Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternates (TI-LFA)
The Juniper Cloud-Native Router supports Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternates (TI-LFA) with fast reroute (FRR) for SR-MPLS implementations.
TI-LFA Overview
Fast Reroute (FRR)
Fast Reroute (FRR) technology is used in modern routing protocols to minimize disruption and packet loss in the event of a network failure. Unlike traditional routing protocols, FRR speeds up the convergence process by proactively pre-computing backup paths for critical traffic flows. The backup paths are readily available and instantly activated upon failure, ensuring minimum loss of data communication.
Loop-Free Alternates (LFAs) play a critical role in FRR implementations. LFAs are pre-calculated, loop-free backup paths that are leveraged by FRR protocols to quicky switch traffic to the chosen backup path.
There are two key aspects to FRR:
-
Detection:
-
Fault Detection—Rapidly identify link or node failures within a network through continuous monitoring of network elements.
-
Detection Methods—Applying one of the various methods for fault detection, including proactive methods such as periodic link probing or reactive methods that sense failure when it occurs. In some cases Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) may be used for quick fault detection. Cloud-Native Router detects failure by monitoring the link status events from the Poll Mode Driver (PMD).
-
-
Handling:
-
Precomputed Backup Paths—Using predetermined and optimised backup paths that are quickly activated when a failure is detected.
-
Fast Switchover—Network devices participating in the FRR process quickly switching to precomputed backup paths to minimize the impact on the network's forwarding capabilities.
-
Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternates (TI-LFA)
IS-IS and OSPF can calculate LFA backup paths in a plain IP network. However, the LFA feature requires any backup path to be guaranteed loop-free. For this reason, in a plain IP network, LFA cannot offer backup paths to every single known destination. LFA only offers partial topology coverage. TI-LFA is a topology independent implementation of LFA. TI-LFA can push a Segment ID stack that can navigate around any potential loops along the backup path. In other words, backup paths can be calculated independent of the topology. It defines LFAs based on the traffic flow itself and can function effectively regardless of the underlying network layout. TI-LFA uses the pre-computed post-convergence path of the routing protocol. TI-LFA finds the path that would be calculated in the event of a particular link or node failure, and uses that exact path as the backup path. This is not always possible in regular LFA, due to the requirement for a loop-free backup path. By using the post-convergence path, TI-LFA reduces jitter during failover and the network operator only needs to ensure the network has enough capacity to carry the traffic on the post-convergence path after a failure. TI-LFA has multiple advantages:
-
Simplified configuration—TI-LFA automatically computes backup paths, eliminating the need to manually configurate LFAs for each network element.
-
Faster failover—TI-LFA uses the pre-computed post-convergence path of the routing protocol that enables it to activate backup paths significantly faster than traditional LFAs.
-
Improved scalability—TI-LFA scales efficiently in large and complex networks because it is topology independent in contrast to LDP and RSVP which require additional state to create backup paths.
Cloud-Native Router supports TI-LFA for SR-MPLS implementations with link and node failure protection. You can read more about TI-LFA in the Junos documentation.
An IGP identifies the primary and post-convergence (backup for TI-LFA) paths for a prefix based on its criterion. The paths are associated with a weight metric to signify priority (numerically lower the weight, higher the priority). The paths are calculated during the network's initial setup and stored in the routers' forwarding tables.
When link protection is implemented, TI-LFA uses the pre-computed post-convergence path of the routing protocol as the backup path to bypass a protected link. When an upstream node detects a link failure, it immediately initiates the pre-computed backup path to reroute the packet, bypassing the failed failed link.
When node protection is implemented, TI-LFA uses the pre-computed post-convergence path of the routing protocol as the backup path to bypass a protected node's Segment Identifier (SID). When an upstream node detects an intermediate node failure, it immediately initiates the pre-computed backup path to reroute the packet, bypassing the failed node entirely. This process ensures minimal packet loss and maintains network connectivity even in the event of node failures.
When both link-protection and node-protection are implemented, the Cloud-Native Router prefers backup paths that avoid the failed node entirely, rather than just the failed link.
The Cloud-Native Router control plane (cRPD) sends the primary and backup path to the data plane via the vRouter agent. The vRouter data plane implements FRR by identifying the primary path and quickly switching over to backup path if a link failure was detected.
Key points to note about the Cloud-Native Router TI-LFA implementation:
-
TI-LFA is supported for SR-MPLS on IS-IS implementations.
-
TI-LFA is supported for SR-MPLS on OSPF implementations (Tech Preview Feature Only)
-
TI-LFA is supported when Cloud-Native Router is deployed as head-end, transit or egress node in an SR-MPLS domain.
- Both TI-LFA node and link protection are supported.
-
Multiple primary and single backup path is supported.
-
Both physical and bond interfaces are supported (FRR is triggered for bond interfaces only if all the links in the bond are down).
-
BGP Multipath with underlay ECMP deployments are supported.
-
FRR is triggered based on link status events detected by the Poll Mode Drivers (PMD) followed by Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) updates.
TI-LFA Configuration (SR-MPLS on IS-IS)
Steps to configure TI-LFA
You must perform configuration on the Cloud-Native Router control plane using a Configlet. Review Customize Cloud-Native Router Configuration for more details.
Consider the following topology that uses IS-IS as IGP and BGP for VPN services.
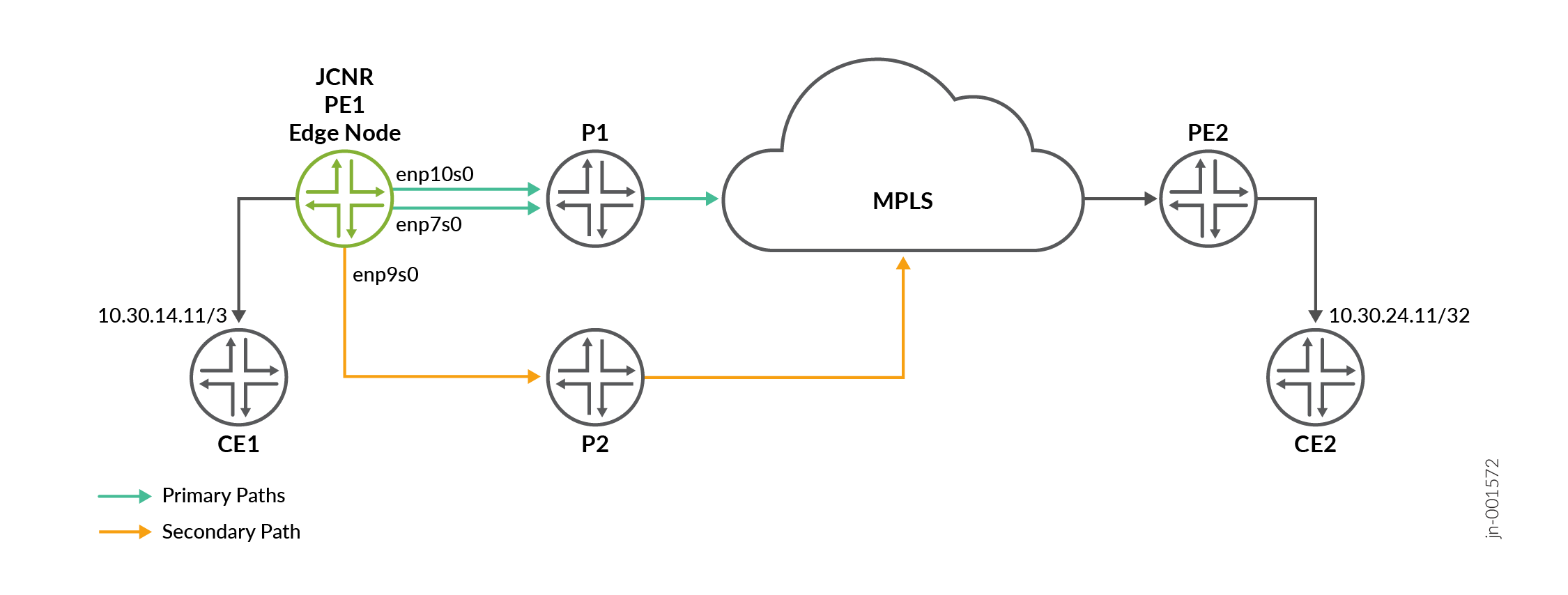
The configlet configures segment routing for IS-IS protocol. Key points to note:
- Segment routing configuration defines a node SID and segment routing global block (SRGB) range.
- Link protection is supported by default.
- The
maximum-backup-pathsis set to 1 since Cloud-Native Router supports only one backup path. -
The interfaces are configured to install backup route along the link-protecting post-convergence path.
-
The interfaces are also configured with node protection (Optional, if node protection is required).
apiVersion: configplane.juniper.net/v1 kind: Configlet metadata: name: configlet-sample namespace: jcnr spec: config: |- set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.23.23/32 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:192:168:23::23/128 set interfaces lo0 unit 0 family iso address 49.0001.000a.0a0a.0a00 set interfaces enp7s0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.133.3/24 set interfaces enp7s0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:172:16:133::3/64 set interfaces enp7s0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces enp9s0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.155.3/24 set interfaces enp9s0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:172:16:155::3/64 set interfaces enp9s0 unit 0 family iso set interfaces enp10s0 unit 0 family inet address 172.16.200.3/24 set interfaces enp10s0 unit 0 family inet6 address 2001:db8:172:16:23::23/64 set interfaces enp10s0 unit 0 family iso set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 type internal set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 multihop set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 local-address 192.168.23.23 set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 family inet-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 family inet6-vpn unicast set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 local-as 64512 set protocols bgp group jcnr-pe2 neighbor 192.168.23.24 set protocols mpls ultimate-hop-popping set protocols mpls ipv6-tunneling set protocols mpls interface lo0.0 set protocols mpls interface enp7s0 set protocols mpls interface enp9s0 set protocols mpls interface enp10s0 set protocols isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv4-index 1000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing node-segment ipv6-index 2000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing srgb start-label 400000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing srgb index-range 64000 set protocols isis source-packet-routing explicit-null set protocols isis backup-spf-options use-source-packet-routing set protocols isis backup-spf-options use-post-convergence-lfa maximum-backup-paths 1 set protocols isis interface enp7s0 level 2 post-convergence-lfa node-protection set protocols isis interface enp9s0 level 2 post-convergence-lfa node-protection set protocols isis interface enp10s0 level 2 post-convergence-lfa node-protection set protocols isis interface lo0.0 passive crpdSelector: matchLabels: node: workerVerify Configuration
- To verify the TI-LFA configuration you can access the cRPD shell
and verify Cloud-Native Router's support in a topology with multiple primary and
backup paths for the destination
10.30.24.11:user@host> show route 10.30.24.11/32 detail srmpls.inet.0: 3 destinations, 3 routes (3 active, 0 holddown, 0 hidden) 10.30.24.11/32 (1 entry, 1 announced) *BGP Preference: 170/-101 Route Distinguisher: 10.87.3.248:4 Next hop type: Indirect, Next hop index: 0 Address: 0x5906af9115fc Next-hop reference count: 4 Kernel Table Id: 0 Source: 192.168.23.24 Next hop type: Router, Next hop index: 0 Next hop: 172.16.200.2 via enp10s0 weight 0x1, selected Label operation: Push 34, Push 14400(top) Label TTL action: prop-ttl, prop-ttl(top) Load balance label: Label 34: None; Label 14400: None; Label element ptr: 0x5906ad31ef60 Label parent element ptr: 0x5906ad31e5d0 Label element references: 4 Label element child references: 0 Label element lsp id: 0 Session Id: 0 Next hop: 172.16.133.2 via enp7s0 weight 0x1 Label operation: Push 34, Push 14400(top) Label TTL action: prop-ttl, prop-ttl(top) Load balance label: Label 34: None; Label 14400: None; Label element ptr: 0x5906ad31ef60 Label parent element ptr: 0x5906ad31e5d0 Label element references: 4 Label element child references: 0 Label element lsp id: 0 Session Id: 0 Next hop: 172.16.155.6 via enp9s0 weight 0xf000 Label operation: Push 34, Push 17(top) Label TTL action: prop-ttl, prop-ttl(top) Load balance label: Label 34: None; Label 17: None; Label element ptr: 0x5906afa28288 Label parent element ptr: 0x5906afa282d0 Label element references: 2 Label element child references: 0 Label element lsp id: 0 Session Id: 0 Protocol next hop: 192.168.23.24 Label operation: Push 34 Label TTL action: prop-ttl Load balance label: Label 34: None; Indirect next hop: 0x5906ad550488 191 INH Session ID: 0, INH non-key opaque: (nil), INH key opaque: (nil) State: <Secondary Active Int Ext ProtectionCand> Peer AS: 64512 Age: 38 Metric2: 2 Validation State: unverified Task: BGP_64512_64512.192.168.23.24 Announcement bits (3): 2-KRT MFS 3-KRT 5-KRT-vRouter AS path: I Communities: target:64512:4 Import Accepted VPN Label: 34 Localpref: 100 Router ID: 192.168.23.24 Primary Routing Table: bgp.l3vpn.0 Thread: junos-main
-
Use the vRouter CLI to verify the interface list:
bash-5.1# vif --get 1 Vrouter Interface Table vif0/1 PCI: 0000:0a:00.0 NH: 6 MTU: 9000 Type:Physical HWaddr:52:54:00:48:cc:3f IPaddr:172.16.200.3 DDP: OFF SwLB: ON Vrf:0 Mcast Vrf:65535 Flags:L3Vof QOS:0 Ref:11 RX device packets:16897 bytes:1366043 errors:0 RX port packets:16897 errors:0 RX queue packets:16006 errors:0 RX queue errors to lcore 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Fabric Interface: 0000:0a:00.0 Status: UP Driver: net_virtio RX packets:16897 bytes:1366043 errors:0 TX packets:6997 bytes:619574 errors:0 Drops:0 TX queue packets:6551 errors:0 TX port packets:6997 errors:0 TX device packets:7012 bytes:620872 errors:0 bash-5.1# vif --get 2 Vrouter Interface Table vif0/2 PCI: 0000:07:00.0 NH: 8 MTU: 9000 Type:Physical HWaddr:52:54:00:fe:c1:b8 IPaddr:172.16.133.3 DDP: OFF SwLB: ON Vrf:0 Mcast Vrf:65535 Flags:L3Vof QOS:0 Ref:11 RX device packets:8745 bytes:734002 errors:0 RX port packets:8745 errors:0 RX queue packets:6691 errors:0 RX queue errors to lcore 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Fabric Interface: 0000:07:00.0 Status: UP Driver: net_virtio RX packets:8745 bytes:734002 errors:0 TX packets:18638 bytes:1480527 errors:0 Drops:0 TX queue packets:16768 errors:0 TX port packets:18638 errors:0 TX device packets:18654 bytes:1481955 errors:0 bash-5.1# vif --get 4 Vrouter Interface Table vif0/4 PCI: 0000:09:00.0 NH: 12 MTU: 9000 Type:Physical HWaddr:52:54:00:a0:7c:7f IPaddr:172.16.155.3 DDP: OFF SwLB: ON Vrf:0 Mcast Vrf:65535 Flags:L3Vof QOS:0 Ref:15 RX device packets:6893 bytes:614723 errors:0 RX port packets:6847 errors:0 RX queue packets:5956 errors:0 RX queue errors to lcore 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Fabric Interface: 0000:09:00.0 Status: UP Driver: net_virtio RX packets:6847 bytes:608077 errors:0 TX packets:6843 bytes:614550 errors:0 Drops:0 TX queue packets:6398 errors:0 TX port packets:6843 errors:0 TX device packets:6894 bytes:620209 errors:0 - On the vRouter
CLI use the
frr --dumpcommand to verify the FRR state before any FRR trigger.vif1andvif2are primary interfaces whilevif4is secondary. Thenhchain --getcommand shows the hierarchical next hops.bash-5.1# frr --dump FRR VIF Entry Table Flags: Delete Marked=Dm, Active=A VifID Type Flags Count NH(Composite,Component) ------------------------------------------------------------ 4 VIF A 10 (53,18), (54,24), (57,18), (58,18), (73,24), (76,74), (77,74), (78,74), (79,74), (83,74), 1 VIF A 12 (53,46), (54,56), (57,56), (58,61), (71,46), (72,56), (73,46), (76,61), (77,61), (78,61), (79,61), (83,61), 2 VIF A 10 (54,50), (57,50), (71,50), (72,48), (73,48), (76,51), (77,51), (78,51), (79,51), (83,51),bash-5.1# rt --get 10.30.24.11/32 --vrf 3 Match 10.30.24.11/32 in vRouter inet4 table 0/3/unicast Flags: L=Label Valid, P=Proxy ARP, T=Trap ARP, F=Flood ARP, Ml=MAC-IP learnt route vRouter inet4 routing table 0/3/unicast Destination PPL Flags Label Nexthop Stitched MAC(Index) 10.30.24.11/32 0 PT - 81 -
bash-5.1# nhchain --get 81 Id:81 Type:Indirect Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:77 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:6509475 Flags:Valid, Etree Root, Id:77 Type:Composite Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:0 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:6509475 Flags:Valid, Policy, Weighted Ecmp, FRR, Etree Root, Sub NH(label): 61(34) 51(34) 74(34) ECMP Weights: 1, 1, 61440, FRR State: 0 -> 1 FRR Updates: 0 FRR State Valid List: 1, 1, 1,bash-5.1# nhchain --get 77 Id:77 Type:Composite Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:0 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:6625699 Flags:Valid, Policy, Weighted Ecmp, FRR, Etree Root, Sub NH(label): 61(34) 51(34) 74(34) ECMP Weights: 1, 1, 61440, FRR State: 0 -> 1 FRR Updates: 0 FRR State Valid List: 1, 1, 1, Id:61 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_MPLS Rid:0 Ref_cnt:7 Vrf:0 Next NH:56 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:6625699 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, MPLS, Oif:1 Len:14 Data:52 54 00 4b 16 43 52 54 00 48 cc 3f 88 47 Number of Transport Labels:1 Transport Labels:14400, Id:56 Type:Encap Fmly:AF_INET/6 Rid:0 Ref_cnt:11 Vrf:0 Next NH:-1 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:6625699 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:1 Len:14 Encap Data: 52 54 00 4b 16 43 52 54 00 48 cc 3f Id:51 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_MPLS Rid:0 Ref_cnt:6 Vrf:0 Next NH:50 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:0 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, MPLS, Oif:2 Len:14 Data:52 54 00 ee 73 9b 52 54 00 fe c1 b8 88 47 Number of Transport Labels:1 Transport Labels:14400, Id:50 Type:Encap Fmly:AF_INET/6 Rid:0 Ref_cnt:11 Vrf:0 Next NH:-1 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:0 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:2 Len:14 Encap Data: 52 54 00 ee 73 9b 52 54 00 fe c1 b8 Id:74 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_MPLS Rid:0 Ref_cnt:6 Vrf:0 Next NH:18 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:0 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, MPLS, Oif:4 Len:14 Data:52 54 00 00 a9 14 52 54 00 a0 7c 7f 88 47 Number of Transport Labels:1 Transport Labels:17, Id:18 Type:Encap Fmly:AF_INET/6 Rid:0 Ref_cnt:17 Vrf:0 Next NH:-1 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:0 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:4 Len:14 Encap Data: 52 54 00 00 a9 14 52 54 00 a0 7c 7fIn the output above, only the primary next-hop (Id: 61) shows an increasing NH count, indicating that traffic is being forwarded exclusively through the primary path. The NH counts for the other next-hops remain at zero.
-
When primary interface
enp10s0is down, verify the FRR state:bash-5.1# frr --dump FRR VIF Entry Table Flags: Delete Marked=Dm, Active=A VifID Type Flags Count NH(Composite,Component) ------------------------------------------------------------ 4 VIF A 12 (47,20), (54,18), (57,18), (59,24), (60,20), (64,24), (65,18), (66,24), (67,24), (68,24), (69,24), (61,24), 1 VIF A 1 (72,56), 2 VIF A 13 (72,48), (47,50), (54,50), (57,51), (59,50), (60,48), (64,48), (65,48), (66,51), (67,51), (68,51), (69,51), (61,51),bash-5.1# rt --get 10.30.24.11/32 --vrf 3 Match 10.30.24.11/32 in vRouter inet4 table 0/3/unicast Flags: L=Label Valid, P=Proxy ARP, T=Trap ARP, F=Flood ARP, Ml=MAC-IP learnt route vRouter inet4 routing table 0/3/unicast Destination PPL Flags Label Nexthop Stitched MAC(Index) 10.30.24.11/32 0 PT - 46 -
bash-5.1# nhchain --get 46 Id:46 Type:Indirect Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:61 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:2710144 Flags:Valid, Etree Root, Id:61 Type:Composite Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:0 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:2710144 Flags:Valid, Policy, Weighted Ecmp, FRR, Etree Root, Sub NH(label): 51(34) 24(34) ECMP Weights: 1, 61440, FRR State: 0 -> 1 FRR Updates: 0 FRR State Valid List: 1, 1,bash-5.1# nhchain --get 61 Id:61 Type:Composite Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:0 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:2960544 Flags:Valid, Policy, Weighted Ecmp, FRR, Etree Root, Sub NH(label): 51(34) 24(34) ECMP Weights: 1, 61440, FRR State: 0 -> 1 FRR Updates: 0 FRR State Valid List: 1, 1, Id:51 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_MPLS Rid:0 Ref_cnt:12 Vrf:0 Next NH:50 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:3217248 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, MPLS, Oif:2 Len:14 Data:52 54 00 ee 73 9b 52 54 00 fe c1 b8 88 47 Number of Transport Labels:1 Transport Labels:14400, Id:50 Type:Encap Fmly:AF_INET/6 Rid:0 Ref_cnt:267 Vrf:0 Next NH:-1 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:3217248 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:2 Len:14 Encap Data: 52 54 00 ee 73 9b 52 54 00 fe c1 b8 Id:24 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_MPLS Rid:0 Ref_cnt:8 Vrf:0 Next NH:18 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:0 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, MPLS, Oif:4 Len:14 Data:52 54 00 00 a9 14 52 54 00 a0 7c 7f 88 47 Number of Transport Labels:1 Transport Labels:17, Id:18 Type:Encap Fmly:AF_INET/6 Rid:0 Ref_cnt:18 Vrf:0 Next NH:-1 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:0 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:4 Len:14 Encap Data: 52 54 00 00 a9 14 52 54 00 a0 7c 7fIn the output above, only the primary next-hop (Id: 51) shows an increasing NH count, indicating that traffic is being forwarded exclusively through the primary path. The NH counts for the other next-hops remain at zero. The FRR state for
vif1is cleared since the interface is down. -
Upon bringing the second primary interface
enp7s0down, verify the FRR state:bash-5.1# frr --dump FRR VIF Entry Table Flags: Delete Marked=Dm, Active=A VifID Type Flags Count NH(Composite,Component) ------------------------------------------------------------ 4 VIF A 1 (59,24), 1 VIF 0 2 VIF A 1 (59,50),bash-5.1# rt --get 10.30.24.11/32 --vrf 3 Match 10.30.24.11/32 in vRouter inet4 table 0/3/unicast Flags: L=Label Valid, P=Proxy ARP, T=Trap ARP, F=Flood ARP, Ml=MAC-IP learnt route vRouter inet4 routing table 0/3/unicast Destination PPL Flags Label Nexthop Stitched MAC(Index) 10.30.24.11/32 0 LPT 34 45 -
bash-5.1# nhchain --get 45 Id:45 Type:Indirect Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:2 Vrf:0 Next NH:23 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:2729760 Flags:Valid, Etree Root, Id:23 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_MPLS Rid:0 Ref_cnt:7 Vrf:0 Next NH:18 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:2729760 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, MPLS, Oif:4 Len:14 Data:52 54 00 00 a9 14 52 54 00 a0 7c 7f 88 47 Number of Transport Labels:1 Transport Labels:14400, Id:18 Type:Encap Fmly:AF_INET/6 Rid:0 Ref_cnt:530 Vrf:0 Next NH:-1 NH Label:0 NH Hit Count:2743094 Flags:Valid, Policy, Etree Root, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:4 Len:14 Encap Data: 52 54 00 00 a9 14 52 54 00 a0 7c 7fWith both primary paths down, only a single next-hop remains in the forwarding list. As a result, no FRR state is maintained. The VPN route now points to the tunnel that previously served as the secondary path.
- To verify the TI-LFA configuration you can access the cRPD shell
and verify Cloud-Native Router's support in a topology with multiple primary and
backup paths for the destination
