ON THIS PAGE
Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol (TWAMP)
The Cloud-Native Router supports Two-Way Active Management Protocol (TWAMP) for network performance measurement and monitoring in 5G transport networks. It supports managed and light TWAMP.
The Two-Way Active Management Protocol (TWAMP), described in RFC 5357, is a network performance measurement and monitoring service used for active performance monitoring of 5G transport networks. TWAMP is an extension of the One-Way Active Management Protocol (OWAMP) providing two-way or round-trip measurements instead of unidirectional capabilities. Two-way measurements do not require local and remote clock synchronization. The remote host support can be limited to a simple echo function. TWAMP defines an open protocol for measuring two-way or round-trip metrics with greater accuracy than other methods by using time-stamps, while accounting for processing delays. Please review Understanding Two-Way Active Measurement Protocol topic for more details.
Juniper Cloud-Native Router supports two flavors of TWAMP implementation:
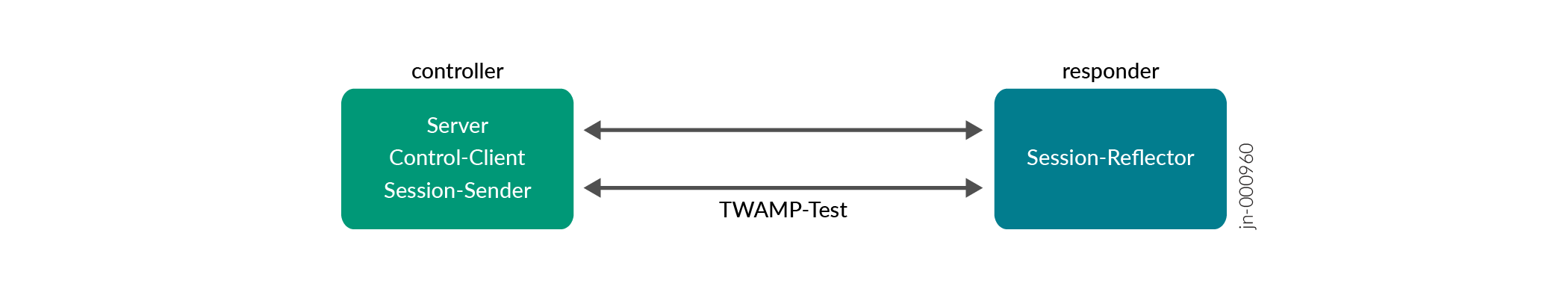
- Managed TWAMP—A TCP control connection is established between control client and responder server for exchanging test session information. Measurement and monitoring tests run between session-sender and session-reflector.
- Light TWAMP—No control connection is established between the control client and responder
server. The session-sender directly runs measurement and monitoring tests with the
session-reflector. The session-reflector has no knowledge of the session state.
Cloud-Native Router supports timestamping the TWAMP test packets by either the cRPD or vRouter. The cRPD timestamps are enabled by default. Since the Round Trip Time (RTT) for cRPD timestamps has higher jitter due to latency in the host network stack, vRouter timestamps may be preferred. The vRouter uses hardware timestamping if the underlying NIC supports it, else it defaults to the kernel system clock.
vRouter timestamping is supported for TWAMP light mode only.
Configuration
To enable vRouter timestamping, you must enable the twampPort
configuration in the Cloud-Native Router helm chart at the time of installation. The vRouter
listens to TWAMP test messages on the configured twampPort and overwrites
timestamps in TWAMP test packets. Please review the Customizing
Cloud-Native Router Helm Chart for more details. When not configured, cRPD
timestamps the TWAMP test packets.
You can configure the TWAMP server and client with minimum configuration. There are additional configuration parameters with default values which may be modified as per your requirement. Please review edit services rpm twamp command for more information on each configuration option. The default values for the options is provided in the below tables:
|
Option |
Default value |
|---|---|
|
control-type (light | managed) |
managed |
| destination-port (862 - 65535) |
862 |
|
history-size (0 - 512) |
50 |
|
moving-average-size (0 - 512) |
0 |
| persistent-results (enable | disable) |
disable |
|
target-address |
An IPv4 address. This field is mandatory for managed control-type. The configuration commit fails if configured for light control-type. |
|
tcp-keepcnt (1 - 50) |
6 |
|
tcp-keepidle (1 - 600 seconds) |
120 |
|
tcp-keepintvl (1 - 600 seconds) |
5 |
|
test-count (0 - 4294967290) |
0 |
|
test-interval (1 - 255) |
1 |
|
test-session (name) |
Mandatory |
|
data-size (60 - 1400) |
60 |
|
destination-port (862 - 65535) |
862 |
|
dscp-code-points |
000000 |
| probe-count (1 - 4294967290) | 1 |
|
probe-interval (1 - 255) |
1 |
|
Options |
Values |
|---|---|
|
port (862 - 65535) [light] |
862 |
|
max-connection-duration (0 - 120 hours) |
24 |
|
maximum-connections (0 - 1000) |
64 |
|
maximum-connections-per-client (1 - 500) |
64 |
|
maximum-sessions (1 - 2048) |
64 |
|
maximum-sessions-per-connection (1 - 1024) |
64 |
|
port (1 - 65535) [server] |
862 |
|
port (1 - 65535) [routing-instance-list] |
862 |
|
server-inactivity-timeout (0 - 30 minutes) |
15 |
|
tcp-keepcnt (1 - 50) |
6 |
|
tcp-keepidle (1 - 600 seconds) |
120 |
|
tcp-keepintvl (1 - 600 seconds) |
5 |
Sample TWAMP client and server configurations for managed or TWAMP light are provided below. Use the configlet resource to configure cRPD:
- TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Managed, Minimum Configuration)
- TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Managed, Optional Configuration)
- TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Light, Minimum Configuration)
- TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Light, Optional Configuration)
TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Managed, Minimum Configuration)
Client Configuration
set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 target-address 1.1.1.29 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session myTs1 target-address 21.21.21.29
Server Configuration
set services rpm twamp server client-list myClients address 21.21.21.0/24
TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Managed, Optional Configuration)
Client Configuration
set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 control-type managed set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 destination-interface ens2f0 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 destination-port 10000 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 history-size 50 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 moving-average-size 50 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 persistent-results set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 routing-instance routing-instance set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 source-address 2.2.2.29 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 target-address 21.21.21.29 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 tcp-keepcnt 10 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 tcp-keepidle 60 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 tcp-keepintvl 600 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-count 3 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-interval 10 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 data-fill-with-zeros set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 data-size 100 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 destination-port 65000 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 dscp-code-points 000001 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 probe-count 10 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 probe-interval 1 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 source-address 21.21.21.30 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 target-address 21.21.21.29 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcManaged1 test-session test1 ttl 5
Server Configuration
set services rpm twamp server authentication-mode none set services rpm twamp server client-list 192.168.11.0/24 set services rpm twamp server max-connection-duration 1 set services rpm twamp server maximum-connections 20 set services rpm twamp server maximum-connections-per-client 20 set services rpm twamp server maximum-sessions 30 set services rpm twamp server maximum-sessions-per-connection 30 set services rpm twamp server port 10000 set services rpm twamp server routing-instance-list <routing-instance> <port> set services rpm twamp server server-inactivity-timeout 10 set services rpm twamp server tcp-keepcnt 10 set services rpm twamp server tcp-keepidle 60 set services rpm twamp server tcp-keepintvl 600
TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Light, Minimum Configuration)
Client Configuration
set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 control-type light set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session myTs1 target-address 21.21.21.29
Server Configuration
set services rpm twamp server light
TWAMP Client/Server Configuration (Light, Optional Configuration)
Client Configuration
set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 control-type light set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 data-fill-with-zeros set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 data-size 100 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 destination-port 65000 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 dscp-code-points 000001 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 probe-count 10 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 probe-interval 1 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 source-address 21.21.21.30 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 target-address 21.21.21.29 set services rpm twamp client control-connection myTcLight1 test-session test1 ttl 5
Server Configuration
set services rpm twamp server control-type light
By default the client control connection test-count is set to zero. In
this case the TWAMP test automatically starts after the configuration is committed and
continues to run until the configuration is deleted. If test-count is
configured to a non-zero value, the TWAMP test must be started or stopped using below
commands:
user@host> request services rpm twamp start client control-client-name user@host> request services rpm twamp stop client control-client-name
Verification
- You can use the
show services rpm twamp client probe-resultscommand to verify the TWAMP probe results on cRPD shell:user@host> show services rpm twamp client probe-results Owner: myTcManaged1, Test: myTs1 server-address: 1.1.1.29, server-port: 862, Client address: 21.21.21.30, Client port: 35109 TWAMP-Server-Status: Connected, Number-Of-Retries-With-TWAMP-Server: 222 Reflector address: 21.21.21.29, Reflector port: 10029, Sender address: 21.21.21.30, sender-port: 10029 Test size: 1 probes Probe results: Response received Probe sent time: Thu Jun 13 06:34:14 2024 Probe rcvd/timeout time: Thu Jun 13 06:34:14 2024 Rtt: 968 usec, Egress jitter: 63 usec, Ingress jitter: -22 usec, Round trip jitter: 28 usec Egress interarrival jitter: 40 usec, Ingress interarrival jitter: 9 usec, Round trip interarrival jitter: 32 usec Results over current test: Probes sent: 1, Probes received: 1, Loss percentage: 0.000000 Measurement: Round trip time Samples: 1, Minimum: 968 usec, Maximum: 968 usec, Average: 968 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 968 usec Measurement: Positive egress jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 63 usec, Maximum: 63 usec, Average: 63 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 63 usec Measurement: Negative ingress jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 22 usec, Maximum: 22 usec, Average: 22 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 22 usec Measurement: Positive round trip jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 28 usec, Maximum: 28 usec, Average: 28 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 28 usec Results over last test: Probes sent: 1, Probes received: 1, Loss percentage: 0.000000 Test completed on Thu Jun 13 06:34:14 2024 Measurement: Round trip time Samples: 1, Minimum: 968 usec, Maximum: 968 usec, Average: 968 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 968 usec Measurement: Positive egress jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 63 usec, Maximum: 63 usec, Average: 63 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 63 usec Measurement: Negative ingress jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 22 usec, Maximum: 22 usec, Average: 22 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 22 usec Measurement: Positive round trip jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 28 usec, Maximum: 28 usec, Average: 28 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 28 usec Results over all tests: Probes sent: 5, Probes received: 5, Loss percentage: 0.000000 Measurement: Round trip time Samples: 5, Minimum: 892 usec, Maximum: 1186 usec, Average: 992 usec, Peak to peak: 294 usec, Stddev: 102 usec, Sum: 4958 usec Measurement: Positive egress jitter Samples: 3, Minimum: 63 usec, Maximum: 229 usec, Average: 125 usec, Peak to peak: 166 usec, Stddev: 74 usec, Sum: 375 usec Measurement: Negative egress jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 354 usec, Maximum: 354 usec, Average: 354 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 354 usec Measurement: Positive ingress jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 60 usec, Maximum: 60 usec, Average: 60 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 60 usec Measurement: Negative ingress jitter Samples: 3, Minimum: 22 usec, Maximum: 48 usec, Average: 33 usec, Peak to peak: 26 usec, Stddev: 11 usec, Sum: 98 usec Measurement: Positive round trip jitter Samples: 3, Minimum: 28 usec, Maximum: 203 usec, Average: 98 usec, Peak to peak: 175 usec, Stddev: 75 usec, Sum: 295 usec Measurement: Negative round trip jitter Samples: 1, Minimum: 298 usec, Maximum: 298 usec, Average: 298 usec, Peak to peak: 0 usec, Stddev: 0 usec, Sum: 298 usec
- Additional show commands
include:
show services rpm twamp client show services rpm twamp client connection connection-name show services rpm twamp client history-results show services rpm twamp client history-results brief show services rpm twamp client history-results control-connection control-connection show services rpm twamp client history-results detail show services rpm twamp client history-results detail control-connection control-connection show services rpm twamp client history-results detail control-connection control-connection test-session test-session show services rpm twamp client history-results detail since YYYY-MM-DD.HH:MM:SS show services rpm twamp client probe-results show services rpm twamp client probe-results control-connection control-connection show services rpm twamp client probe-results control-connection control-connection test-session test-session show services rpm twamp client session show services rpm twamp client session control-connection control-connection test-session test-session show services rpm twamp server show services rpm twamp server connection connection-id show services rpm twamp server session session-id
- If vRouter timestamping is enabled, you can verify hardware timestamping support for a
fabric interface by executing the following command on the vRouter
CLI:
bash-5.1# dpdkinfo -p 1 ********************* Infos for port 0 ********************* MAC address: B4:96:91:DA:D4:F8 Device name: 0000:af:00.0 Driver name: net_ice .. .. .. Max segment number per packet: 0 Max segment number per MTU/TSO: 0 Hardware timestamping support: Rx:Yes, Tx:Yes Device capabilities: 0x0( )
- If the underlying NIC supports hardware timestamping and vRouter timestamping is
enabled, you can verify hardware timestamp support for the fabric interface by executing
the following command on the vRouter CLI:
bash-5.1# vif --get 1 Flags: P=Policy, X=Cross Connect, S=Service Chain, Mr=Receive Mirror Mt=Transmit Mirror, Tc=Transmit Checksum Offload, L3=Layer 3, L2=Layer 2 D=DHCP, Vp=Vhost Physical, Pr=Promiscuous, Vnt=Native Vlan Tagged Mnp=No MAC Proxy, Dpdk=DPDK PMD Interface, Rfl=Receive Filtering Offload, Mon=Interface is Monitored Uuf=Unknown Unicast Flood, Vof=VLAN insert/strip offload, Df=Drop New Flows, L=MAC Learning Enabled Proxy=MAC Requests Proxied Always, Er=Etree Root, Mn=Mirror without Vlan Tag, HbsL=HBS Left Intf HbsR=HBS Right Intf, Ig=Igmp Trap Enabled, Ml=MAC-IP Learning Enabled, Me=Multicast Enabled LsDp=Link down in DP only, Ccc=CCC Enabled, HwTs=Hardware support for Timestamp vif0/1 PCI: 0000:af:00.0 (Speed 10000, Duplex 1) NH: 6 MTU: 9000 Type:Physical HWaddr:b4:96:91:da:d4:f8 IPaddr:110.110.110.22 IP6addr:110:110::110:22 DDP: OFF SwLB: ON Vrf:0 Mcast Vrf:0 Flags:TcL3VofHwTs QOS:0 Ref:14 RX port packets:93509698 errors:0 RX queue errors to lcore 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Fabric Interface: 0000:af:00.0 Status: UP Driver: net_ice RX packets:93509698 bytes:8602892343 errors:0 TX packets:124162093 bytes:11422912735 errors:0 Drops:324 TX port packets:124162084 errors:0
bash-5.1# vif --get 2 Flags: P=Policy, X=Cross Connect, S=Service Chain, Mr=Receive Mirror Mt=Transmit Mirror, Tc=Transmit Checksum Offload, L3=Layer 3, L2=Layer 2 D=DHCP, Vp=Vhost Physical, Pr=Promiscuous, Vnt=Native Vlan Tagged Mnp=No MAC Proxy, Dpdk=DPDK PMD Interface, Rfl=Receive Filtering Offload, Mon=Interface is Monitored Uuf=Unknown Unicast Flood, Vof=VLAN insert/strip offload, Df=Drop New Flows, L=MAC Learning Enabled Proxy=MAC Requests Proxied Always, Er=Etree Root, Mn=Mirror without Vlan Tag, HbsL=HBS Left Intf HbsR=HBS Right Intf, Ig=Igmp Trap Enabled, Ml=MAC-IP Learning Enabled, Me=Multicast Enabled LsDp=Link down in DP only, Ccc=CCC Enabled, HwTs=Hardware support for Timestamp vif0/2 PMD: enp175s0f0 NH: 9 MTU: 9000 Type:Host HWaddr:b4:96:91:da:d4:f8 IPaddr:110.110.110.22 IP6addr:110:110::110:22 DDP: OFF SwLB: ON Vrf:0 Mcast Vrf:65535 Flags:L3DProxyEr QOS:-1 Ref:11 TxXVif:1 RX device packets:182 bytes:17063 errors:0 RX queue packets:182 errors:0 RX queue errors to lcore 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Twamp RX packets:84 errors:0 Twamp TX packets:84 errors:0 RX packets:182 bytes:17063 errors:0 TX packets:174 bytes:16189 errors:0 Drops:0 TX queue packets:174 errors:0 TX device packets:174 bytes:16189 errors:0
