Install Juniper BNG CUPS
This section describes installation procedures and system requirements for Juniper BNG CUPS.
Juniper BNG CUPS disaggregates the broadband network gateway (BNG) function running in Junos OS into separate control plane and user plane components. The control plane is a cloud-native application that runs in a Kubernetes environment. The user plane component continues to run on Junos OS on a dedicated hardware platform.
The installation instructions in this guide are for the disaggregated control plane component of the Juniper BNG CUPS solution. In the Juniper BNG CUPS solution, the control plane is referred to as Juniper BNG CUPS Controller (BNG CUPS Controller). The BNG CUPS Controller component requires a Kubernetes cluster that consists of multiple nodes.
The BNG CUPS Controller can be installed on a single Kubernetes cluster or on a multiple geographical, multiple cluster setup. The installation requirements and installation process for these two types of setups are different. See the followings sections for your BNG CUPS Controller setup:
BNG CUPS Controller Installation Requirements
To install BNG CUPS Controller, you need the hardware and software requirements listed in this section.
- BNG CUPS Controller Requirements for a Single Geography Setup
- BNG CUPS Controller Requirements for a Multiple Geography Setup
- Additional Requirements
BNG CUPS Controller Requirements for a Single Geography Setup
BNG CUPS Controller installs on a Kubernetes cluster that consists of physical or virtual machines. For availability, you must have at least three nodes in the cluster.
BNG CUPS Controller requires the minimum resources listed in Table 1, from the Kubernetes cluster.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes cluster |
The Kubernetes cluster requires the following:
This specification establishes a cluster that can run BNG CUPS Controller as well as its companion applications such as BBE Event Collection and Visualization and Address Pool Manager (APM) simultaneously. |
|
Jump host |
The jump host requires the following:
|
|
Jump host software |
The jump host requires the following software:
|
|
Storage |
A storage class named jnpr-bbe-storage. |
|
Network load balancer address |
Two for TCP and UDP load balancing services. |
|
Registry storage |
Each BNG CUPS Controller release requires 2 gibibytes (GiB) of container images. |
BNG CUPS Controller Requirements for a Multiple Geography Setup
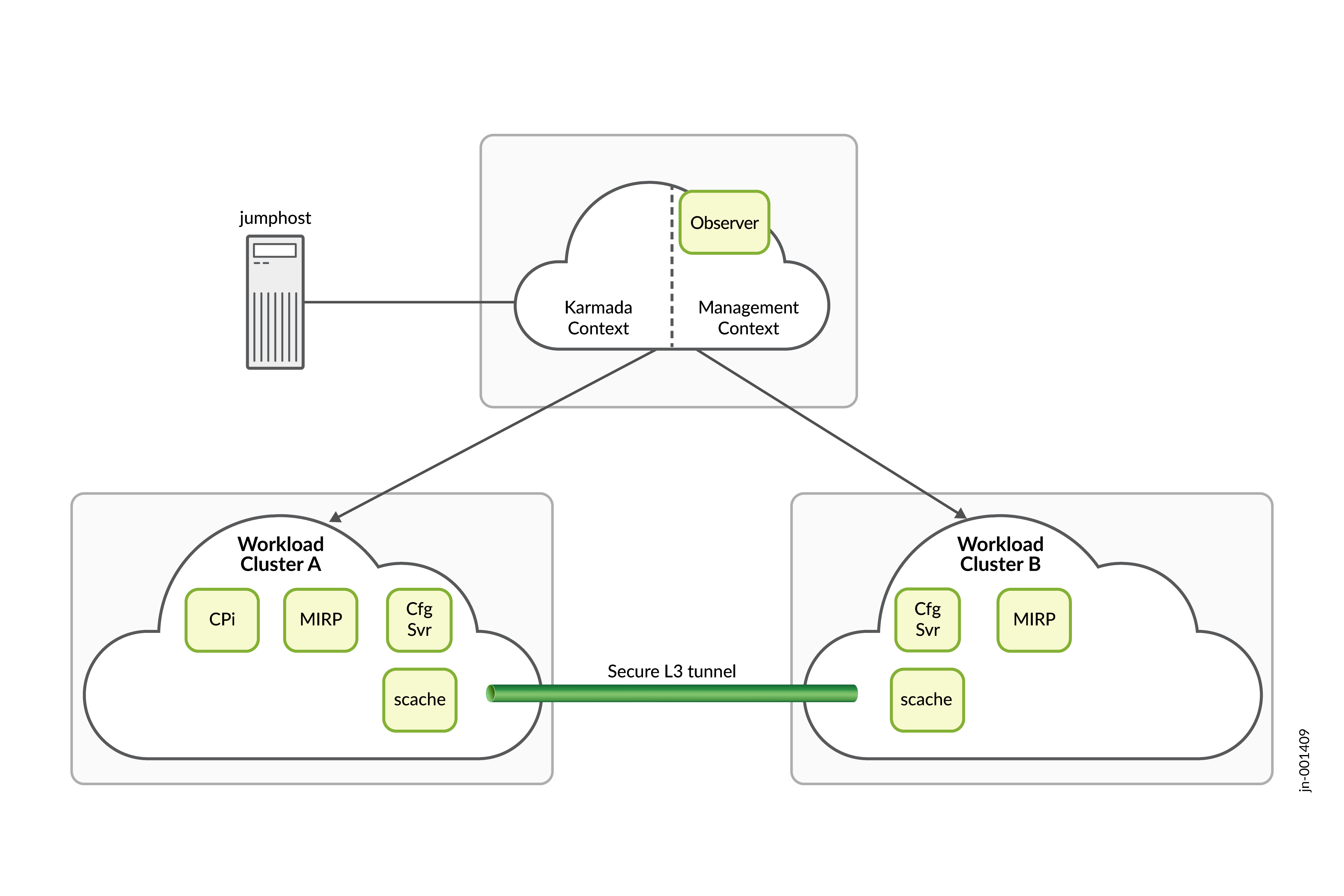
A geographically redundant, multiple cluster BNG CUPS Controller setup consists of three separate Kubernetes clusters. Each of the three clusters is geographically separated, so that service impacting events affecting one cluster do not affect the other clusters. The clusters which comprise the multiple cluster setup take on specific roles.
One cluster takes on the role of the management cluster and the other two clusters take on the role of workload clusters. The workload clusters provided a redundant platform where most of BNG CUPS Controller application runs. The management cluster runs software that monitors the health of the workload clusters and determines whether BNG CUPS Controller should switchover from one workload cluster to the other.
Each Kubernetes cluster in the multiple cluster consists of physical or virtual machines (VMs).
For POC installations, you cannot use the BBE cloudsetup utility to build the clusters used in a multiple geography multiple cluster setup. A separate procedure is available through support to build a POC multiple geography multiple cluster setup.
BNG CUPS Controller requires the minimal resources listed in Table 2, from the Kubernetes cluster.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
|
Cluster |
The multiple cluster consists of three clusters with each cluster consisting of 3 hybrid nodes. The three clusters must consist of one management cluster and two workload clusters. Note:
Make sure that the pod and service CIDRs for each workload cluster do not overlap. The cluster internal networks of each workload cluster are connected by a Submariner IP tunnel. The internal CIDRS must be distinct. |
|
Management cluster |
The management cluster requires the following:
|
| Workload cluster |
Each workload cluster requires the following:
This specification establishes a cluster that can run BNG CUPS Controller as well as its companion applications such as BBE Event Collection and Visualization and APM simultaneously. |
|
Jump host |
The jump host requires the following:
|
|
Jump host software |
The jump host requires the following software for production systems:
|
|
Storage |
A storage class named jnpr-bbe-storage |
|
Network load balancer address |
Two for the TCP and UDP load balancing services for each workload cluster. One for the TCP load balancing service for the management cluster |
|
Registry storage |
Each BNG CUPS Controller release requires 2.5 gibibytes (GiB) of container images. Required for each cluster. |
In a single geography BNG CUPS Controller setup, you can make some basic assumptions about the cluster's parameters. You can use a quick start tool like BBE Cloudsetup to create a single geography BNG CUPS Controller. The construction of a production environment BNG CUPS Controller setup with multiple geographies and multiple clusters requires much more input from you to build.
Additional Requirements
To use Juniper BNG CUPS, you must purchase a license for both the Juniper BNG CUPS Controller (control plane) and the Juniper BNG User Planes (user planes) associated to the Juniper BNG CUPS Controller. For information about how to purchase a software license, contact your Juniper Networks sales representative at https://www.juniper.net/in/en/contact-us/.
The MX Series devices that you are using in your Juniper BNG CUPS environment also require their own separate licenses. For information about how to purchase hardware, contact your Juniper Networks sales representative at https://www.juniper.net/in/en/contact-us/.
Confirm that you have a juniper.net user account with permissions to download the BNG CUPS Controller software package. Download and install the BNG CUPS Controller software from a machine that will not be part of the Kubernetes cluster.
Install Juniper BNG CUPS Controller in a Single Geography Setup
Use the procedures in this section to install Juniper BNG CUPS Controller in a single geography setup for the first time.
Before you begin, confirm that you have met the requirements for the BNG CUPS Controller installation (see Table 1).
You have the following two options for creating the Kubernetes cluster that you can install BNG CUPS Controller on:
-
BBE Cloudsetup—For installation instructions, see BBE Cloudsetup Installation Guide.
Note:BBE Cloudsetup is a utility that you can use to quickly get started with using BNG CUPS Controller. It is not a life cycle tool for the cluster. You cannot expand the width of the cluster, perform node maintenance, upgrade infrastructure components, and so on. A Kubernetes cluster for production purposes should be designed and constructed with the requirements of the production environment and with appropriate support to maintain its life cycle.
-
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform—For installation instructions, see the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform documentation.
Before starting the BNG CUPS Controller installation, make sure that you have the following information:
Required Information:
-
Container registry details:
-
If you are using a BBE Cloudsetup created cluster:
-
External registry address
-
External registry port number (usually 5000)
-
-
If you are using a Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform cluster:
-
External registry (FQDN)
-
Internal (Docker) registry address
-
Internal (Docker) registry port number
-
-
Optional Information:
- Storage class name for persistent volume claim (PVC) creation (default is jnpr-bbe-storage).
- PVC Size (defaults is 90 MiB).
-
Syslog server details—Syslog server information is required if you are planning to export BNG CUPS Controller logs to an external syslog collector.
-
Syslog server address
-
Syslog server port number
-
Install the BNG CUPS Controller Application (Single Geography)
Start BNG CUPS Controller in a Single Geography Setup
Use this procedure to configure and to start BNG CUPS Controller in a single geography setup.
Install Juniper BNG CUPS Controller in a Multiple Geography Setup
Use the installation procedures in this section for a BNG CUPS Controller setup that consists of multiple BNG CUPS Controllers that are located in different geographical locations.
Before you begin, confirm that you have met the requirements for the BNG CUPS Controller installation (see Table 2).
Before starting the BNG CUPS Controller installation, make sure that you have the following information:
You must collect the information listed below for all three clusters.
-
The cluster context names of the workload clusters, the management cluster's karmada context and the management cluster's working context
-
Karmada kubeconfig secret name—The kubeconfig file for the Karmada context on the management cluster. You can extract the kubeconfig file for the Karmada context from the management cluster context in the karmada-system namespace.
For an example of the command to run, see the following:
kubectl get secrets -n karmada-system --context <management-context-name> -o jsonpath='{.data.karmada \.config}' | base64 -d > karmada-secret-file -
Container registry details for each cluster:
-
External registry address
-
External registry port number (usually 5000)
-
-
Syslog server details—Syslog server information is required if you are planning to export BNG CUPS Controller logs to an external syslog collector.
-
Syslog server address
-
Syslog server port number
-
-
Kubeconfig for the management cluster.
Install the BNG CUPS Controller Application (Multiple Geography Setup)
Start BNG CUPS Controller in a Multiple Geography Setup
Use this procedure to configure and to start BNG CUPS Controller in a multiple geography setup.
Install a BNG User Plane
The BNG User Planes that you use as part of Juniper BNG CUPS are the MX Series routers that you have installed in your network. BNG User Planes (MX Series routers) run Junos OS, if you need to install a BNG User Plane, see Junos® OS Software Installation and Upgrade Guide.