Stateful Firewall and NAT Traffic Flow in Dual MX Series Routers (ECMP-Based Consistent Hashing) and Scaled-Out SRX Series Firewalls (MNHA)
In this topic, you’ll see how stateful firewall traffic flows in a dual MX Series router with ECMP-based Consistent Hashing load balancing with the SRX Series Firewalls in MNHA.
Figure 1 illustrates the topology for dual MX Series routers with ECMP-based Consistent Hashing and scaled-out SRX Series Firewalls using MNHA.
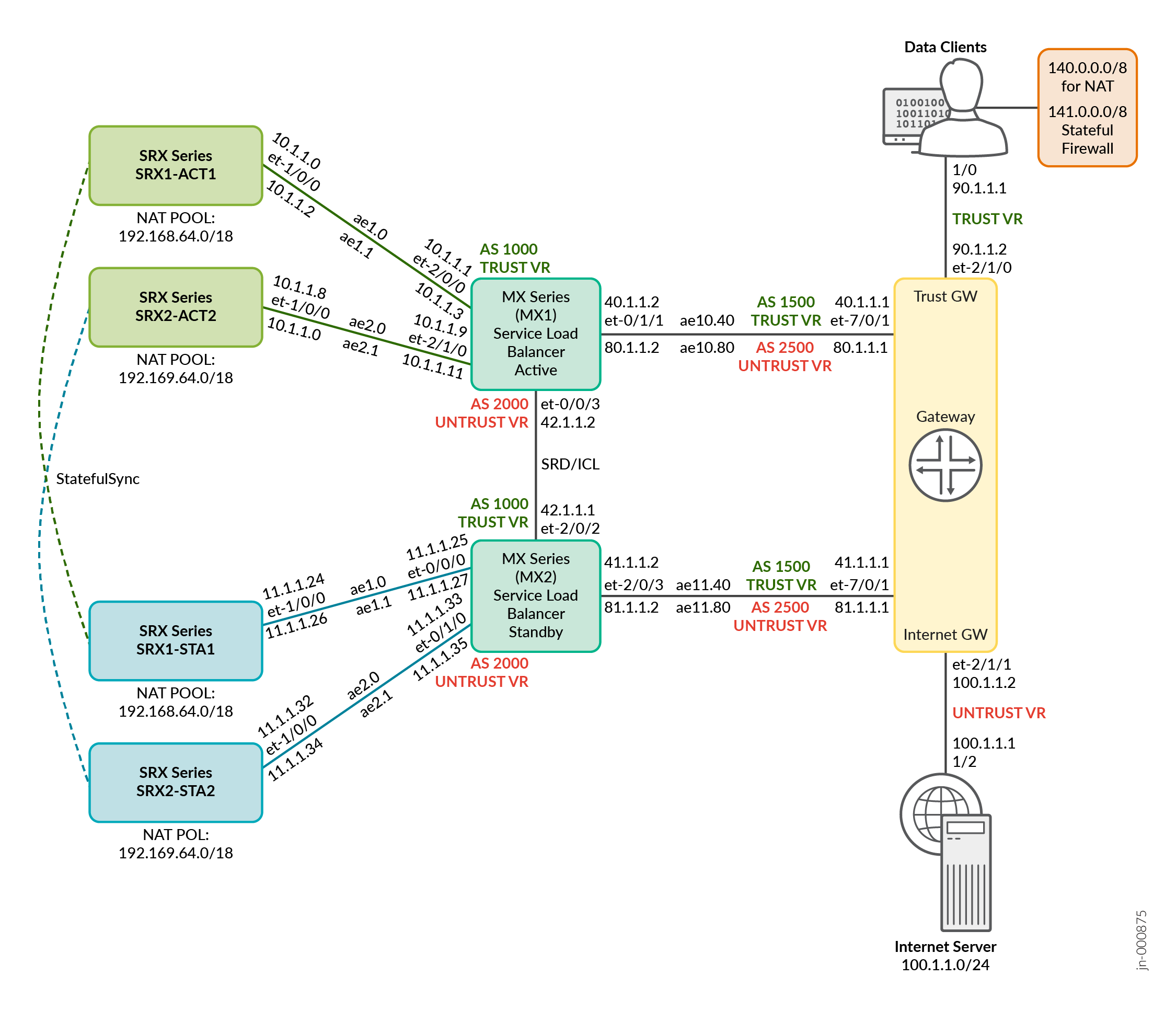
In this topology:
- Configure the pair of MX Series routers in HA with Active/Standby mode.
- Configure the SRX Series Firewalls in MNHA pair in Active/Backup mode with session synchronization. SRX1-ACT1 and SRX2-ACT2 are in MNHA pair and SRX1-STA1 and SRX2-STA2 form the other MNHA pair. SRX1-ACT1 and SRX1-STA1 are in stateful synchronization and SRX1-ACT2 and SRX1-STA2 are in stateful synchronization.
- When you deploy SRX Series Firewalls in MNHA pair, session synchronization occurs in both the directions depending on where traffic is received.
- Configure the pair of MX Series routers with service redundancy daemon (SRD) redundancy for the user management of the MX Series HA pair. See Service Redundancy Daemon.
- The pair of MX Series routers monitor links towards the TRUST and Internet gateway router, and the links between MX Series routers and SRX Series Firewalls. The SRD triggers automatic switchover to the other MX Series router if any of the links fail. Failover happens even when the primary MX Series router is down.
- The MX Series router with 4x100G interface connected to the SRX Series Firewalls as an AE bundle contains 3 VLANs (trust, untrust, and HA management).
- Primary MX Series remains as the primary ECMP path and the secondary MX Series router is the standby ECMP path.
- Use SRD for the MX Series routers redundancy and control the primary MX Series router state transition.
- The SRD process installs a signal route on the primary MX Series router that is used for route advertisement with preference.
- The primary MX Series router advertises routes as it is, whereas the standby MX Series advertises routes with as-path-prepend. Expanding an AS path makes a shorter AS path look longer and therefore less preferable to BGP. See Understanding Adding AS Numbers to BGP AS Paths.
- Interfaces on the primary MX Series towards SRX Series Firewall and Secondary MX Series towards SRX Series Firewall must be provisioned using similar interface numbering with similar I/O card (IOC). This helps in maintaining the same unilist next-hop ordering on both the MX Series routers.
- Unilist next-hop ordering is decided by the routing protocol daemon (RPD) based on the logical interface (ifl) index number (Ascending order of logical interface (ifl) numbers).
- Since unilist next-hop ordering is same in both MX Series routers, there won’t be any issue with hash (source or destination) post any router switchover.
Figure 2 illustrates the stateful synchronization in MNHA pair. Here, the pairs SRX1-ACT1 and SRX1-STA1 are in stateful synchronization. The pairs SRX1-ACT2 and SRX1-STA2 are in stateful synchronization.
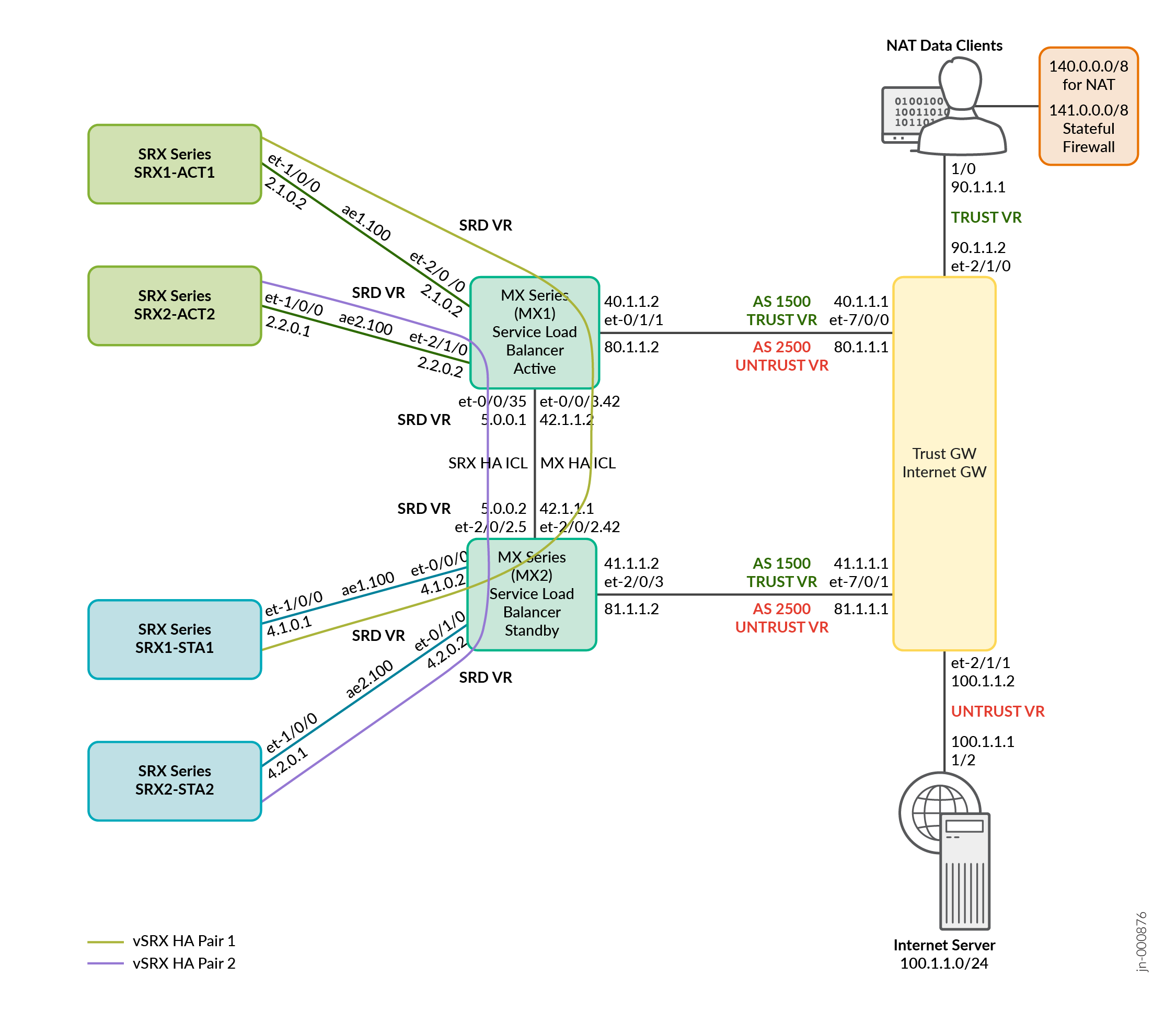
Figure 3 illustrates the NAT traffic flow.
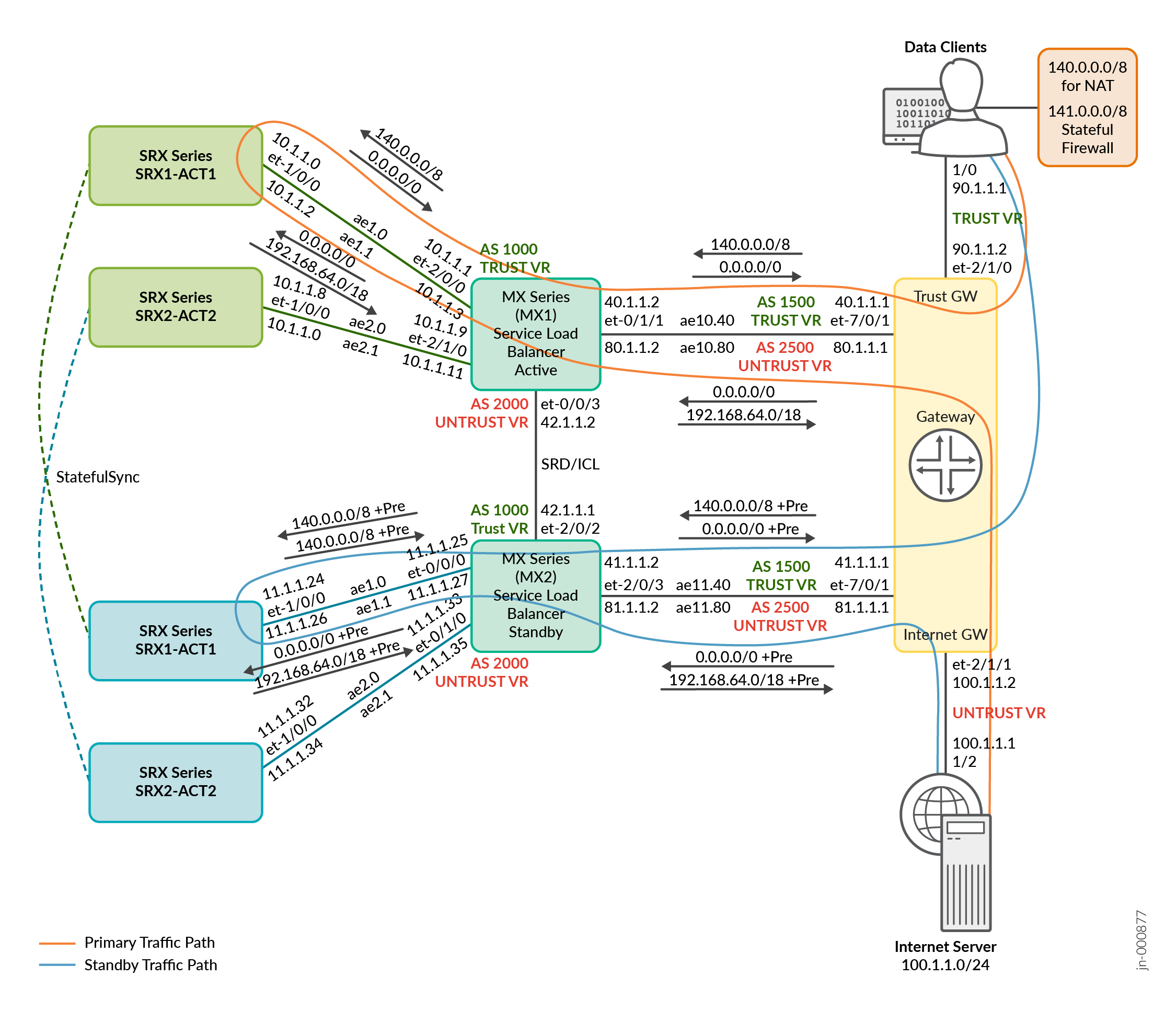
Figure 4 illustrates the stateful firewall traffic flow.

