How Does CSDS Traffic Orchestrator Work
In this topic, you’ll learn how CSDS Traffic Orchestrator works in the MX Series routers.
What Is CSDS Traffic Orchestrator in MX Series Routers
Connected Security Distributed Services Traffic Orchestrator (CSDS-TO) provides stateless translated and non-translated traffic load balancing functionality as an inline Packet Forwarding Engine service in MX Series routers. Load balancing in this context is a method that involves the distribution of incoming transit traffic by the device (MX Series with CSDS-TO) across the configured servers (SRX Series Firewalls) that are in service.
Benefits
- Less overhead information—Perform stateless load balancing, which means no state information is created for a connection with CSDS-TO.
- Easy scalability—Scale the solution without limitations.
- Better throughput—Get throughput closer to the line rate.
Traffic Orchestrator for CSDS Architecture
You can operate CSDS-TO in the following modes in MX Series routers:
-
Translated (L3)—Do not use this mode for CSDS solution.
-
Non-translated Direct Server Return (L3)—Use this mode for the CSDS scale-out solution.
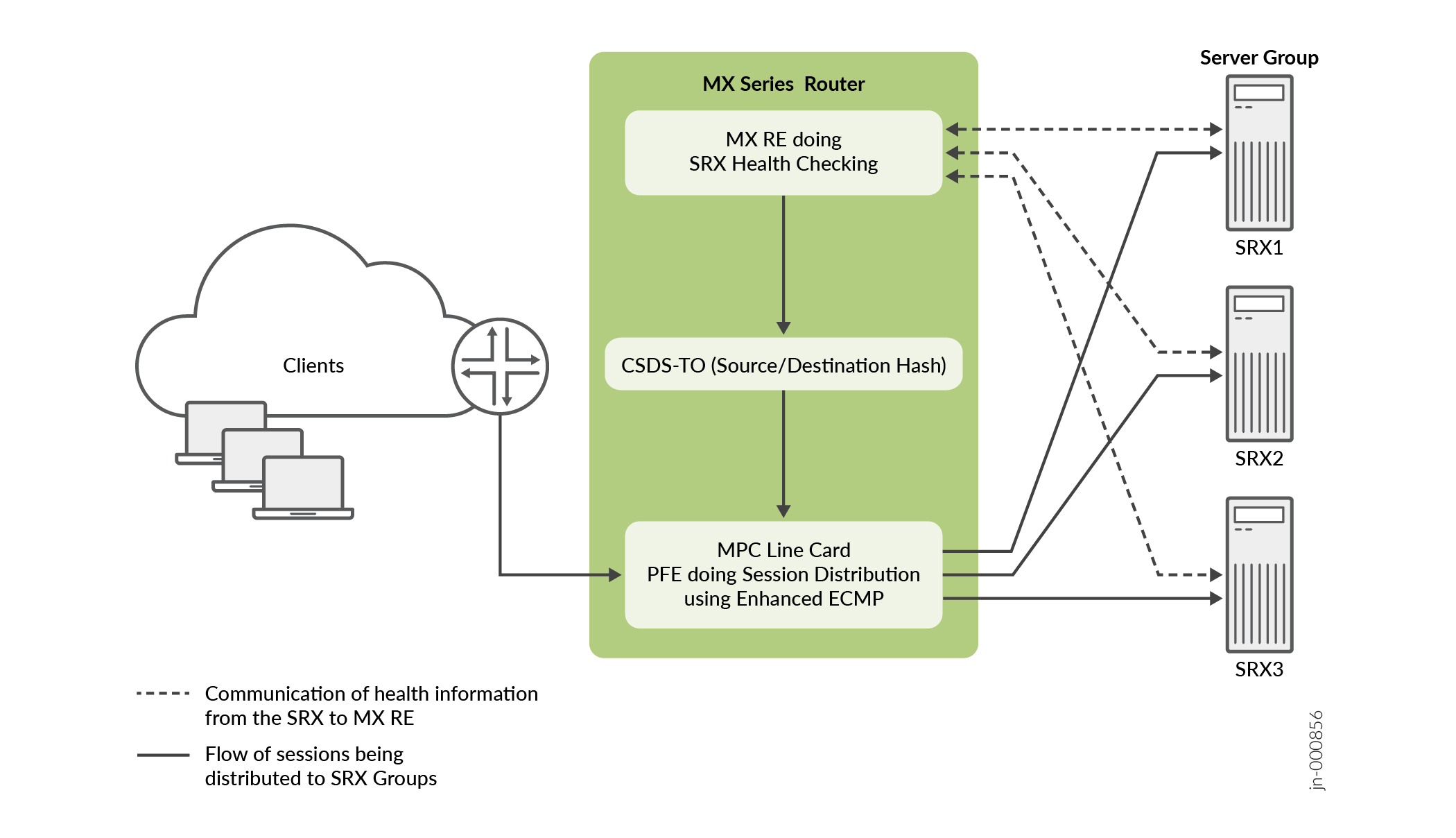
See Figure 1 to understand CSDS-TO in MX Series. The CSDS-TO functionality on the MX Series router:
-
Configures a list of available SRX Series Firewall addresses. The Packet Forwarding Engine programs the selector table based on these firewalls.
-
Performs ICMP-based health check for each SRX Series Firewall using the Routing Engine of the MX Series router. The RE-based health checks support probe types such as ICMP, TCP, UDP, HTTP, and SSL. When a firewall passes the health check, CSDS-TO installs either a specific IP route or a wildcard IP route in the routing table with a next hop that represents a composite next hop.
The MX Series router programs the composite next hop in the Packet Forwarding Engine with all available SRX Series Firewalls in the selector table. Filter-based forwarding enables the client-to-server traffic to be directed to the CSDS-TO. The MX Series router matches the specific IP route or the wildcard IP route to distribute the traffic between the available SRX Series Firewalls by using source or destination hash. The server-to-client is directly routed back to the client, bypassing the CSDS-TO.
RE-Based Health Check for CSDS Traffic Orchestrator
CSDS-TO runs the health check process on the Routing Engine instead of the service PIC on the next generation MX Series routers. This feature is applicable for both multiservices PICs (MSP) and unified services framework (USF).
To enable the health-check
process,net-monitord
on
the
Routing
Engine,
you can use the command
set services traffic-load-balance
routing-engine-mode. This configuration
ensures
that the process responsible for managing and orchestrating traffic
distribution and redirection connects to the local instance of the
network monitoring process instead of the remote instance running on
the service
PIC.
The supported health-check probe types are ICMP, TCP, UDP, HTTP, and SSL probes.
The loopback interface is used instead of the service interface for the CSDS-TO configuration.
CSDS-TO doesn't need the interfaces ms-x/y/0 or vms-x/y/0 respectively, for MSP and USF when net-monitord is running on Routing Engine. Replace reference of the ms-x/y/0 or vms-x/y/0 interface with loopback interface lo.x.
instance Instance_V4 {
interface lo0.0; #loop back interface instead of ms-interface#
client-interface ge-2/2/4.0;
server-interface ge-2/2/5.0;
client-vrf client_vrf_1;
server-vrf server_vrf_1;
group group1 {
real-services [ rs_1 rs_2 rs_3 rs_4 rs_5 rs_6 rs_7 rs_8 ];
routing-instance server_vrf_1;
health-check-interface-subunit 0;
network-monitoring-profile nm_prof_icmp;
}
}To enable Routing Engine-based health checks, you must configure
the routing-engine-mode
option
to
enable
net-monitord on
the
Routing Engine.
Junos
OS
validates
the configuration and
ensures
that both interface ms-x/y/0.0 or
interface vms-x/y/0.0 cannot be configured together in the
respective mode of operation, namely, MSP or USF.
