their sites. |
||
Alerts |
Alerts are generated for a tenant's site or device and the alerts are shared with its tenant’s OpCo and global service provider. The tenant user can only view tenant-specific alerts and the OpCo users can view alerts of the OpCo's tenants. Global SP users can view all alerts across all tenants. |
|
Alert Definition – Security Alert |
Tenants can create security alert definitions. OpCo and Global SP users can view security alert definitions. |
|
Alarms |
Alarms are generated for a specific tenant and shared with an OpCo’s tenant and Global SP users. Global SP users can view alarms across all tenants and the OpCo users can view alarms specific to their tenants. Global SP users can view alarms specific to global devices (for example, cloud hub devices). |
|
Tenants SLA Performance |
SLA performance is measured for each tenant. Global SP users can view the SLA performance of all tenants. OpCo users can view the SLA performance of their tenants. |
|
Jobs – All |
Global SP users can view and edit the scheduled jobs across all tenants. OpCo users can view and edit scheduled jobs of the OpCo’s tenants. Tenants can view and edit their scheduled jobs. |
|
Jobs – Scheduled |
Global SP users can view scheduled jobs across all tenants. OpCo users can view scheduled jobs specific to their tenants. |
|
Resources—Global SP and OpCo users can create and manage POPs, tenant devices, cloud hub devices, device profiles, and device images. POPs and cloud hub devices are shared globally. Both Global SP and OpCo users can view all POPs and cloud hub devices. |
||
POP |
Global SP users can create POPs and share the POPs with all operating companies and their tenants. Operating companies and tenants of global service provider have read-only access to POPs. |
|
Tenant Devices |
Tenants own tenant devices and share the devices with the tenant’s OpCo and global service provider. |
|
Cloud Hub Devices |
Global SP users can create and manage all cloud hub devices and share the devices with operating companies and tenants. Operating companies and tenants have read-only access to cloud hub devices. |
|
Virtual Route Reflector (VRR) |
The VRR is created during CSO deployment and is available to all operating companies and tenants. A virtual route reflector (VRR) resides on a virtual machine (VM) on each regional microservices server. During the CSO installation, a VRR is installed on the regional servers. The VRR has a fixed configuration that you cannot modify. Use of a VRR enhances scaling of the BGP network with low cost and removes the need for hardware-based route reflectors that require space in a data center and ongoing maintenance. Note:
VRR is not a UI element. |
|
Device Profiles |
Device profiles can be managed by:
|
|
Images |
Global SP users can upload all device images, and the images are available to all operating companies and tenants associated with global service provider and operating companies. |
|
Configuration—Global SP and OpCo users can create and manage application traffic types, application SLA profiles, shared objects, and network services and share them with other operating companies. |
||
Application Traffic Type Profiles |
Global SP users can create and manage application traffic type profiles. Operating companies and tenants have read-only access to application traffic type profiles. |
|
Application SLA Profiles |
Application SLA profiles can be managed by:
|
|
Shared Objects |
Global SP users can create and manage shared objects. Operating companies and tenants have read-only access to the shared objects of the global service provider. |
|
Network Services (VNF and NSD) |
Global SP users can create and manage network services and share them with operating companies and tenants. |
|
Tenants—Global SP and OpCo users can create and manage tenants for the global service provider and operating companies. |
||
Global Tenants |
Global SP users can create and manage their tenants. However, if the global service provider user has privilege to access an OpCo, then the user can switch to OpCo scope and manage OpCo tenants. |
|
Operating companies |
Operating companies can be managed only by the Global SP users. OpCo users are not allowed to create operating companies. |
|
OpCo Tenants |
OpCo users can create and manage their tenants. The Global SP user has read-only access to the OpCo’s tenants. |
|
Administration—Global SP and OpCo users can create and manage users, and manage application databases, licenses, and preferences. Both Global SP and OpCo users can configure authentication methods and SMTP settings, and customize e-mail templates for their tenants. |
||
Users |
Users can be managed by:
|
|
Authentication |
Authentication methods can be configured at:
|
|
Licenses |
Global SP users can upload and manage licenses. OpCo and tenant users can upload their licenses. |
|
Signature Database |
Global SP users can manage and share application signature database with all operating companies and tenants. |
|
SMTP |
SMTP settings can be configured for:
|
|
Preferences (Portal Customization) |
Global SP users can create and manage themes for all operating companies and tenants. Operating companies can use the same theme used by the global service provider. Only the Global SP users can view and modify the theme settings. |
|
E-mail Templates |
Global SP users can customize e-mail messages. OpCo users can create their e-mail templates for their tenants. |
|
Benefits of Operating Companies
An OpCo relieves the global service provider of the responsibility of tenant management for a specified region. For example, the OpCo can look after a country-specific regulatory, billing, or operational need for the global service provider.
With the creation and configuration of operating companies, the Global SP administrator needs to define only a single solution across various regions and countries, and yet enable the operating companies to manage their assigned sets of tenants.
Each OpCo can use a shared CSO cloud-hosted solution instead of using its own CSO installation. OpCo administrators can access a centrally deployed CSO instance, and local resources, and offer SD-WAN services to their tenants.
