DNS Tunnel Detection Overview
DNS Tunneling is a cyber-attack method that encodes the data of other programs or protocols in DNS queries and responses. It indicates that DNS traffic is likely to be subverted to transmit data of another protocol or malware beaconing.
When a DNS packet is detected as tunneled, the SRX Series Firewall can take permit, deny or sinkhole action.
DNS Tunneling detection is available only with ATP Cloud license. For feature specific licensing information, see Software Licenses for ATP Cloud.
SRX Series Firewall exports the tunneling metadata to Juniper ATP Cloud. To view the DNS tunneling detections, log in to Juniper ATP Cloud Web portal and navigate to Monitor > DNS. Click on the Tunnel tab to view the DNS tunnel detections as shown in Figure 1. You can click on a domain name to view more details of the hosts that have contacted the domain.
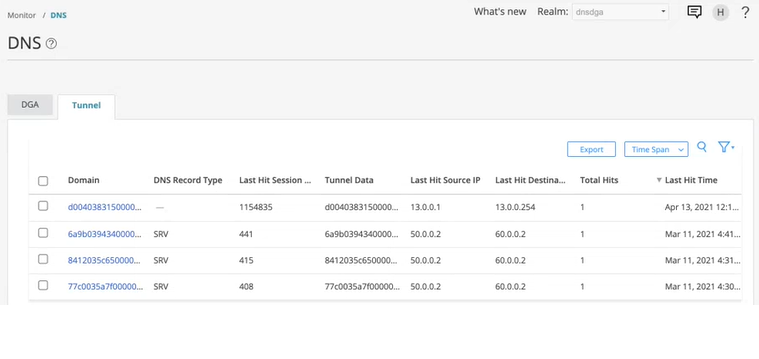
To enable DNS tunnel detections on SRX Series Firewalls, see Juniper Advanced Threat Prevention Cloud Administration Guide.
DNS Tunneling Procedure
Here's how DNS tunneling works:
- A cyber attacker registers a malicious domain, for example, “badsite.com”.
- The domain’s name server points to the attacker’s server, where DNS Tunneling malware program is running.
- DNS Tunnel client program running on the infected host generates DNS requests to the malicious domain.
- DNS resolver routes the query to the attacker’s command-and-control server.
- Connection is established between victim and attacker through DNS resolver.
- This tunnel can be used to exfiltrate data or for other malicious purposes.
